(Press-News.org) Oncotarget published "Folinic acid in colorectal cancer: esquire or fellow knight? Real-world results from a mono institutional, retrospective study" which reported that the stock of therapeutic weapons available in metastatic colorectal cancer has been progressively grown over the years, with improving both survival and patients' clinical outcome: notwithstanding advances in the knowledge of mCRC biology, as well as advances in treatment, fluoropyrimidine antimetabolite drugs have been for 30 years the mainstay of chemotherapy protocols for this malignancy.
5-Fluorouracil seems to act differently depending on administration method: elastomer-mediated continuous infusion better inhibits Thymidylate Synthase, an enzyme playing a pivotal role in DNA synthetic pathway.
TS overexpression is an acknowledged poor prognosis predicting factor.
The simultaneous combination of 5FU and folinate salt synergistically strengthens fluorouracil cytotoxic effect.
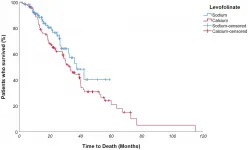
In their experience, levofolinate and 5FU together in continuous infusion prolong progression free survival of patients suffering from mCRC, moreover decreasing death risk and showing a clear clinical benefit for patients, irrespective of RAS mutational status, primitive tumor side and metastases surgery.
Showing a clear clinical benefit for patients, irrespective of RAS mutational status, primitive tumor side and metastases surgery
Dr. Francesco Jacopo Romano from The Antonio Cardarelli Hospital, Oncology Unit in Naples Italy said, "Notwithstanding advances in the knowledge of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) biology, as well as advances in treatment, fluoropyrimidine antimetabolite drugs are currently the mainstay of chemotherapy protocols for this malignancy."
5FU seems to act differently depending on administration method: quick bolus mainly increases incorporation of 5FU in RNA, even yielding a more severe hematological and gastrointestinal toxicity than continuous infusion, whereas elastomer-mediated continuous infusion long inhibits Thymidylate Synthase.
Modulation of 5FU activity has been studied for several years, with the aim to enhance antineoplastic effect by combining bolus and continuous infusion administration to maximize 5FU antitumor efficacy.
Therefore, therapeutic strategies combining bolus and continuous infusion have been made to better exploit both genotoxic effects of fluoropyrimidines incorporation and TS inhibition, with extending infusion time to 48 hours and adding folinic acid.
Usually, 5FU bolus is administered at the middle of a 2-hours folinic acid infusion.
This retrospective, single-center observational study is the first with the aim of evaluating differences between these administration modalities: in particular, the authors wondered if co-administration of 5FU and folinic acid in continuous infusion was as effective as the classic sequential administration, or even more effective in terms of progression free- and overall survival, especially considering the aforementioned preclinical data.
The Romano Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Paper that increased survival for patients undergoing NaLF based therapy could be the consequence of a greater and more effective TS inhibition.
A plausible reason for ALL RAS absence of significance on OS multivariate compared to univariate analysis can be found in extremely wide expression of TS in colon cancer cells.
Indeed, on one hand they have an oncogene addiction toward EGFR pathways in ALL RAS wild type cells, but on the other hand we know that TS is essential for non-oncogenic pathways of cancer cells regardless of EGFR or RAS activation.
Noteworthy, there are coincidentally more RAS mutated patients in NaLF group than the CaLF counterpart.
Finally, they highlight the therapy switch over of a large number of patients who underwent NaLF-based therapy in the second line after first-line CaLF-based therapy, partially disguising the overall survival difference between the two groups.
INFORMATION:
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27872
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/27872/text/
Correspondence to - Francesco Jacopo Romano - francesco_jacopo@libero.it
Keywords -
colorectal cancer,
folinic acid,
sodium levofolinate,
thymidylate synthase,
non oncogene addiction
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a weekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit http://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
18009220957x105
Oncotarget published "A novel isoform of Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 promotes YAP/TEAD transcriptional activity in NSCLC cells" which reported that In this study, the authors show that a new HIPK2 isoform increases TEAD reporter activity in NSCLC cells.
They detected and cloned a novel HIPK2 isoform 3 and found that its forced overexpression promotes TEAD reporter activity in NSCLC cells.
Expressing HIPK2 isoform 3_K228A kinase-dead plasmid failed to increase TEAD reporter activity in NSCLC cells.
Next, they showed that two siRNAs targeting HIPK2 decreased HIPK2 isoform 3 and YAP protein levels in NSCLC cells.
In summary, this Oncotarget study indicates that HIPK2 isoform 3, the main HIPK2 isoform ...
The cover for issue 51 of Oncotarget features Figure 5, "miR-4287 overexpression regulates EMT in prostate cancer cell lines," published in "MicroRNA-4287 is a novel tumor suppressor microRNA controlling epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer" by Bhagirath, et al. which reported that the authors analyzed the role of miR-4287 in PCa using clinical tissues and cell lines.
Receiver operating curve analysis showed that miR-4287 distinguishes prostate cancer from normal with a specificity of 88.24% and with an Area under the curve of 0.66. Further, these authors found that miR-4287 ...
NEW YORK, NY (March 15, 2021)--A cytokine "hurricane" centered in the lungs drives respiratory symptoms in patients with severe COVID-19, a new study by immunologists at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons suggests.
Two cytokines, CCL2 and CCL3, appear critical in luring immune cells, called monocytes, from the bloodstream into the lungs, where the cells launch an overaggressive attempt to clear the virus.
Targeting these specific cytokines with inhibitors may calm the immune reaction and prevent lung tissue damage. Currently, one drug that blocks immune responses to CCL2 is being studied in clinical trials of patients with severe COVID-19.
Survivors of severe COVID-19, the study also found, had a greater abundance of antiviral T cells in their lungs ...
Philadelphia, March 15, 2021 - Biomarker testing surveys specific disease-associated molecules to predict treatment response and disease progression; however its use has complicated the diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In a new study in The Journal of Molecular Diagnosis, published by Elsevier, investigators provide for the first time a complete overview of biomarker testing, spanning multiple treatment lines, in a single cohort of patients.
Using exploratory data analysis and process-mining techniques in a real-world setting, investigators identified significant variation in test utilization and treatment. They also found that while ...
BOSTON - Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have uncovered new clues that add to the growing understanding of how female mammals, including humans, "silence" one X chromosome. Their new study, published in Molecular Cell, demonstrates how certain proteins alter the "architecture" of the X chromosome, which contributes to its inactivation. Better understanding of X chromosome inactivation could help scientists figure out how to reverse the process, potentially leading to cures for devastating genetic disorders.
Female mammals have two copies of the X chromosome in all of their cells. Each X chromosome contains many genes, but only one of the pair ...
Ingo Burgert and his team at Empa and ETH Zurich has proven it time and again: Wood is so much more than "just" a building material. Their research aims at extending the existing characteristics of wood in such a way that it is suitable for completely new ranges of application. For instance, they have already developed high-strength, water-repellent and magnetizable wood. Now, together with the Empa research group of Francis Schwarze and Javier Ribera, the team has developed a simple, environmentally friendly process for generating electricity from a type of wood sponge, as they reported last week in the journal Science Advances.
Voltage through deformation
If you want to generate electricity ...
AUSTIN, Texas -- Using NASA satellite images and machine learning, researchers with The University of Texas at Austin have mapped changes in the landscape of northwestern Belize over a span of four decades, finding significant losses of forest and wetlands, but also successful regrowth of forest in established conservation zones that protect surviving structures of the ancient Maya.
The research serves as a case study for other rapidly developing and tropical regions of the globe, especially in places struggling to balance forest and wetland conservation with agricultural needs and food security.
"Broad-scale global studies show that tropical deforestation and wetland destruction is occurring ...
Modeling - Urban climate impacts
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have identified a statistical relationship between the growth of cities and the spread of paved surfaces like roads and sidewalks. These impervious surfaces impede the flow of water into the ground, affecting the water cycle and, by extension, the climate.
"We've shown that there is a specific mathematical shape to the relationship between a city's population and the total paved area," ORNL's Christa Brelsford said. "Using that, we examined climate model predictions and determined they correctly represent some important attributes ...
In order to withstand the rigors of space on deep-space missions, food grown outside of Earth needs a little extra help from bacteria. Now, a recent discovery aboard the International Space Station (ISS) has researchers may help create the 'fuel' to help plants withstand such stressful situations.
Publishing their findings to END ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - Women veterinarians make less than their male counterparts, new research from Cornell University's College of Veterinary Medicine has found ¬- with an annual difference of around $100,000 among the top quarter of earners.
The disparity predominantly affects recent graduates and the top half of earners, according to the research, the first overarching study of the wage gap in the veterinary industry.
"Veterinarians can take many paths in their careers, all of which affect earning potential," said the paper's senior author, Dr. Clinton Neill, assistant professor in the Department of Population Medicine and Diagnostic Sciences.
"Similar to what's been found in the human medicine world, we found the wage gap was more prominent ...