(Press-News.org) Do BMMFs, the novel infectious agents found in dairy products and bovine sera, play a role in the development of colorectal cancer? Scientists led by Harald zur Hausen detected the pathogens in colorectal cancer patients in close proximity to tumors. The researchers show that the BMMFs trigger local chronic inflammation, which can cause mutations via activated oxygen molecules and thus promote cancer development in the long term. BMMFs and inflammatory markers were significantly more frequently detectable in the vicinity of malignant intestinal tumors than in the intestinal tissue of tumor-free individuals.
A few years ago, scientists led by Ethel-Michele de Villiers at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) discovered a novel form of infectious agents in dairy products and bovine sera. These were ring-shaped DNA elements that showed great similarity to sequences of certain bacterial plasmids. They were named "Bovine Meat and Milk Factors" (BMMFs) after their origin in bovine products.
De Villiers, together with Harald zur Hausen, had tracked down the infectious agents while testing a hypothesis: Based on epidemiological observations, the Nobel Prize winner zur Hausen had postulated a possible link between the consumption of beef or dairy products and the incidence of colorectal cancer. "It seemed likely to us that an infectious agent transmitted from European domestic cattle to humans was associated with the development of colorectal cancer," zur Hausen said.
Meanwhile, de Villiers was able to isolate more than a hundred different of these agents from dairy products. The BMMFs can multiply in human cells, where they produce a protein product, Rep, which they need to multiply. But how might they contribute to the development of colorectal cancer?
Scientists from Timo Bund's team at the DKFZ have now carefully investigated this question using tissue samples from colorectal cancer and from healthy intestine. To detect the pathogens, the researchers used antibodies generated against the Rep protein. This enabled them to detect BMMFs in 15 of 16 colorectal cancer tissue samples.
To the surprise of the scientists, staining tissue sections using these antibodies revealed: Not the cancer cells themselves contained the Rep protein, but the cells in the immediate vicinity of the tumors. In particular, the antibody detected the Rep protein in the lamina propria, the connective tissue layer located under the intestinal mucosa, and there especially in the vicinity of the intestinal crypts. From these Rep-positive cells, the researchers were also able to isolate BMMF DNA that was closely related to the pathogens already isolated from milk samples.
The research team suspected that the presence of BMMFs could trigger chronic inflammatory processes in intestinal tissue. One indication of an inflammation would be the presence of pro-inflammatory macrophages. Indeed, these inflammatory cells were found in the immediate vicinity of the tumors. Interestingly, the signals for the Rep protein and for the macrophage marker CD68 were almost congruent: Rep is thus present immediately around or in the macrophages.
But is the presence of BMMFs and the associated chronic inflammation really associated with colorectal cancer? To find out, Bund and colleagues looked for combined Rep/CD68 signaling in colorectal cancer samples and compared them with colorectal tissue samples from a group of younger cancer-free control subjects. In the cancer patients, 7.3 percent of all intestinal cells in the tumor environment were positive for combined Rep/CD68 signals. In the intestinal cells of the control group, this figure was significantly lower at only 1.7 percent.
Another indication of inflammatory processes were the elevated levels of reactive oxygen species that Ethel-Michele de Villiers, Timo Bund and colleagues detected in the environment of Rep-positive cells. "Such oxygen radicals promote the development of genetic mutations," explains Harald zur Hausen. The inflammations were particularly localized in the immediate vicinity of the intestinal crypts. These tubular cavities are home to the intestinal stem cells, which are responsible for the constant regeneration of the intestinal mucosa. Intestinal stem cells continuously produce large quantities of progenitor cells, which divide rapidly and are exposed to this mutation-promoting influence. The more mutations accumulate, the higher the risk that genes will also be hit that will cause cell growth to spiral out of control. Chronic inflammation is known to drive cancer, a well-known example being the development of liver cancer as a result of chronic infection with the hepatitis C virus.
"We therefore regard BMMFs as indirect carcinogens, which probably act on the dividing cells of the intestinal mucosa for decades," zur Hausen said. He hypothesizes that infection with BMMFs usually occurs early in life, around the time of weaning.
"The results support our hypothesis that the consumption of milk and beef are causally linked to the development of colorectal cancer, and at the same time open up possibilities for preventive intervention," explains zur Hausen. For example, early detection of BMMFs could identify individuals who are particularly at risk, who should then seek timely colorectal cancer screening.
INFORMATION:
Timo Bund, Ekaterina Nikitina, Deblina Chakraborty, Claudia Ernst, Karin Gunst, Boyana Boneva, Claudia Tessmer, Nadine Volk, Alexander Brobeil, Achim Weber, Mathias Heikenwälder, Harald zur Hausen and Ethel-Michele de Villiers: Analysis of chronic inflammatory lesions of the colon for BMMF Rep antigen expression and CD68 macrophage interactions
PNAS 2021, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2025830118
The German Cancer Research Center (Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, DKFZ) with its more than 3,000 employees is the largest biomedical research institution in Germany. More than 1,300 scientists at the DKFZ investigate how cancer develops, identify cancer risk factors and search for new strategies to prevent people from developing cancer. They are developing new methods to diagnose tumors more precisely and treat cancer patients more successfully. The DKFZ's Cancer Information Service (KID) provides patients, interested citizens and experts with individual answers to all questions on cancer.
Jointly with partners from the university hospitals, the DKFZ operates the National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT) in Heidelberg and Dresden, and the Hopp Children's Tumour Center KiTZ in Heidelberg. In the German Consortium for Translational Cancer Research (DKTK), one of the six German Centers for Health Research, the DKFZ maintains translational centers at seven university partner locations. NCT and DKTK sites combine excellent university medicine with the high-profile research of the DKFZ. They contribute to the endeavor of transferring promising approaches from cancer research to the clinic and thus improving the chances of cancer patients.
The DKFZ is 90 percent financed by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research and 10 percent by the state of Baden-Württemberg. The DKFZ is a member of the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centers.
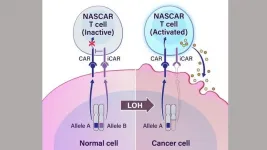
Researchers developed a prototype for a new cancer immunotherapy that uses engineered T cells to target a genetic alteration common among all cancers. The approach, which stimulates an immune response against cells that are missing one gene copy, called loss of heterozygosity (LOH), was developed by researchers at the Ludwig Center, Lustgarten Laboratory and the Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
Genes have two alleles, or copies, with one copy inherited from each parent. Cancer-related genetic alterations commonly involve the loss of one of these gene copies.
"This copy loss, or LOH, is one of the most common genetic events in cancer," says Kenneth Kinzler, Ph.D., co-director of the Ludwig Center, professor of oncology and ...
HOUSTON - (March 15, 2021) - Increased internet-access spending by Texas public schools improved academic performance but also led to more disciplinary problems among students, a study of 9,000 schools conducted by a research team from Rice University, Texas A&M University and the University of Notre Dame shows.
Whether students benefit from increased internet access in public schools has been an open question, according to the researchers. For example, some parents and policy advocates contend it increases children's access to obscene or harmful content and disciplinary problems. Others believe it promotes personalized learning and higher student engagement.
To address these policy questions, the research team created a multiyear dataset (2000-14) of 1,243 school districts ...
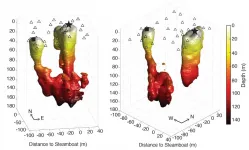
When Steamboat Geyser, the world's tallest, started erupting again in 2018 in Yellowstone National Park after decades of relative silence, it raised a few tantalizing scientific questions. Why is it so tall? Why is it erupting again now? And what can we learn about it before it goes quiet again?
The University of Utah has been studying the geology and seismology of Yellowstone and its unique features for decades, so U scientists were ready to jump at the opportunity to get an unprecedented look at the workings of Steamboat Geyser. Their findings provide a picture of the depth of the geyser as well as a redefinition of a long-assumed relationship between the geyser and a nearby spring. The findings are published in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth.
"We ...
If you are a consumer and/or entrepreneur who can make decisions based on cost, competition, supply and demand, you probably possess an element of marketplace literacy.
"Marketplace literacy" is defined as the knowledge and skills that enable individuals to participate in a marketplace both as consumers and entrepreneurs. San Diego State University marketing professor Nita Umashankar, along with professors Madhubalan Viswanathan (Loyola Marymount University), Arun Sreekumar (University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign) and Ashley Goreczny (Iowa State University), explored the impact on marketplace literacy on ...
HSE University researchers together with specialists from the Humanitarian Action Charitable Fund (St. Petersburg) and the University of Michigan School of Public Health (USA) studied the specifics of remote work with Russian people who use drugs to reduce the harm of drug use. They discovered that the use of online platforms increases the § who use drugs to seek help. Online platforms also serve as a kind of 'gateway' for people with problematic drug use to receive a wider range of qualified help. The authors concluded that remote work in this field should be developed and built upon in ...
Forest landscape restoration is attaining new global momentum this year under the Decade of Ecosystem Restoration (2021-2030), an initiative launched by the United Nations. Burkina Faso, in West Africa, is one country that already has a head start in forest landscape restoration, and offers valuable lessons. An assessment of achievements there and in other countries with a history of landscape restoration is critical to informing a new wave of projects aiming for more ambitious targets that are being developed thanks to renewed global interest and political will to improve the environment.
Burkina Faso has been fighting with desertification and climate change, and has seen a progressive degradation of its forested landscapes due to the expansion of agriculture. In 2018, the country ...
In the last 20 years, Black adults living in rural areas of the United States experienced high mortality rates due to diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease and stroke compared to white adults. According to a research letter published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, racial disparities improved minimally in rural areas over the last two decades, with larger improvements occurring in urban areas.
"While modest gains have been made in reducing racial health inequities in urban areas, large gaps in death rates between Black and white adults persist in rural areas, particularly for diabetes and hypertension. We haven't meaningfully ...
March 15, 2021 - After arthroscopic surgery on the meniscus of the knee, patients using telemedicine for postoperative follow-up are just as satisfied with their care as those making in-person visits, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
"Patient satisfaction with overall care is equivalent between telemedicine and office-based follow-up after an arthroscopic meniscal surgical procedure in the immediate postoperative period," according to the randomized trial report by Christina P. Herrero, MD, and colleagues of NYU Langone Health, New York , and colleagues.
Telemedicine is 'a reasonable alternative' for postoperative visits
The ...
Immigrants imprisoned in immigration facilities across the country face health conditions and often have chronic illnesses that would expose them to greater risk with COVID-19, a new University of California, Davis, study suggests.
"The research is clear: immigration detention is not only unnecessary for facilitating a just immigration system, but also causes extensive harm to detained people, perhaps especially to those facing chronic health conditions," said the study's lead author, Caitlin Patler, professor of sociology. "This is particularly alarming in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. The government must act quickly to permanently reduce reliance ...
Prior to COVID-19, communication via the internet was already a regular feature of everyday interactions for most people, including those on the autism spectrum. Various studies have shown how autistic people use information and communication technology (ICT) since the early 2000s, some finding that autistic people may prefer to communicate using the internet instead of in-person. However, no systematic review has been conducted to summarize these findings.
To understand what has been discovered so far, researchers from Drexel University's A.J. Drexel Autism Institute collected and reviewed published research about how autistic youth and adults use the internet to communicate and provide a framework ...