(Press-News.org) March 15, 2021 - After arthroscopic surgery on the meniscus of the knee, patients using telemedicine for postoperative follow-up are just as satisfied with their care as those making in-person visits, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
"Patient satisfaction with overall care is equivalent between telemedicine and office-based follow-up after an arthroscopic meniscal surgical procedure in the immediate postoperative period," according to the randomized trial report by Christina P. Herrero, MD, and colleagues of NYU Langone Health, New York , and colleagues.
Telemedicine is 'a reasonable alternative' for postoperative visits
The study included 122 patients who underwent arthroscopic surgery of the meniscus - sometimes called the "shock absorber" of the knee. About 88 percent of patients underwent removal of the meniscus (meniscectomy), and the rest underwent meniscal repair procedures. Arthroscopic meniscal surgery is one of the most common orthopaedic surgical procedures.
Patients were randomly assigned to either office-based or telemedicine follow-up, scheduled for 5 to 14 days postoperatively. During both types of follow-up visits, the surgeon talked to the patient about the surgical findings, the patient's pain, and the postoperative recovery period and performed a physical examination that included range-of-motion testing.
Of course, surgeons could not feel or touch the knee during telemedicine follow-ups - but they were still able to perform a visual assessment of wound healing, drainage, and swelling. Telemedicine follow-ups were performed using the patient's home computer or mobile device via a telemedicine program that was compliant with privacy rules.
In patient surveys, overall satisfaction ratings were almost identical between groups. Average patient satisfaction scores (on a 0-to-10 scale) were 9.77 with office-based follow-up and 9.79 for telemedicine follow-up. In both groups, only about 20 percent of patients said they would have preferred the other type of visit. Pain scores also showed similar improvement between groups: from about 5 (out of 10) on the day of the surgery to 3 at the follow-up visit.
Both groups had low complication rates. Two patients in each group had pain and swelling, raising concern about a possible blood clot-related complication (venous thromboembolism, or VTE). All four patients were sent for same-day Doppler ultrasound scans, which found no evidence of VTE. "All potential complications were identified, and there were no subsequent or missed complications identified on subsequent chart review," Dr. Herrero and colleagues write.
Telemedicine is a promising approach to delivering "direct, long-range care" to patients with many different conditions. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of telemedicine in routine medical care has greatly accelerated; the researchers began their study well before the start of the pandemic.
Although studies have reported a wide range of benefits from telemedicine visits, there are mixed data regarding satisfaction with telemedicine visits among patients undergoing common orthopaedic procedures. The new study is the first to directly compare telemedicine with standard office-based follow-up after orthopaedic surgery.
"Telemedicine may be a reasonable alternative to office-based follow-up after knee arthroscopy," Dr. Herrero and coauthors conclude. "[Our] study only evaluated the first postoperative visit, but future studies may benefit from expanding the use of telemedicine to longer-term follow-ups or to additional surgical procedures."
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "Patient Satisfaction Is Equivalent Using Telemedicine Versus Office-Based Follow-up After Arthroscopic Meniscal Surgery."
DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.20.01413
About The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery
The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (JBJS) has been the most valued source of information for orthopaedic surgeons and researchers for over 125 years and is the gold standard in peer-reviewed scientific information in the field. A core journal and essential reading for general as well as specialist orthopaedic surgeons worldwide, The Journal publishes evidence-based research to enhance the quality of care for orthopaedic patients. Standards of excellence and high quality are maintained in everything we do, from the science of the content published to the customer service we provide. JBJS is an independent, non-profit journal.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the clinicians, nurses, accountants, lawyers, and tax, finance, audit, risk, compliance, and regulatory sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with advanced technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2019 annual revenues of €4.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 19,000 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students with advanced clinical decision support, learning and research and clinical intelligence. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
For more information, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
Immigrants imprisoned in immigration facilities across the country face health conditions and often have chronic illnesses that would expose them to greater risk with COVID-19, a new University of California, Davis, study suggests.
"The research is clear: immigration detention is not only unnecessary for facilitating a just immigration system, but also causes extensive harm to detained people, perhaps especially to those facing chronic health conditions," said the study's lead author, Caitlin Patler, professor of sociology. "This is particularly alarming in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. The government must act quickly to permanently reduce reliance ...
Prior to COVID-19, communication via the internet was already a regular feature of everyday interactions for most people, including those on the autism spectrum. Various studies have shown how autistic people use information and communication technology (ICT) since the early 2000s, some finding that autistic people may prefer to communicate using the internet instead of in-person. However, no systematic review has been conducted to summarize these findings.
To understand what has been discovered so far, researchers from Drexel University's A.J. Drexel Autism Institute collected and reviewed published research about how autistic youth and adults use the internet to communicate and provide a framework ...
(BOSTON) ¬-- Trillions of commensal microbes live on the mucosal and epidermal surfaces of the body and it is firmly established that this microbiome affects its host's tolerance and sensitivity of the host to a variety of pathogens. However, host tolerance to infection with pathogens is not equally developed in all organisms. For example, it is known that the gut microbiome of mice protects more effectively against infection with certain pathogens, such as the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium, than the human gut microbiome.
This raises the interesting possibility that analyzing differences between host-microbiome ...
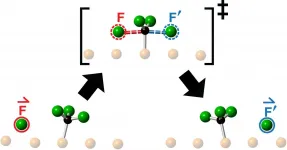
TORONTO, ON - Research by a team of chemists at the University of Toronto, led by Nobel Prize-winning researcher John Polanyi, is shedding new light on the behaviour of molecules as they collide and exchange atoms during chemical reaction. The discovery casts doubt on a 90-year old theoretical model of the behavior of the "transition state", intermediate between reagents and products in chemical reactions, opening a new area of research.
The researchers studied collisions obtained by launching a fluorine atom at the centre of a fluoromethyl molecule - made up of one carbon atom and three fluorine atoms - and observed the resulting reaction using Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. What they saw following each collision ...
Fingerprints may be more useful to us than helping us nab criminal suspects: they also improve our sense of touch. Sensory neurons in the finger can detect touch on the scale of a single fingerprint ridge, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
The hand contains tens of thousands of sensory neurons. Each neuron tunes in to a small surface area on the skin -- a receptive field -- and detects touch, vibration, pressure, and other tactile stimuli. The human hand possesses a refined sense of touch, but the exact sensitivity of a single sensory neuron has not been studied before.
To ...
Key Points
19.3% of children and adolescents in the United States have obesity and therefore have a higher likelihood of having obesity as adults and developing weight-related diseases.
This AJCN study assessed how strongly mothers' diets during pregnancy were associated with their children's growth rates during specific periods from birth through adolescence.
Study results suggest maternal nutrition during pregnancy may influence her offspring's weight gain during specific periods from birth to adolescence.
A pregnancy diet with higher inflammatory potential was associated with accelerated BMI growth trajectories in children, specifically those between three and ten years of age.
Rockville, ...
Recent summer droughts in Europe are far more severe than anything in the past 2,100 years, according to a new study.
An international team, led by the University of Cambridge, studied the chemical fingerprints in European oak trees to reconstruct summer climate over 2,110 years. They found that after a long-term drying trend, drought conditions since 2015 suddenly intensified, beyond anything in the past two thousand years.
This anomaly is likely the result of human-caused climate change and associated shifts in the jet stream. The results are reported in the journal Nature Geoscience.
Recent summer droughts and heatwaves in Europe have had devastating ecological and economic consequences, which will worsen as the global climate continues to warm.
"We're ...
In their study, which is now published in the journal Nature Aging, they show that the level of non-coding RNAs in the blood of a Parkinson's patient can be used to track the course of the disease. For their study, the team led by bioinformatics professor Andreas Keller and his doctoral student Fabian Kern created and analyzed the molecular profiles of more than 5,000 blood samples from over 1,600 Parkinson's patients. This resulted in around 320 billion data points, which the researchers analyzed for biomarkers of Parkinson's disease using artificial intelligence methods. ...
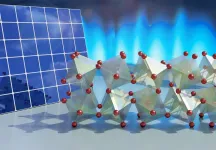
DURHAM, N.C. -- Researchers at Duke University have revealed long-hidden molecular dynamics that provide desirable properties for solar energy and heat energy applications to an exciting class of materials called halide perovskites.
A key contributor to how these materials create and transport electricity literally hinges on the way their atomic lattice twists and turns in a hinge-like fashion. The results will help materials scientists in their quest to tailor the chemical recipes of these materials for a wide range of applications in an environmentally friendly way.
The results appear online March 15 in the journal Nature Materials.
"There is a broad ...
An epigenetic modification that occurs in a major cell type in the brain's reward circuitry controls how stress early in life increases susceptibility to additional stress in adulthood, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have learned. In a study in Nature Neuroscience, the team also reported that a small-molecule inhibitor of the enzyme responsible for this modification, currently being developed as an anti-cancer drug, was able to reverse increased vulnerability to lifelong stress in animal models.
"It has long been known that stress exposures throughout life control lifelong susceptibility to subsequent stress. Here ...