(Press-News.org) When Steamboat Geyser, the world's tallest, started erupting again in 2018 in Yellowstone National Park after decades of relative silence, it raised a few tantalizing scientific questions. Why is it so tall? Why is it erupting again now? And what can we learn about it before it goes quiet again?
The University of Utah has been studying the geology and seismology of Yellowstone and its unique features for decades, so U scientists were ready to jump at the opportunity to get an unprecedented look at the workings of Steamboat Geyser. Their findings provide a picture of the depth of the geyser as well as a redefinition of a long-assumed relationship between the geyser and a nearby spring. The findings are published in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth.
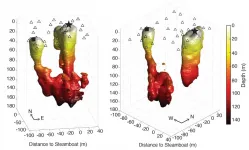
"We scientists don't really know what controls a geyser from erupting regularly, like Old Faithful, versus irregularly, like Steamboat," says Fan-Chi Lin, an associate professor with the Department of Geology and Geophysics. "The subsurface plumbing structure likely controls the eruption characteristics for a geyser. This is the first time we were able to image a geyser's plumbing structure down to more than 325 feet (100 m) deep."
Meet Steamboat Geyser
If you're asked to name a Yellowstone geyser and "Old Faithful" is the only one that comes to mind, then you're past due for an introduction to Steamboat. Recorded eruption heights reach up to 360 feet (110 m), tall enough to splash the top of the Statue of Liberty.
"Watching a major eruption of Steamboat Geyser is quite amazing," says Jamie Farrell, a research assistant professor with the University of Utah Seismograph Stations. "The thing that I remember most is the sound. You can feel the rumble and it sounds like a jet engine. I already knew that Steamboat was the tallest active geyser in the world, but seeing it in major eruption blew me away."
Unlike its famous cousin, Steamboat Geyser is anything but faithful. It's only had three periods of sustained activity in recorded history--one in the 1960s, one in the 1980s and one that began in 2018 and continues today. But the current phase of geyser activity has already seen more eruptions than either of the previous phases.
Near Steamboat Geyser is a pool called Cistern Spring. Because Cistern Spring drains when Steamboat erupts, it's been assumed that the two features are directly connected.
"With our ability to quickly deploy seismic instruments in a nonintrusive way, this current period is providing the opportunity to better understand the dynamics of Steamboat Geyser and Cistern Spring which goes a long way to help us understand eruptive behavior," says Farrell.
Giving the geyser a CT scan
For several years now, U scientists have been studying the features of Yellowstone National Park, including Old Faithful, using small, portable seismometers. The football-sized instruments can be deployed by the dozens wherever the researchers need for up to one month per deployment in order to get a picture of what's happening under the ground. Each slight small movement of the ground, even the periodic swells of crowds on Yellowstone's boardwalks, is felt and recorded.
And just as doctors can use multiple X-rays to create a CT scan of the interior of a human body, seismologists can use multiple seismometers recording multiple seismic events (in this case, bubbling within the geyser's superheated water column) to build a sort of image of the subsurface.
In the summers of 2018 and 2019, Farrell and colleagues collaborated with the National Park Service and placed 50 portable seismometers in an array around Steamboat Geyser. The 2019 deployment recorded seven major eruptions, with a range of inter-eruption periods of three to eight days apart, each providing a wealth of data.
Plumbing the depths
The results showed that the underground channels and fissures that comprise Steamboat Geyser extend down at least 450 feet (140 m). That's much deeper than the plumbing of Old Faithful, which is around 260 feet (80 m).
The results didn't show a direct connection between Steamboat Geyser and Cistern Spring, however.
"This finding rules out the assumption that the two features are connected with something like an open pipe, at least in the upper 140 meters," says Sin-Mei Wu, a recently graduated doctoral student working with Lin and Farrell. That's not to say that the two features are totally separate, though. The fact that the pool drains when Steamboat erupts suggests that they are still connected somehow, but probably through small fractures or pores in the rock that aren't detectable using the seismic signals the researchers recorded. "Understanding the exact relationship between Steamboat and Cistern will help us to model how Cistern might affect Steamboat eruption cycles," added Wu.
Will scientists eventually be able to predict when the geyser will erupt? Maybe, Wu says, with a better understanding of hydrothermal tremor and a long-term monitoring system. But, in the meantime, Wu says, this study is really just the beginning of understanding how Steamboat Geyser works.
"We now have a baseline of what eruptive activity looks like for Steamboat," Lin pointed out. "When it becomes less active in the future, we can re-deploy our seismic sensors and get a baseline of what non-active periods look like. We then can continuously monitor data coming from real-time seismic stations by Steamboat and assess whether it looks like one or the other and get a more real-time analysis of when it looks like it is switching to a more active phase."
INFORMATION:
Find the full study here.
If you are a consumer and/or entrepreneur who can make decisions based on cost, competition, supply and demand, you probably possess an element of marketplace literacy.
"Marketplace literacy" is defined as the knowledge and skills that enable individuals to participate in a marketplace both as consumers and entrepreneurs. San Diego State University marketing professor Nita Umashankar, along with professors Madhubalan Viswanathan (Loyola Marymount University), Arun Sreekumar (University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign) and Ashley Goreczny (Iowa State University), explored the impact on marketplace literacy on ...
HSE University researchers together with specialists from the Humanitarian Action Charitable Fund (St. Petersburg) and the University of Michigan School of Public Health (USA) studied the specifics of remote work with Russian people who use drugs to reduce the harm of drug use. They discovered that the use of online platforms increases the § who use drugs to seek help. Online platforms also serve as a kind of 'gateway' for people with problematic drug use to receive a wider range of qualified help. The authors concluded that remote work in this field should be developed and built upon in ...
Forest landscape restoration is attaining new global momentum this year under the Decade of Ecosystem Restoration (2021-2030), an initiative launched by the United Nations. Burkina Faso, in West Africa, is one country that already has a head start in forest landscape restoration, and offers valuable lessons. An assessment of achievements there and in other countries with a history of landscape restoration is critical to informing a new wave of projects aiming for more ambitious targets that are being developed thanks to renewed global interest and political will to improve the environment.
Burkina Faso has been fighting with desertification and climate change, and has seen a progressive degradation of its forested landscapes due to the expansion of agriculture. In 2018, the country ...
In the last 20 years, Black adults living in rural areas of the United States experienced high mortality rates due to diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease and stroke compared to white adults. According to a research letter published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, racial disparities improved minimally in rural areas over the last two decades, with larger improvements occurring in urban areas.
"While modest gains have been made in reducing racial health inequities in urban areas, large gaps in death rates between Black and white adults persist in rural areas, particularly for diabetes and hypertension. We haven't meaningfully ...
March 15, 2021 - After arthroscopic surgery on the meniscus of the knee, patients using telemedicine for postoperative follow-up are just as satisfied with their care as those making in-person visits, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
"Patient satisfaction with overall care is equivalent between telemedicine and office-based follow-up after an arthroscopic meniscal surgical procedure in the immediate postoperative period," according to the randomized trial report by Christina P. Herrero, MD, and colleagues of NYU Langone Health, New York , and colleagues.
Telemedicine is 'a reasonable alternative' for postoperative visits
The ...
Immigrants imprisoned in immigration facilities across the country face health conditions and often have chronic illnesses that would expose them to greater risk with COVID-19, a new University of California, Davis, study suggests.
"The research is clear: immigration detention is not only unnecessary for facilitating a just immigration system, but also causes extensive harm to detained people, perhaps especially to those facing chronic health conditions," said the study's lead author, Caitlin Patler, professor of sociology. "This is particularly alarming in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. The government must act quickly to permanently reduce reliance ...
Prior to COVID-19, communication via the internet was already a regular feature of everyday interactions for most people, including those on the autism spectrum. Various studies have shown how autistic people use information and communication technology (ICT) since the early 2000s, some finding that autistic people may prefer to communicate using the internet instead of in-person. However, no systematic review has been conducted to summarize these findings.
To understand what has been discovered so far, researchers from Drexel University's A.J. Drexel Autism Institute collected and reviewed published research about how autistic youth and adults use the internet to communicate and provide a framework ...
(BOSTON) ¬-- Trillions of commensal microbes live on the mucosal and epidermal surfaces of the body and it is firmly established that this microbiome affects its host's tolerance and sensitivity of the host to a variety of pathogens. However, host tolerance to infection with pathogens is not equally developed in all organisms. For example, it is known that the gut microbiome of mice protects more effectively against infection with certain pathogens, such as the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium, than the human gut microbiome.
This raises the interesting possibility that analyzing differences between host-microbiome ...
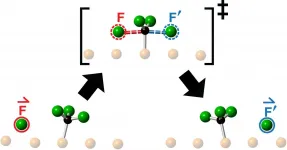
TORONTO, ON - Research by a team of chemists at the University of Toronto, led by Nobel Prize-winning researcher John Polanyi, is shedding new light on the behaviour of molecules as they collide and exchange atoms during chemical reaction. The discovery casts doubt on a 90-year old theoretical model of the behavior of the "transition state", intermediate between reagents and products in chemical reactions, opening a new area of research.
The researchers studied collisions obtained by launching a fluorine atom at the centre of a fluoromethyl molecule - made up of one carbon atom and three fluorine atoms - and observed the resulting reaction using Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. What they saw following each collision ...
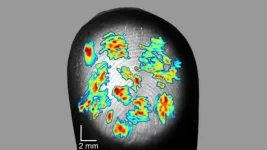
Fingerprints may be more useful to us than helping us nab criminal suspects: they also improve our sense of touch. Sensory neurons in the finger can detect touch on the scale of a single fingerprint ridge, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
The hand contains tens of thousands of sensory neurons. Each neuron tunes in to a small surface area on the skin -- a receptive field -- and detects touch, vibration, pressure, and other tactile stimuli. The human hand possesses a refined sense of touch, but the exact sensitivity of a single sensory neuron has not been studied before.
To ...