Combination therapy may provide significant protection against lethal influenza
Targeting a receptor involved in exaggerated immune response to influenza infection improves survival in animal models, investigators report in The American Journal of Pathology
2021-03-16
(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, March 16, 2021 - A significant proportion of hospitalized patients with influenza develop complications of acute respiratory distress syndrome, driven by virus-induced cytopathic effects as well as exaggerated host immune response. Reporting in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, investigators have found that treatment with an immune receptor blocker in combination with an antiviral agent markedly improves survival of mice infected with lethal influenza and reduces lung pathology in swine-influenza-infected piglets. Their research also provides insights into the optimal timing of treatment to prevent acute lung injury.
Previously, the investigators found that an excessive influx of neutrophils, infection fighting immune cells, and the networks they create to kill pathogens, known as neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), contribute to acute lung injury in influenza infection. Formation of NETs by activated neutrophils occurs via a cell death mechanism called NETosis and the released NETs contain chromatin fibers that harbor toxic components.
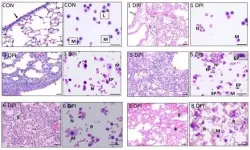
A mouse model, commonly used in exploring influenza pathophysiology and drug therapies, was used in the current study. Because mice are not natural hosts for influenza, further validation in larger animals is necessary before testing in humans. Therefore, researchers also tested piglets infected with swine influenza virus. The animals were treated with a combination of a CXCR2 antagonist, SCH527123, together with an antiviral agent, oseltamivir.
The combination of SCH527123 and oseltamivir significantly improved survival in mice compared to either of the drugs administered alone. The combination therapy also reduced pulmonary pathology in piglets.
"Combination therapy reduces lung inflammation, alveolitis, and vascular pathology, indicating that aberrant neutrophil activation and release in NETs exacerbate pulmonary pathology in severe influenza," explains lead investigator Narasaraju Teluguakula, PhD, Center for Veterinary Health Sciences, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, USA. "These findings support the evidence that antagonizing CXCR2 may alleviate lung pathology and may have significant synergistic effects with antiviral treatment to reduce influenza-associated morbidity and mortality."
It can be challenging to balance the suppression of excessive neutrophil influx without compromising the beneficial host immunity conferred by neutrophils. Therefore, the researchers examined the temporal dynamics of NETs release in correlation with pathological changes during the course of infection in mice. During the early inflammatory phase, three to five days post infection, significant neutrophil activation and NETs release with relatively few hemorrhagic lesions was observed. In the late hemorrhagic exudative phase, significant vascular injury with declining neutrophil activity was seen.
Dr. Teluguakula also emphasizes that these findings provide the first evidence to support the strategy of testing combination therapy in a large animal influenza model. "In view of the close similarities in pulmonary pathology and immune responses between swine and humans, pig-influenza pneumonia models can serve as a common platform in understanding pathophysiology and host-directed drug therapies in human influenza infections and may be useful in advancing the translational impact of drug treatment studies in human influenza infections."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-16
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a new intravascular imaging technique that could one day be used to detect coronary plaques that are likely to lead to a heart attack. Heart attacks are often triggered when an unstable plaque ruptures and then blocks a major artery that carries blood and oxygen to the heart.
"If unstable coronary plaques could be detected before they rupture, pharmacological or other treatments could be initiated early to prevent heart attacks and save lives," said research team leader Seemantini Nadkarni from the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital. "Our new imaging technique represents a major step toward achieving this."
In The Optical Society (OSA) journal Biomedical ...
2021-03-16
MADISON, Wis. -- Millions of people are administered general anesthesia each year in the United States alone, but it's not always easy to tell whether they are actually unconscious.
A small proportion of those patients regain some awareness during medical procedures, but a new study of the brain activity that represents consciousness could prevent that potential trauma. It may also help both people in comas and scientists struggling to define which parts of the brain can claim to be key to the conscious mind.
"What has been shown for 100 years in an unconscious state like sleep are these slow ...
2021-03-16
Low doses of propylparaben - a chemical preservative found in food, drugs and cosmetics - can alter pregnancy-related changes in the breast in ways that may lessen the protection against breast cancer that pregnancy hormones normally convey, according to University of Massachusetts Amherst research.
The findings, published March 16 in the journal Endocrinology, suggest that propylparaben is an endocrine-disrupting chemical that interferes with the actions of hormones, says environmental health scientist Laura Vandenberg, the study's senior author. Endocrine ...
2021-03-16
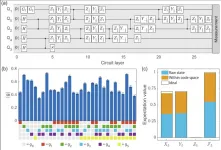
Universal fault-tolerant quantum computing relies on the implementation of quantum error correction. An essential milestone is the achievement of error-corrected logical qubits that genuinely benefit from error correction, outperforming simple physical qubits. Although tremendous efforts have been devoted to demonstrate quantum error correcting codes with different quantum hardware, previous realizations are limited to be against certain types of errors or to prepare special logical states. It remains one of the greatest and also notoriously difficult challenges to realize a universal quantum error correcting code for more than a decade.
In a new research article published in the ...
2021-03-16
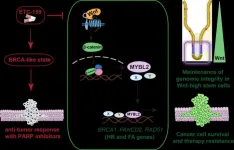
SINGAPORE, 16 March 2021 - ETC-159, a made-in-Singapore anti-cancer drug that is currently in early phase clinical trials for use in a subset of colorectal and gynaecological cancers, could also prevent some tumours from resisting therapies by blocking a key DNA repair mechanism, researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) in Singapore reported in the journal EMBO Molecular Medicine.
Among the many therapies used to treat cancers, inhibitors of the enzyme poly (ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP) prevent cancer cells from repairing naturally occurring DNA damage, including unwanted/harmful breaks in the DNA. When too many breaks accumulate, the cell dies.
"Some cancers have an overactive Wnt signalling pathway that may make them ...
2021-03-16
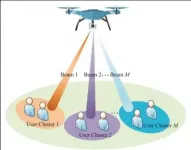
Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and millimeter-wave (mmWave) are two crucial techniques of 5G to meet the explosive capacity demands. On the other hand, UAVs deployed as aerial base stations are potential to provide ubiquitous coverage and satisfy users' multifarious requirements due to their flexibility and mobility. Nevertheless, the finite onboard energy is a fundamental limit of UAVs, which can deter the performance of UAV communication networks. Therefore, the researchers Xiaowei PANG and Nan ZHAO from Dalian University of Technology, Jie TANG and Xiuyin ZHANG from South China University of Technology, and Yi QIAN from University of Nebraska-Lincoln have focused on designing energy-efficient ...
2021-03-16
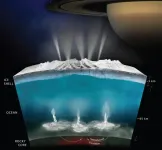
SAN ANTONIO -- March 16, 2021 -- One of the most profound discoveries in planetary science over the past 25 years is that worlds with oceans beneath layers of rock and ice are common in our solar system. Such worlds include the icy satellites of the giant planets, like Europa, Titan and Enceladus, and distant planets like Pluto.
In a report presented at the 52nd annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC 52) this week, Southwest Research Institute planetary scientist S. Alan Stern writes that the prevalence of interior water ocean worlds (IWOWs) in our solar system suggests they may be prevalent in other star systems as well, vastly expanding the conditions for planetary habitability and biological survival over time.
It has been known for many years that worlds like Earth, ...
2021-03-16
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a well-studied neurodegenerative disorder that affects between 7 and 10 million people worldwide. Despite PD being a recurrent topic in the medical literature for over 200 years, its mechanisms are largely unclear, and existing treatments are aimed at improving the patient's symptoms.
Among PD's most common symptoms are motor problems, including as tremors, slowness, and muscular rigidity. These, combined with many non-motor symptoms, cause many PD patients to develop facial abnormalities, such as face skin problems and difficulties making facial expressions. Such problems are not to be taken lightly, as one's face plays a crucial ...
2021-03-16
Superconductivity is a complete loss of electrical resistance. Superconductors are not merely very good metals: it is a fundamentally different electronic state. In normal metals, electrons move individually, and they collide with defects and vibrations in the lattice. In superconductors, electrons are bound together by an attractive force, which allows them to move together in a correlated way and avoid defects.
In a very small number of known superconductors, the onset of superconductivity causes spontaneous electrical currents to flow. These currents ...
2021-03-16
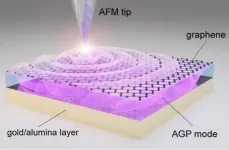
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new methodology for direct near-field optical imaging of acoustic graphene plasmon fields. This strategy will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of acoustic graphene plasmon platforms in next-generation, high-performance, graphene-based optoelectronic devices with enhanced light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss.
It was recently demonstrated that 'graphene plasmons' - collective oscillations of free electrons in graphene coupled to electromagnetic waves of light - can be used to trap and compress optical waves inside a very thin dielectric ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Combination therapy may provide significant protection against lethal influenza
Targeting a receptor involved in exaggerated immune response to influenza infection improves survival in animal models, investigators report in The American Journal of Pathology