(Press-News.org) A team of scientists led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a device that can deliver electrical signals to and from plants, opening the door to new technologies that make use of plants.
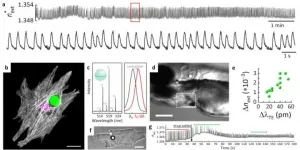
The NTU team developed their plant 'communication' device by attaching a conformable electrode (a piece of conductive material) on the surface of a Venus flytrap plant using a soft and sticky adhesive known as hydrogel. With the electrode attached to the surface of the flytrap, researchers can achieve two things: pick up electrical signals to monitor how the plant responds to its environment, and transmit electrical signals to the plant, to cause it to close its leaves.
Scientists have known for decades that plants emit electrical signals to sense and respond to their environment. The NTU research team believe that developing the ability to measure the electrical signals of plants could create opportunities for a range of useful applications, such as plant-based robots that can help to pick up fragile objects, or to help enhance food security by detecting diseases in crops early.
However, plants' electrical signals are very weak, and can only be detected when the electrode makes good contact with plant surfaces. The hairy, waxy, and irregular surfaces of plants make it difficult for any thin-film electronic device to attach and achieve reliable signal transmission.
To overcome this challenge, the NTU team drew inspiration from the electrocardiogram (ECG), which is used to detect heart abnormalities by measuring the electrical activity generated by the organ.
Transmitting electrical signals to create an on demand plant-based robot
As a proof-of concept, the scientists took their plant 'communication' device and attached it to the surface of a Venus flytrap - a carnivorous plant with hairy leaf-lobes that close over insects when triggered.
The device has a diameter of 3 mm and is harmless to the plant. It does not affect the plant's ability to perform photosynthesis while successfully detecting electrical signals from the plant. Using a smartphone to transmit electric pulses to the device at a specific frequency, the team elicited the Venus flytrap to close its leaves on demand, in 1.3 seconds.
The researchers have also attached the Venus flytrap to a robotic arm and, through the smartphone and the 'communication' device, stimulated its leaf to close and pick up a piece of wire half a millimetre in diameter.
Their findings, published in the scientific journal Nature Electronics in January, demonstrate the prospects for the future design of plant-based technological systems, say the research team. Their approach could lead to the creation of more sensitive robot grippers to pick up fragile objects that may be harmed by current rigid ones.
Picking up electrical signals to monitor crop health monitoring
The research team envisions a future where farmers can take preventive steps to protect their crops, using the plant 'communication' device they have developed.
Lead author of the study, Chen Xiaodong, President's Chair Professor in Materials Science and Engineering at NTU Singapore said: "Climate change is threatening food security around the world. By monitoring the plants' electrical signals, we may be able to detect possible distress signals and abnormalities. When used for agriculture purpose, farmers may find out when a disease is in progress, even before full?blown symptoms appear on the crops, such as yellowed leaves. This may provide us the opportunity to act quickly to maximise crop yield for the population."
Prof Chen, who is also Director of the Innovative Centre for Flexible Devices (iFLEX) at NTU, added that the development of the 'communication' device for plants monitoring exemplifies the NTU Smart Campus vision which aims to develop technologically advanced solutions for a sustainable future.
Next generation improvement: Liquid glue with stronger adhesive strength
Seeking to improve the performance of their plant 'communication' device, the NTU scientists also collaborated with researchers at the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE), a unit of Singapore's Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR).
Results from this separate study, published in the scientific journal Advanced Materials in March, found that by using a type of hydrogel called thermogel - which gradually transforms from liquid to a stretchable gel at room temperature - it is possible to attach their plant 'communication' device to a greater variety of plants (with various surface textures) and achieve higher quality signal detection, despite plants moving and growing in response to the environment.
Elaborating on this study, co-lead author Professor Chen Xiaodong said, "The thermogel-based material behaves like water in its liquid state, meaning that the adhesive layer can conform to the shape of the plant before it turns into a gel. When tested on hairy stems of the sunflower for example, this improved version of the plant 'communication' device achieved four to five times the adhesive strength of common hydrogel and recorded significantly stronger signals and less background noise."
Co-lead author of the Advanced Materials study and Executive Director of IMRE, Professor Loh Xian Jun, said: "The device can now stick to more types of plant surfaces, and more securely so, marking an important step forward in the field of plant electrophysiology. It opens up new opportunities for plant-based technologies."
Moving forward, the NTU team is looking to devise other applications using the improved version of their plant 'communication' device.
INFORMATION:
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) uncover potential novel therapeutic strategies for oral and esophageal carcinomas
Tokyo, Japan - Discovering and treating tumors before they spread throughout the body is key for cancer patients to achieve positive outcomes. When tumor cells spread, which is known as metastasis, they can take over other organs and lead to death. Oral and esophageal carcinomas, or mouth and throat cancers, frequently metastasize to the lymph nodes. Unfortunately, there are currently no therapies that are specific to treating these particular cancers. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identified several drugs ...
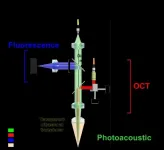
A quadruple fusion optical and ultrasound imaging system has been developed that allows diagnosis of eye conditions or tumors or to see the environment inside the body using a transparent ultrasound transducer.
Professor Chulhong Kim of POSTECH's Department of Electrical Engineering, Convergence IT Engineering, and Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Byullee Park of Department of Convergence IT Engineering, Ph.D. candidate Jeongwoo Park of School of Interdisciplinary Bioscience and Bioengineering, Professor Hyung Ham Kim of Department of Convergence IT Engineering, and Professor Unyong Jeong of Department of Materials ...
The research, by an international team from the Autonomous University of Madrid and the Technical University of Denmark, used 3D printing to create scaffolds for engineered flat brain organoids. The scaffolds allowed the brain organoid size to be significantly increased and after 20 days, self-generated folding was observed. END ...
Military expenditures are highly counterproductive to green economic growth- documented by a recent study conducted by UrFU economist collaboration with an international research team. Sustainable economic development or green growth requires cleaner energy and green technology that can mitigate the negative externalities (e.g., carbon emission) of economic growth. The study utilized various macroeconomic indicators for 21 OECD countries over the year 1980-2016. This empirical study focusing on the dynamic impact of innovation, militarization and renewable energy on the green economy is published in the journal "Environmental Science and Pollution Research".
On the one hand, the military-industry (land vehicles, aircraft, and sea-vessels) consume a gargantuan ...
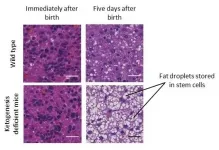
Ketone bodies are generally an alternative energy source during starvation, but in newborns, ketogenesis is active regardless of nutritional status. In a recent study from END ...
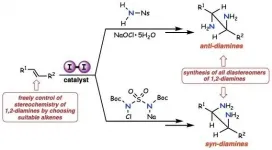
Osaka, Japan - Synthesizing pharmaceuticals for cancer, viral diseases, and other medical conditions is slow work. A particularly challenging chemical transformation is to start with what's known as an unactivated alkene--a common molecular building block--and end up with a vicinal diamine; i.e., installation of two nitrogen units into carbon--carbon double bonds. The result is a chemical unit that's present in medications for influenza and colorectal cancer.
Commonly, researchers must use rare, toxic metals and harsh reaction conditions to complete this transformation. Using a more sustainable catalyst for the reaction could solve such problems. Previous research has attempted to do so, ...
Label-free optical sensors based on optical whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) microresonators exhibit extraordinary sensitivity for detecting physical, chemical, and biological entities, even down to single molecules. This extreme advancement in label-free optical detection is made possible by application of the optical microresonator, i.e. a 100 um glass microspheres, as optical cavity to enhance the detection signal. Akin to a spherical micromirror, the WGM cavity reflects the light by near-total internal reflection and thereby creates multiple cavity passes ...
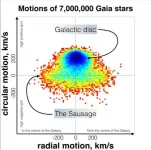
Note: The dwarf galaxy corresponding to the Gaia-Sausage structure of the Milky Way was named Enceladus by astronomers, after one of the hundred-handed giants in Greek mythology who opposed the rule of Zeus.
Looking up at the starry sky, the deep Universe appears quiet and mysterious. It is hard to imagine that the ancient dwarf galaxy Enceladus violently collided and was torn apart by our own Milky Way Galaxy, leaving behind the cries of a whole new generation of children from the hundred-handed giant. Recently, SCIENCE CHINA: Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy published an (Editor's Focus) article titled "Low-α Metal-rich stars with sausage kinematics in the LAMOST survey: Are they ...
WASHINGTON--Low doses of propylparaben--an estrogen-like chemical used as a preservative in personal care products and foods--can alter pregnancy-related changes in the breast in ways that may reduce the normal protection against breast cancer that pregnancy hormones convey, according to a new study being published in the Endocrine Society's journal Endocrinology.
These results, from an animal study that also will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, lend evidence that propylparaben is an endocrine-disrupting chemical, the researchers say.
An endocrine-disrupting chemical interferes with the actions of hormones in the body. These chemicals can affect ...
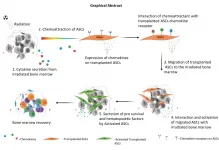
Durham, NC - Nuclear power offers an efficient, reliable way to provide energy to large populations - as long as all goes well. Accidents involving nuclear reactors such as those that took place in 1986 at Chernobyl and at Fukushima Daiichi after the March 2011 tsunami raise major concerns about what happens if the worst occurs and large numbers of people are simultaneously exposed to high levels of radiation. Currently, there are no effective, safe therapies for total body irradiation (TBI) - a condition known as acute radiation syndrome (ARS). That could change, ...