(Press-News.org) In 1966, US Army scientists drilled down through nearly a mile of ice in northwestern Greenland--and pulled up a fifteen-foot-long tube of dirt from the bottom. Then this frozen sediment was lost in a freezer for decades. It was accidentally rediscovered in 2017.
In 2019, University of Vermont scientist Andrew Christ looked at it through his microscope--and couldn't believe what he was seeing: twigs and leaves instead of just sand and rock. That suggested that the ice was gone in the recent geologic past--and that a vegetated landscape, perhaps a boreal forest, stood where a mile-deep ice sheet as big as Alaska stands today.
Over the last year, Christ and an international team of scientists--led by Paul Bierman at UVM, Joerg Schaefer at Columbia University and Dorthe Dahl-Jensen at the University of Copenhagen--have studied these one-of-a-kind fossil plants and sediment from the bottom of Greenland. Their results show that most, or all, of Greenland must have been ice-free within the last million years, perhaps even the last few hundred-thousand years.
"Ice sheets typically pulverize and destroy everything in their path," says Christ, "but what we discovered was delicate plant structures--perfectly preserved. They're fossils, but they look like they died yesterday. It's a time capsule of what used to live on Greenland that we wouldn't be able to find anywhere else."
The discovery helps confirm a new and troubling understanding that the Greenland ice has melted off entirely during recent warm periods in Earth's history--periods like the one we are now creating with human-caused climate change.
Understanding the Greenland Ice Sheet in the past is critical for predicting how it will respond to climate warming in the future and how quickly it will melt. Since some twenty feet of sea-level rise is tied up in Greenland's ice, every coastal city in the world is at risk. The new study provides the strongest evidence yet that Greenland is more fragile and sensitive to climate change than previously understood--and at grave risk of irreversibly melting off.
"This is not a twenty-generation problem," says Paul Bierman, a geoscientist at UVM in the College of Arts & Sciences, Rubenstein School of Environment & Natural Resources, and fellow in the Gund Institute for Environment. "This is an urgent problem for the next 50 years."
The new research was published March 15 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
BENEATH THE ICE
The material for the new PNAS study came from Camp Century, a Cold War military base dug inside the ice sheet far above the Arctic Circle in the 1960s. The real purpose of the camp was a super-secret effort, called Project Iceworm, to hide 600 nuclear missiles under the ice close to the Soviet Union. As cover, the Army presented the camp as a polar science station.
The military mission failed, but the science team did complete important research, including drilling a 4560-foot-deep ice core. The Camp Century scientists were focused on the ice itself--part of the burgeoning effort at the time to understand the deep history of Earth's ice ages. They, apparently, took less interest in a bit of dirt gathered from beneath the ice core. Then, in a truly cinematic set of strange plot twists, the ice core was moved from an Army freezer to the University of Buffalo in the 1970s, to another freezer in Copenhagen, Denmark, in the 1990s, where it languished for decades--until it surfaced when the cores were being moved to a new freezer.
More about how the core was lost, rediscovered in some cookie jars, and then studied by an international team gathered at the University of Vermont in 2019 can be read here: END
Scientists stunned to discover plants beneath mile-deep Greenland ice
Long-lost ice core provides direct evidence that giant ice sheet melted off within the last million years and is highly vulnerable to a warming climate
2021-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
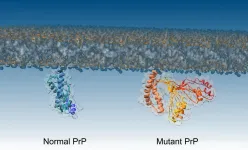
Crucial step in formation of deadly brain diseases discovered
2021-03-15
For the first time, researchers have pinpointed what causes normal proteins to convert to a diseased form, causing conditions like CJD and Kuru.
The research team, from Imperial College London and the University of Zurich, also tested a way to block the process, which could lead to new drugs for combatting these diseases.
The research concerned prion diseases - a group of brain diseases caused by proteins called prions that malfunction and 'misfold', turning into a form that can accumulate and kill brain cells. These diseases can take decades to manifest, but are then are aggressive and fatal.
They include Kuru, mad cow disease and its human equivalent Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), and a heritable condition called fatal familial ...
Race influences flood risk behaviors
2021-03-15
If you live in a flood prone area, would you -- or could you -- take measures to mitigate flood risks? What about others in your community? We are running out of time to ask this question according to The World Resources Institute, because global flood risk is increasing and loss projections for rivers alone put the cost over 500 billion dollars by midcentury.
Research published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences from scientists from the University of Connecticut, the University of Maryland's National Socio-Environmental Synthesis Center (SESYNC), the University of Massachusetts Amherst, and the London School of Economics suggests that in the United States, race and stream flow are ...
How novel pathogens may cause the development of colorectal cancer
2021-03-15
Do BMMFs, the novel infectious agents found in dairy products and bovine sera, play a role in the development of colorectal cancer? Scientists led by Harald zur Hausen detected the pathogens in colorectal cancer patients in close proximity to tumors. The researchers show that the BMMFs trigger local chronic inflammation, which can cause mutations via activated oxygen molecules and thus promote cancer development in the long term. BMMFs and inflammatory markers were significantly more frequently detectable in the vicinity of malignant intestinal tumors than in the intestinal tissue of tumor-free individuals.
A few years ago, ...
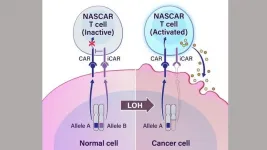
Cancer immunotherapy approach targets common genetic alteration
2021-03-15
Researchers developed a prototype for a new cancer immunotherapy that uses engineered T cells to target a genetic alteration common among all cancers. The approach, which stimulates an immune response against cells that are missing one gene copy, called loss of heterozygosity (LOH), was developed by researchers at the Ludwig Center, Lustgarten Laboratory and the Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
Genes have two alleles, or copies, with one copy inherited from each parent. Cancer-related genetic alterations commonly involve the loss of one of these gene copies.
"This copy loss, or LOH, is one of the most common genetic events in cancer," says Kenneth Kinzler, Ph.D., co-director of the Ludwig Center, professor of oncology and ...
Internet-access spending improves academic outcomes, according to study of Texas public schools
2021-03-15
HOUSTON - (March 15, 2021) - Increased internet-access spending by Texas public schools improved academic performance but also led to more disciplinary problems among students, a study of 9,000 schools conducted by a research team from Rice University, Texas A&M University and the University of Notre Dame shows.
Whether students benefit from increased internet access in public schools has been an open question, according to the researchers. For example, some parents and policy advocates contend it increases children's access to obscene or harmful content and disciplinary problems. Others believe it promotes personalized learning and higher student engagement.
To address these policy questions, the research team created a multiyear dataset (2000-14) of 1,243 school districts ...
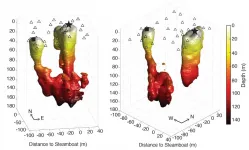
University of Utah scientists plumb the depths of the world's tallest geyser
2021-03-15
When Steamboat Geyser, the world's tallest, started erupting again in 2018 in Yellowstone National Park after decades of relative silence, it raised a few tantalizing scientific questions. Why is it so tall? Why is it erupting again now? And what can we learn about it before it goes quiet again?
The University of Utah has been studying the geology and seismology of Yellowstone and its unique features for decades, so U scientists were ready to jump at the opportunity to get an unprecedented look at the workings of Steamboat Geyser. Their findings provide a picture of the depth of the geyser as well as a redefinition of a long-assumed relationship between the geyser and a nearby spring. The findings are published in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth.
"We ...
Marketplace literacy as a pathway to a better world: evidence from field experiments
2021-03-15
If you are a consumer and/or entrepreneur who can make decisions based on cost, competition, supply and demand, you probably possess an element of marketplace literacy.
"Marketplace literacy" is defined as the knowledge and skills that enable individuals to participate in a marketplace both as consumers and entrepreneurs. San Diego State University marketing professor Nita Umashankar, along with professors Madhubalan Viswanathan (Loyola Marymount University), Arun Sreekumar (University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign) and Ashley Goreczny (Iowa State University), explored the impact on marketplace literacy on ...
How can new technologies help reduce the harm of drug use?
2021-03-15
HSE University researchers together with specialists from the Humanitarian Action Charitable Fund (St. Petersburg) and the University of Michigan School of Public Health (USA) studied the specifics of remote work with Russian people who use drugs to reduce the harm of drug use. They discovered that the use of online platforms increases the § who use drugs to seek help. Online platforms also serve as a kind of 'gateway' for people with problematic drug use to receive a wider range of qualified help. The authors concluded that remote work in this field should be developed and built upon in ...
Lessons learned in Burkina Faso can contribute to a new decade of forest restoration
2021-03-15
Forest landscape restoration is attaining new global momentum this year under the Decade of Ecosystem Restoration (2021-2030), an initiative launched by the United Nations. Burkina Faso, in West Africa, is one country that already has a head start in forest landscape restoration, and offers valuable lessons. An assessment of achievements there and in other countries with a history of landscape restoration is critical to informing a new wave of projects aiming for more ambitious targets that are being developed thanks to renewed global interest and political will to improve the environment.
Burkina Faso has been fighting with desertification and climate change, and has seen a progressive degradation of its forested landscapes due to the expansion of agriculture. In 2018, the country ...
Racial disparities in heart disease, hypertension, and diabetes death rates have minimally improved over last two decades
2021-03-15
In the last 20 years, Black adults living in rural areas of the United States experienced high mortality rates due to diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease and stroke compared to white adults. According to a research letter published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, racial disparities improved minimally in rural areas over the last two decades, with larger improvements occurring in urban areas.
"While modest gains have been made in reducing racial health inequities in urban areas, large gaps in death rates between Black and white adults persist in rural areas, particularly for diabetes and hypertension. We haven't meaningfully ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
[Press-News.org] Scientists stunned to discover plants beneath mile-deep Greenland iceLong-lost ice core provides direct evidence that giant ice sheet melted off within the last million years and is highly vulnerable to a warming climate