Oncotarget: MicroRNA-4287 is controlling epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer
miR-4287 has potential diagnostic and therapeutic significance in preventing advanced, metastatic disease
2021-03-15
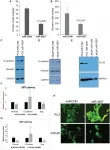
(Press-News.org) The cover for issue 51 of Oncotarget features Figure 5, "miR-4287 overexpression regulates EMT in prostate cancer cell lines," published in "MicroRNA-4287 is a novel tumor suppressor microRNA controlling epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer" by Bhagirath, et al. which reported that the authors analyzed the role of miR-4287 in PCa using clinical tissues and cell lines.
Receiver operating curve analysis showed that miR-4287 distinguishes prostate cancer from normal with a specificity of 88.24% and with an Area under the curve of 0.66. Further, these authors found that miR-4287 levels correlate inversely with patients' serum prostate-specific antigen levels.
Ectopic over-expression of miR-4287 in PCa cell lines showed that miR-4287 plays a tumor suppressor role.
miR-4287 led to an increase in G2/M phase of cell cycle in PCa cell lines.
Further, ectopic miR-4287 inhibited PCa epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by directly repressing SLUG and stem cell marker CD44. Since miR-4287 specifically targets metastasis pathway mediators, miR-4287 has potential diagnostic and therapeutic significance in preventing advanced, metastatic disease.
miR-4287 has potential diagnostic and therapeutic significance in preventing advanced, metastatic disease
Dr. Sharanjot Saini from The Augusta University said, "Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second leading cause of cancer related deaths among men in the United States."
Prostate Specific Antigen, a glycoprotein that is synthesized and released by normal and tumor cells, is often used for early detection and diagnosis of prostate cancer.
Previous research from these researcher's laboratory has shown an important tumor suppressor role of these miRNAs including miR-3622a, miR-3622b, miR-383 and miR4288 whereby these miRNAs are down-regulated in prostate tumors, mediate an anti-proliferative effect on tumor cells and are involved in inhibiting the metastasis and progression of the disease.
In the present study, they studied the function of a novel miRNA, miR-4287, another miRNA that falls on chromosome 8p 21.1 within the intron of gene scavenger receptor class A member 5, in prostate cancer cell lines.
They observed a similar tumor suppressor role of miR-4287 in prostate cancer as it was found to be downregulated in PCa clinical samples.
Chr8p region has traditionally been associated with PCa initiation through a significantly higher deletion frequency has been reported in advanced PCa reference suggesting its role in PCa progression.
The Saini Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Paper, "in the present study we define a tumor-suppressor role of a novel miRNA- miR-4287- in prostate cancer via its regulation of prostate cancer EMT and stemness. This role of miR-4287 is in line with our earlier defined tumor suppressive role of other miRNAs located within this frequently deleted region on chromosome 8p [14–17, 23], implicating an important mechanistic role of chr8p in driving prostate cancer progression, metastasis and tumor recurrence. Given that these miRNAs play essential roles in PCa progression and are lost in advanced prostate cancer, it will be important to devise strategies to re-instate their expression in tumors via therapeutic interventions to successfully treat aggressive prostate cancer."
INFORMATION:
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27849
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/27849/text/
Correspondence to - Sharanjot Saini - ssaini@augusta.edu
Keywords -
miR-4287,
prostate cancer,
chromosome 8p,
EMT,
SLUG
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a biweekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit http://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
18009220957x105
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-15
NEW YORK, NY (March 15, 2021)--A cytokine "hurricane" centered in the lungs drives respiratory symptoms in patients with severe COVID-19, a new study by immunologists at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons suggests.
Two cytokines, CCL2 and CCL3, appear critical in luring immune cells, called monocytes, from the bloodstream into the lungs, where the cells launch an overaggressive attempt to clear the virus.
Targeting these specific cytokines with inhibitors may calm the immune reaction and prevent lung tissue damage. Currently, one drug that blocks immune responses to CCL2 is being studied in clinical trials of patients with severe COVID-19.
Survivors of severe COVID-19, the study also found, had a greater abundance of antiviral T cells in their lungs ...
2021-03-15
Philadelphia, March 15, 2021 - Biomarker testing surveys specific disease-associated molecules to predict treatment response and disease progression; however its use has complicated the diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In a new study in The Journal of Molecular Diagnosis, published by Elsevier, investigators provide for the first time a complete overview of biomarker testing, spanning multiple treatment lines, in a single cohort of patients.
Using exploratory data analysis and process-mining techniques in a real-world setting, investigators identified significant variation in test utilization and treatment. They also found that while ...
2021-03-15
BOSTON - Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have uncovered new clues that add to the growing understanding of how female mammals, including humans, "silence" one X chromosome. Their new study, published in Molecular Cell, demonstrates how certain proteins alter the "architecture" of the X chromosome, which contributes to its inactivation. Better understanding of X chromosome inactivation could help scientists figure out how to reverse the process, potentially leading to cures for devastating genetic disorders.
Female mammals have two copies of the X chromosome in all of their cells. Each X chromosome contains many genes, but only one of the pair ...
2021-03-15
Ingo Burgert and his team at Empa and ETH Zurich has proven it time and again: Wood is so much more than "just" a building material. Their research aims at extending the existing characteristics of wood in such a way that it is suitable for completely new ranges of application. For instance, they have already developed high-strength, water-repellent and magnetizable wood. Now, together with the Empa research group of Francis Schwarze and Javier Ribera, the team has developed a simple, environmentally friendly process for generating electricity from a type of wood sponge, as they reported last week in the journal Science Advances.
Voltage through deformation
If you want to generate electricity ...
2021-03-15
AUSTIN, Texas -- Using NASA satellite images and machine learning, researchers with The University of Texas at Austin have mapped changes in the landscape of northwestern Belize over a span of four decades, finding significant losses of forest and wetlands, but also successful regrowth of forest in established conservation zones that protect surviving structures of the ancient Maya.
The research serves as a case study for other rapidly developing and tropical regions of the globe, especially in places struggling to balance forest and wetland conservation with agricultural needs and food security.
"Broad-scale global studies show that tropical deforestation and wetland destruction is occurring ...
2021-03-15
Modeling - Urban climate impacts
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have identified a statistical relationship between the growth of cities and the spread of paved surfaces like roads and sidewalks. These impervious surfaces impede the flow of water into the ground, affecting the water cycle and, by extension, the climate.
"We've shown that there is a specific mathematical shape to the relationship between a city's population and the total paved area," ORNL's Christa Brelsford said. "Using that, we examined climate model predictions and determined they correctly represent some important attributes ...
2021-03-15
In order to withstand the rigors of space on deep-space missions, food grown outside of Earth needs a little extra help from bacteria. Now, a recent discovery aboard the International Space Station (ISS) has researchers may help create the 'fuel' to help plants withstand such stressful situations.
Publishing their findings to END ...
2021-03-15
ITHACA, N.Y. - Women veterinarians make less than their male counterparts, new research from Cornell University's College of Veterinary Medicine has found ¬- with an annual difference of around $100,000 among the top quarter of earners.
The disparity predominantly affects recent graduates and the top half of earners, according to the research, the first overarching study of the wage gap in the veterinary industry.
"Veterinarians can take many paths in their careers, all of which affect earning potential," said the paper's senior author, Dr. Clinton Neill, assistant professor in the Department of Population Medicine and Diagnostic Sciences.
"Similar to what's been found in the human medicine world, we found the wage gap was more prominent ...
2021-03-15
Do children learning French as a second language see benefits from reading bilingual French-English children's books?
A study recently published in the journal Language and Literacy found that bilingual books, which are not often used in French immersion classrooms, are seen by students as an effective tool for second language learning.
To find out more on this topic, we spoke with the co-author of the paper, Joël Thibeault, Assistant Professor of French education at uOttawa's Faculty of Education.
What is the topic of your research?
"My research focuses on the educational value of bilingual children's books in the teaching of French as a second language. To highlight this value, I zeroed in on elementary students in French immersion ...
2021-03-15
Drugs can only work if they stick to their target proteins in the body. Assessing that stickiness is a key hurdle in the drug discovery and screening process. New research combining chemistry and machine learning could lower that hurdle.
The new technique, dubbed DeepBAR, quickly calculates the binding affinities between drug candidates and their targets. The approach yields precise calculations in a fraction of the time compared to previous state-of-the-art methods. The researchers say DeepBAR could one day quicken the pace of drug discovery and protein engineering.
"Our method is orders of magnitude faster than before, meaning we can have drug discovery that is both efficient and reliable," ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Oncotarget: MicroRNA-4287 is controlling epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer
miR-4287 has potential diagnostic and therapeutic significance in preventing advanced, metastatic disease