SwRI researcher theorizes worlds with underground oceans support, conceal life
Layers of ice and rock obviate the need for "habitable zone" and shield life against threats
2021-03-16
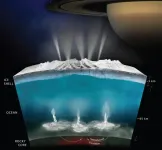
(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO -- March 16, 2021 -- One of the most profound discoveries in planetary science over the past 25 years is that worlds with oceans beneath layers of rock and ice are common in our solar system. Such worlds include the icy satellites of the giant planets, like Europa, Titan and Enceladus, and distant planets like Pluto.
In a report presented at the 52nd annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC 52) this week, Southwest Research Institute planetary scientist S. Alan Stern writes that the prevalence of interior water ocean worlds (IWOWs) in our solar system suggests they may be prevalent in other star systems as well, vastly expanding the conditions for planetary habitability and biological survival over time.
It has been known for many years that worlds like Earth, with oceans that lie on their surface, must reside within a narrow range of distances from their stars to maintain the temperatures that preserve those oceans. However, IWOWs are found over a much wider range of distances from their stars. This greatly expands the number of habitable worlds likely to exist across the galaxy.
Worlds like Earth, with oceans on their exterior, are also subject to many kinds of threats to life, ranging from asteroid and comet impacts, to stellar flares with dangerous radiation, to nearby supernova explosions and more. Stern's paper points out that IWOWs are impervious to such threats because their oceans are protected by a roof of ice and rock, typically several to many tens of kilometers thick, that overlie their oceans.
"Interior water ocean worlds are better suited to provide many kinds of environmental stability, and are less likely to suffer threats to life from their own atmosphere, their star, their solar system, and the galaxy, than are worlds like Earth, which have their oceans on the outside," said Stern.
He also points out that the same layer of rock and ice that protects the oceans on IWOWs also conceals life from being detected by virtually all astronomical techniques. If such worlds are the predominant abodes of life in the galaxy and if intelligent life arises in them -- both big "ifs," Stern emphasizes -- then IWOWs may also help crack the so-called Fermi Paradox. Posed by Nobel Laureate Enrico Fermi in the early 1960s, the Fermi Paradox questions why we don't see obvious evidence of life if it's prevalent across the universe.
"The same protective layer of ice and rock that creates stable environments for life also sequesters that life from easy detection," said Stern.
INFORMATION:
In 2015, NASA created the Ocean Worlds Exploration Program, which seeks to explore an ocean world to determine habitability and seek life. Moons that harbor oceans under a shell of ice, such as Europa and Titan, are already the targets of NASA missions to study the habitability of these worlds.
The paper, "Some Implications for Both Life and Civilizations Regarding Interior Water Ocean Worlds" at LPSC 52 is available at https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2021/pdf/1180.pdf.
To learn more about ocean worlds, watch https://youtu.be/_9AYw2EQm8s and https://youtu.be/086N-X1Bd2o.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/planetary-science.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-16
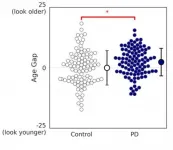
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a well-studied neurodegenerative disorder that affects between 7 and 10 million people worldwide. Despite PD being a recurrent topic in the medical literature for over 200 years, its mechanisms are largely unclear, and existing treatments are aimed at improving the patient's symptoms.
Among PD's most common symptoms are motor problems, including as tremors, slowness, and muscular rigidity. These, combined with many non-motor symptoms, cause many PD patients to develop facial abnormalities, such as face skin problems and difficulties making facial expressions. Such problems are not to be taken lightly, as one's face plays a crucial ...
2021-03-16
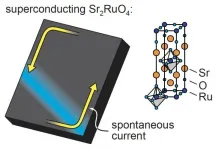
Superconductivity is a complete loss of electrical resistance. Superconductors are not merely very good metals: it is a fundamentally different electronic state. In normal metals, electrons move individually, and they collide with defects and vibrations in the lattice. In superconductors, electrons are bound together by an attractive force, which allows them to move together in a correlated way and avoid defects.
In a very small number of known superconductors, the onset of superconductivity causes spontaneous electrical currents to flow. These currents ...
2021-03-16
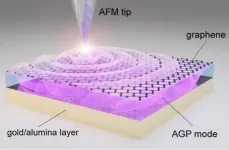
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new methodology for direct near-field optical imaging of acoustic graphene plasmon fields. This strategy will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of acoustic graphene plasmon platforms in next-generation, high-performance, graphene-based optoelectronic devices with enhanced light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss.
It was recently demonstrated that 'graphene plasmons' - collective oscillations of free electrons in graphene coupled to electromagnetic waves of light - can be used to trap and compress optical waves inside a very thin dielectric ...
2021-03-16
An analysis has found deforestation is severely affecting forest bird species in Colombia, home to the greatest number of bird species in the world.
University of Queensland-led research, steered by Dr Pablo Negret, analysed the impact of deforestation on 550 bird species, including 69 only found in the South American nation.
"Our study has shown an astonishing reduction in bird species habitat," Dr Negret said.
"One third of the forest bird species in Colombia have lost at least a third of their historical habitat, and that's just using the most recent data we have available - from 2015.
"Moreover, 18 per cent or 99 species have lost more than half of their historical habitat to date.
"By 2040, we expect this will increase to 38 per cent or 209 species.
"Sadly, many of those ...
2021-03-16
A team of scientists led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a device that can deliver electrical signals to and from plants, opening the door to new technologies that make use of plants.
The NTU team developed their plant 'communication' device by attaching a conformable electrode (a piece of conductive material) on the surface of a Venus flytrap plant using a soft and sticky adhesive known as hydrogel. With the electrode attached to the surface of the flytrap, researchers can achieve two things: pick up electrical signals to monitor how the plant responds to ...
2021-03-16
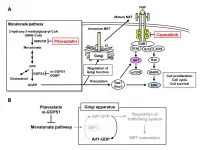
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) uncover potential novel therapeutic strategies for oral and esophageal carcinomas
Tokyo, Japan - Discovering and treating tumors before they spread throughout the body is key for cancer patients to achieve positive outcomes. When tumor cells spread, which is known as metastasis, they can take over other organs and lead to death. Oral and esophageal carcinomas, or mouth and throat cancers, frequently metastasize to the lymph nodes. Unfortunately, there are currently no therapies that are specific to treating these particular cancers. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identified several drugs ...
2021-03-16
A quadruple fusion optical and ultrasound imaging system has been developed that allows diagnosis of eye conditions or tumors or to see the environment inside the body using a transparent ultrasound transducer.
Professor Chulhong Kim of POSTECH's Department of Electrical Engineering, Convergence IT Engineering, and Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Byullee Park of Department of Convergence IT Engineering, Ph.D. candidate Jeongwoo Park of School of Interdisciplinary Bioscience and Bioengineering, Professor Hyung Ham Kim of Department of Convergence IT Engineering, and Professor Unyong Jeong of Department of Materials ...
2021-03-16
The research, by an international team from the Autonomous University of Madrid and the Technical University of Denmark, used 3D printing to create scaffolds for engineered flat brain organoids. The scaffolds allowed the brain organoid size to be significantly increased and after 20 days, self-generated folding was observed. END ...
2021-03-16
Military expenditures are highly counterproductive to green economic growth- documented by a recent study conducted by UrFU economist collaboration with an international research team. Sustainable economic development or green growth requires cleaner energy and green technology that can mitigate the negative externalities (e.g., carbon emission) of economic growth. The study utilized various macroeconomic indicators for 21 OECD countries over the year 1980-2016. This empirical study focusing on the dynamic impact of innovation, militarization and renewable energy on the green economy is published in the journal "Environmental Science and Pollution Research".
On the one hand, the military-industry (land vehicles, aircraft, and sea-vessels) consume a gargantuan ...
2021-03-16
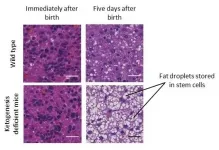
Ketone bodies are generally an alternative energy source during starvation, but in newborns, ketogenesis is active regardless of nutritional status. In a recent study from END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] SwRI researcher theorizes worlds with underground oceans support, conceal life
Layers of ice and rock obviate the need for "habitable zone" and shield life against threats