(Press-News.org) Children who are exposed to abuse before they are eleven years old, and those exposed to abuse both in childhood and adolescence may be more likely to develop conduct problems (such as bullying or stealing) than those exposed to abuse in adolescence only and those who are not exposed to abuse, according to a study published in the open access journal BMC Psychiatry.
A team of researchers at the Universities of Bath and Bristol examined data on 13,793 children and adolescents (51.6% boys), who were followed from ages four to 17 years, included in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children, a cohort of children born in South-West England in the early 1990s.
Andreas Bauer, the lead author said: "Conduct problems refer to antisocial behaviors in childhood and/or adolescence, such as fighting, bullying, lying or stealing. They are associated with various negative outcomes, including mental and physical health problems, and it is important to understand their possible causes and to develop effective prevention and intervention programs. Although we know that child abuse is an important factor linked to conduct problems in children, much less is known about when child abuse is most harmful and how it relates to the development of serious behaviour problems over time."
From the children included in this study, the authors identified three groups who developed elevated levels of conduct problems. There was an early-onset persistent group who developed conduct problems in childhood which continued into adolescence (4.8% of the sample), an adolescence-onset group who developed conduct problems in adolescence (4.5%) and a childhood-limited group who developed conduct problems in childhood only (15.4%). The majority of children (75.3%) did not develop serious conduct problems.
Andreas Bauer said: "We assessed whether abuse was more common in the backgrounds of these three groups than in those who did not develop conduct problems. Our findings showed that abuse was more common in the early-onset persistent group who showed conduct problems in childhood and adolescence, and also in the adolescence-onset group who developed conduct problems in adolescence."
The authors also looked at the timing of child abuse, comparing those who were exposed to abuse only in childhood or only in adolescence with those exposed to abuse in childhood and adolescence. They found that children exposed to abuse in both childhood and adolescence were 10 times more likely to be in the early-onset persistent conduct problems group and 8 times more likely to be in the adolescence-onset conduct problems group. Abuse in childhood was associated with a 4- to 6-fold increase in risk for showing early-onset persistent or adolescence-onset conduct problems. In contrast, abuse in adolescence only was not linked to an increased risk of showing severe conduct problems.
Conduct problems were measured at ages 4, 7, 8, 10, 12, 13, and 17, by asking parents to rate their child's behavior over the last six months. At age 22, individuals were asked to report physical, psychological, or sexual abuse experienced in childhood (before age 11 years) and adolescence (between ages 11-17 years). Complete data for conduct problems as reported by parents and children, and physical, psychological, and sexual abuse as reported by children was available for 3,127 participants. Out of those, one in five (19.6%) participants reported experiencing some form of abuse, with 11.3%, 8.9%, and 8.1% of participants reporting physical, psychological, and sexual abuse, respectively.
A limitation of the study is that experiences of abuse in childhood and adolescence were measured when the participants were aged 22 years, so there may be issues with recall biases and issues surrounding disclosure of earlier abuse. Relying on parent-reported conduct problems in adolescence may have underestimated the level of behavioral problems, as parents may not be aware of their child's behavior outside the home.
Andreas Bauer said: "Our results suggest that abuse is more common in the backgrounds of young people with conduct problems and that conduct problems starting in adolescence may be linked to adverse experiences in childhood, rather than being an exaggerated form of teenage rebellion or due to peer pressure. Preventing child abuse may also help protect children from developing serious behaviour problems. However, it is important to note that many young people who experience abuse do not develop conduct problems, and conduct problems can also occur in the absence of child abuse."
INFORMATION:
Media Contact
Anne Korn
Senior Communications Manager
BMC
T: +44 (0)20 3192 2744
E: anne.korn@biomedcentral.com
Notes to editor:
1. Research article:
Associations between developmental timing of child abuse and conduct problem trajectories in a UK birth cohort
Bauer et al. BMC Psychiatry 2021
DOI: 10.1186/s12888-021-03083-8
For an embargoed copy of the research article please contact Anne Korn at BMC.
After the embargo lifts, the article will be available here:
https://bmcpsychiatry.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12888-021-03083-8
Please name the journal in any story you write. If you are writing for the web, please link to the article. All articles are available free of charge, according to BMC's open access policy.
2. BMC Psychiatry is an open access, peer-reviewed journal that considers articles on all aspects of the prevention, diagnosis and management of psychiatric disorders, as well as related molecular genetics, pathophysiology, and epidemiology.
3. A pioneer of open access publishing, BMC has an evolving portfolio of high quality peer-reviewed journals including broad interest titles such as BMC Biology and BMC Medicine, specialist journals such as Malaria Journal and Microbiome, and the BMC series. At BMC, research is always in progress. We are committed to continual innovation to better support the needs of our communities, ensuring the integrity of the research we publish, and championing the benefits of open research. BMC is part of Springer Nature, giving us greater opportunities to help authors connect and advance discoveries across the world.
Rapid deployment of artificial intelligence and machine learning to tackle coronavirus must still go through ethical checks and balances, or we risk harming already disadvantaged communities in the rush to defeat the disease.
This is according to researchers at the University of Cambridge's Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence (CFI) in two articles, published today in the British Medical Journal, cautioning against blinkered use of AI for data-gathering and medical decision-making as we fight to regain some normalcy in 2021.
"Relaxing ...
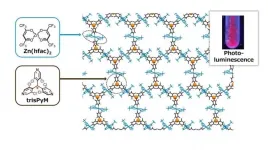
Coordination polymers (CPs) composed of organic radicals have been the focus of much research attention in recent years due to their potential application to a wide variety of next-generation electronics, from more flexible devices to 'spintronics' storage of information. Sadly, they often suffer from their limited stability and poor crystallinity. Researchers from Japan's Institute for Molecular Science (IMS), National Institute of Natural Sciences (NINS) have developed a novel recipe that not only produces a stable material, but offers a variety of other useful attributes.
Their findings appear in the journal ...
The 2020 COVID-19 pandemic is creating a viral archive, an archaeological record of history in the making. One aspect of this archive is increased environmental pollution, not least through discarded face-masks and gloves, collectively known as PPE, that characterise the pandemic.
These items of plastic waste have become symbolic of the pandemic and have now entered the archaeological record, in particular face-masks.
In the UK alone, 748 million items of PPE, amounting to 14 million items a day, were delivered to hospitals in the two or so months from ...
Researchers believe they may have discovered a possible cause of a mystery condition that can leave sufferers suddenly unable to walk, talk or see.
It's hoped the study - led by the University of York and Hull York Medical School and supported by Tees, Esk and Wear Valley NHS Trust - will pave the way for new treatments for Conversion disorder which affects around 800,000 people in the UK alone.
The condition, also known as functional neurological disorder (FND), causes physical symptoms that would appear neurological but doctors can't find an injury or physical condition to explain them.
Professor Christina van der Feltz-Cornelis from the Department of Health Sciences is leading the Conversion And Neuro-inflammation ...
Two-thirds of 1,120 healthcare workers surveyed worldwide would separate mothers and babies with a positive or unknown COVID-19 status.
Implementing Kangaroo Mother Care and keeping mothers and babies together could save more than 125,000 newborn lives, representing 65x decreased risk of newborn death compared to the risk of newborn deaths from COVID-19.
New research underscores the need for decision-makers and providers, particularly in LMICs, to protect and strengthen care for small and sick newborns during the pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic is affecting the quality of care given to small and sick newborn babies in all regions of the world and threatening implementation of life-saving interventions, ...
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Switching from TDF- to TAF-containing ART associated with the development of obesity in people living with HIV
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-4853
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
Switching from antiretroviral therapy ...
In Switzerland about 17 000 people are living with an HIV infection, worldwide there are about 38 million. Today, the disease can be treated so successfully that a normal life can be ensured to a great extent. However, weight increases are often observed at the beginning of HIV therapy due to adaptations of the metabolism, which are part of a successful therapy. Therefore, body weight control plays an important role in HIV therapy. It is important, for example, to avoid metabolic problems that can lead to heart attacks or diabetes over the long term.
Tenofovir is the drug used as part of the standard HIV therapies. The previously, widely used TDF-based therapy (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, TDF) has been associated with renal side effects and ...
An important Maya man buried nearly 1,300 years ago led a privileged yet difficult life. The man, a diplomat named Ajpach' Waal, suffered malnutrition or illness as a child, but as an adult he helped negotiate an alliance between two powerful dynasties that ultimately failed. The ensuing political instability left him in reduced economic circumstances, and he probably died in relative obscurity.
During excavations at El Palmar, a small plaza compound in Mexico near the borders of Belize and Guatemala, archaeologists led by Kenichiro Tsukamoto, an assistant professor of anthropology at UC Riverside, discovered a hieroglyph-adorned stairway ...
(Boston)-- Newly published National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Traumatic Encephalopathy Syndrome (TES) are the first expert consensus criteria developed for the clinical disorder associated with Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) brain pathology. CTE is a degenerative brain disease associated with a history of repetitive head impacts, including those sustained in contact and collision sports such as American football and boxing. At this time, CTE can only be diagnosed after death through a neuropathological examination of brain tissue. There has been no accepted approach or agreed upon criteria for the diagnosis of CTE and its clinical manifestations during life until now.
"The publication of these criteria ...
Exercise during pregnancy may let mothers significantly reduce their children's chances of developing diabetes and other metabolic diseases later in life, new research suggests.
A study in lab mice has found that maternal exercise during pregnancy prevented the transmission of metabolic diseases from an obese parent - either mother or father - to child. If the finding holds true in humans, it will have "huge implications" for helping pregnant women ensure their children live the healthiest lives possible, the researchers report in a new scientific paper.
This means that one day soon, a woman's first trip to the doctor after conceiving might include a prescription for an exercise ...