(Press-News.org) Recent summer droughts in Europe are far more severe than anything in the past 2,100 years, according to a new study.
An international team, led by the University of Cambridge, studied the chemical fingerprints in European oak trees to reconstruct summer climate over 2,110 years. They found that after a long-term drying trend, drought conditions since 2015 suddenly intensified, beyond anything in the past two thousand years.
This anomaly is likely the result of human-caused climate change and associated shifts in the jet stream. The results are reported in the journal Nature Geoscience.
Recent summer droughts and heatwaves in Europe have had devastating ecological and economic consequences, which will worsen as the global climate continues to warm.
"We're all aware of the cluster of exceptionally hot and dry summers we've had over the past few years, but we needed precise reconstructions of historical conditions to see how these recent extremes compare to previous years," said first author Professor Ulf Büntgen from Cambridge's Department of Geography, who is also affiliated with CzechGlobe Centre in Brno, Czech Republic. "Our results show that what we have experienced over the past five summers is extraordinary for central Europe, in terms of how dry it has been consecutively."
Most studies attempting to reconstruct past climates are restricted to temperature, but stable isotopes in tree rings can provide annually-resolved and absolutely-dated information about hydroclimatic changes over long periods of time.
Büntgen and his colleagues from the Czech Republic, Germany and Switzerland studied more than 27,000 measurements of carbon and oxygen isotopic ratios from 147 living and dead European oak trees, covering a period of 2,110 years. The samples came from archaeological remains, subfossil materials, historical constructions and living trees from what is now the Czech Republic and parts of south-eastern Bavaria.
"Generally, our understanding is worse the further back we go back in time, as datasets looking at past drought conditions are rare," said Büntgen, who is a specialist in dendrochronology, the study of data from tree-ring growth. "However, insights before medieval times are particularly vital, because they enable us to get a more complete picture of past drought variations, which were essential for the functioning and productivity of ecosystems and societies."
For each ring in each tree, researchers extracted and analysed carbon and oxygen isotopes independently, enabling them to build the largest and most detailed dataset of summer hydroclimate conditions in central Europe from Roman times to the present.
"These tree-ring stable isotopes give us a far more accurate archive to reconstruct hydroclimate conditions in temperate areas, where conventional tree-ring studies often fail," said co-author Professor Jan Esper from the University of Mainz, Germany.
Stable tree-ring isotopes differ from the usual tree-ring measures of ring width and wood density, as they reflect physical conditions and tree responses rather than net stem growth. "While carbon values depend on the photosynthetic activity, oxygen values are affected by the source water. Together, they closely correlate with the conditions of the growing season," said co-author Professor Paolo Cherubini from the Federal Research Institute WSL in Birmensdorf, Switzerland.
Over the 2,110-year period, the tree-ring isotope data showed there were very wet summers, such as 200, 720 and 1100 CE, and very dry summers, such as 40, 590, 950 and 1510 CE. Despite these 'out of the ordinary years', the results show that for the past two millennia, Europe has been slowly getting drier.
The samples from 2015-2018, however, show that drought conditions in recent summers far exceed anything in the 2,110 years: "We've seen a sharp drop following centuries of a slow, significant decline, which is particularly alarming for agriculture and forestry," said co-author Professor Mirek Trnka from the CzechGlobe Research Centre in Brno, Czech Republic. "Unprecedented forest dieback across much of central Europe corroborates our results."
The researchers say that the recent cluster of abnormally dry summers is most likely the result of anthropogenic climate warming, and the associated changes in the jet stream position. "Climate change does not mean that it will get drier everywhere: some places may get wetter or colder, but extreme conditions will become more frequent, which could be devastating for agriculture, ecosystems and societies as a whole," said Büntgen.
INFORMATION:
In their study, which is now published in the journal Nature Aging, they show that the level of non-coding RNAs in the blood of a Parkinson's patient can be used to track the course of the disease. For their study, the team led by bioinformatics professor Andreas Keller and his doctoral student Fabian Kern created and analyzed the molecular profiles of more than 5,000 blood samples from over 1,600 Parkinson's patients. This resulted in around 320 billion data points, which the researchers analyzed for biomarkers of Parkinson's disease using artificial intelligence methods. ...
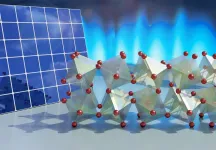
DURHAM, N.C. -- Researchers at Duke University have revealed long-hidden molecular dynamics that provide desirable properties for solar energy and heat energy applications to an exciting class of materials called halide perovskites.
A key contributor to how these materials create and transport electricity literally hinges on the way their atomic lattice twists and turns in a hinge-like fashion. The results will help materials scientists in their quest to tailor the chemical recipes of these materials for a wide range of applications in an environmentally friendly way.
The results appear online March 15 in the journal Nature Materials.
"There is a broad ...
An epigenetic modification that occurs in a major cell type in the brain's reward circuitry controls how stress early in life increases susceptibility to additional stress in adulthood, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have learned. In a study in Nature Neuroscience, the team also reported that a small-molecule inhibitor of the enzyme responsible for this modification, currently being developed as an anti-cancer drug, was able to reverse increased vulnerability to lifelong stress in animal models.
"It has long been known that stress exposures throughout life control lifelong susceptibility to subsequent stress. Here ...
Researchers have found that out of the more than 300 COVID-19 machine learning models described in scientific papers in 2020, none of them is suitable for detecting or diagnosing COVID-19 from standard medical imaging, due to biases, methodological flaws, lack of reproducibility, and 'Frankenstein datasets.'
The team of researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, carried out a systematic review of scientific manuscripts - published between 1 January and 3 October 2020 - describing machine learning models that claimed to be able to diagnose or prognosticate ...
In considering materials that could become the fabrics of the future, scientists have largely dismissed one widely available option: polyethylene.
The stuff of plastic wrap and grocery bags, polyethylene is thin and lightweight, and could keep you cooler than most textiles because it lets heat through rather than trapping it in. But polyethylene would also lock in water and sweat, as it's unable to draw away and evaporate moisture. This antiwicking property has been a major deterrent to polyethylene's adoption as a wearable textile.
Now, MIT engineers have spun polyethylene into fibers ...
The loss of glaciers worldwide enhances the breakdown of complex carbon molecules in rivers, potentially contributing further to climate change.
An international research team led by the University of Leeds has for the first time linked glacier-fed mountain rivers with higher rates of plant material decomposition, a major process in the global carbon cycle.
As mountain glaciers melt, water is channelled into rivers downstream. But with global warming accelerating the loss of glaciers, rivers have warmer water temperatures and are less prone to variable water flow and sediment movement. These conditions are then much more favourable for fungi to establish and ...
Ageing is a common factor in many diseases. So, what if it were possible to treat them by acting on the causes of ageing or, more specifically, by acting on the shortening of telomeres, the structures that protect chromosomes? This strategy is being pursued by the Telomeres and Telomerase Group of the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), which has already succeeded to cure pulmonary fibrosis and infarctions in mice by lengthening telomeres. Now they take a first step towards doing the same with renal fibrosis by demonstrating that short telomeres are at the origin of this disease, ...
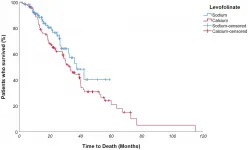
Oncotarget published "Folinic acid in colorectal cancer: esquire or fellow knight? Real-world results from a mono institutional, retrospective study" which reported that the stock of therapeutic weapons available in metastatic colorectal cancer has been progressively grown over the years, with improving both survival and patients' clinical outcome: notwithstanding advances in the knowledge of mCRC biology, as well as advances in treatment, fluoropyrimidine antimetabolite drugs have been for 30 years the mainstay of chemotherapy protocols for this malignancy.
5-Fluorouracil seems to act differently depending on administration method: elastomer-mediated continuous infusion better inhibits Thymidylate ...
Oncotarget published "A novel isoform of Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 promotes YAP/TEAD transcriptional activity in NSCLC cells" which reported that In this study, the authors show that a new HIPK2 isoform increases TEAD reporter activity in NSCLC cells.
They detected and cloned a novel HIPK2 isoform 3 and found that its forced overexpression promotes TEAD reporter activity in NSCLC cells.
Expressing HIPK2 isoform 3_K228A kinase-dead plasmid failed to increase TEAD reporter activity in NSCLC cells.
Next, they showed that two siRNAs targeting HIPK2 decreased HIPK2 isoform 3 and YAP protein levels in NSCLC cells.
In summary, this Oncotarget study indicates that HIPK2 isoform 3, the main HIPK2 isoform ...
The cover for issue 51 of Oncotarget features Figure 5, "miR-4287 overexpression regulates EMT in prostate cancer cell lines," published in "MicroRNA-4287 is a novel tumor suppressor microRNA controlling epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer" by Bhagirath, et al. which reported that the authors analyzed the role of miR-4287 in PCa using clinical tissues and cell lines.
Receiver operating curve analysis showed that miR-4287 distinguishes prostate cancer from normal with a specificity of 88.24% and with an Area under the curve of 0.66. Further, these authors found that miR-4287 ...