(Press-News.org) Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) uncover potential novel therapeutic strategies for oral and esophageal carcinomas
Tokyo, Japan - Discovering and treating tumors before they spread throughout the body is key for cancer patients to achieve positive outcomes. When tumor cells spread, which is known as metastasis, they can take over other organs and lead to death. Oral and esophageal carcinomas, or mouth and throat cancers, frequently metastasize to the lymph nodes. Unfortunately, there are currently no therapies that are specific to treating these particular cancers. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identified several drugs that can possibly be used to treat oral and esophageal carcinomas.
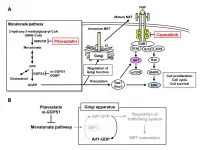
In an article published in Molecular Cancer Research, a group of researchers from TMDU found that combining two drugs, pitavastatin and capmatinib, inhibited the viability of oral cancer cells in culture, as well as the growth of tumors in a mouse model.
Although esophageal carcinoma is the sixth most deadly cancer worldwide and is relatively well understood at the molecular level, the research has not been translated into specific therapeutic development. Because of this urgent need, the TMDU group became interested in drug repurposing, where a drug that has been approved for a certain disease can be used to effectively treat an additional indication. This concept significantly speeds up the drug discovery and development process, increasing the number of patients that can benefit from an established therapeutic.
"Drug repurposing can be extremely helpful for discovering efficacious treatments for diseases lacking approved therapies," says lead author of the study Tomoki Muramatsu "We began this process for oral and esophageal carcinomas by screening an FDA-approved drug library."
The researchers performed the drug screening on a highly metastatic oral cancer cell line. Overall, the drug pitavastatin reduced the growth of these cells most significantly. Through molecular analysis, they determined that pitavastatin acted by inhibiting a cellular pathway called MET signaling. Because of this, the researchers added in a second MET inhibitor drug, known as capmatinib.
"Combining pitavastatin with capmatinib resulted in an even greater reduction in cancer cell growth," describes senior author Johji Inazawa. "Capmatinib by itself had no effect on the cancer cells, but it synergized with pitavastatin."
The researchers then injected these cells into mice to generate tumors and observed a similar effect with the pitavastatin and capmatinib combination.
"Our results in the mouse model corroborated our in vitro findings," says Muramatsu. "The data suggest that MET signaling may be a valuable therapeutic target in these tumors."
The study also identified a potential biomarker for these particular cancers - a gene called GGPS1. Expression levels of this gene may correlate with patient responsiveness to pitavastatin. This work provides knowledge that may be vital for identifying therapeutics for these devastating diseases.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Suppression of MET signaling mediated by pitavastatin and capmatinib inhibits oral and esophageal cancer cell growth," was published in Molecular Cancer Research at DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0688.
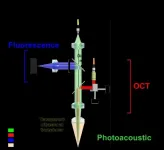
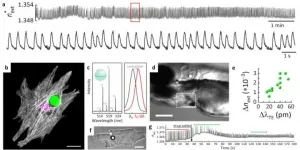
A quadruple fusion optical and ultrasound imaging system has been developed that allows diagnosis of eye conditions or tumors or to see the environment inside the body using a transparent ultrasound transducer.
Professor Chulhong Kim of POSTECH's Department of Electrical Engineering, Convergence IT Engineering, and Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Byullee Park of Department of Convergence IT Engineering, Ph.D. candidate Jeongwoo Park of School of Interdisciplinary Bioscience and Bioengineering, Professor Hyung Ham Kim of Department of Convergence IT Engineering, and Professor Unyong Jeong of Department of Materials ...
The research, by an international team from the Autonomous University of Madrid and the Technical University of Denmark, used 3D printing to create scaffolds for engineered flat brain organoids. The scaffolds allowed the brain organoid size to be significantly increased and after 20 days, self-generated folding was observed. END ...
Military expenditures are highly counterproductive to green economic growth- documented by a recent study conducted by UrFU economist collaboration with an international research team. Sustainable economic development or green growth requires cleaner energy and green technology that can mitigate the negative externalities (e.g., carbon emission) of economic growth. The study utilized various macroeconomic indicators for 21 OECD countries over the year 1980-2016. This empirical study focusing on the dynamic impact of innovation, militarization and renewable energy on the green economy is published in the journal "Environmental Science and Pollution Research".
On the one hand, the military-industry (land vehicles, aircraft, and sea-vessels) consume a gargantuan ...
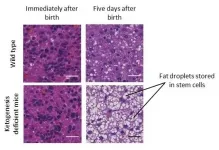
Ketone bodies are generally an alternative energy source during starvation, but in newborns, ketogenesis is active regardless of nutritional status. In a recent study from END ...
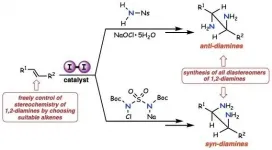
Osaka, Japan - Synthesizing pharmaceuticals for cancer, viral diseases, and other medical conditions is slow work. A particularly challenging chemical transformation is to start with what's known as an unactivated alkene--a common molecular building block--and end up with a vicinal diamine; i.e., installation of two nitrogen units into carbon--carbon double bonds. The result is a chemical unit that's present in medications for influenza and colorectal cancer.
Commonly, researchers must use rare, toxic metals and harsh reaction conditions to complete this transformation. Using a more sustainable catalyst for the reaction could solve such problems. Previous research has attempted to do so, ...
Label-free optical sensors based on optical whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) microresonators exhibit extraordinary sensitivity for detecting physical, chemical, and biological entities, even down to single molecules. This extreme advancement in label-free optical detection is made possible by application of the optical microresonator, i.e. a 100 um glass microspheres, as optical cavity to enhance the detection signal. Akin to a spherical micromirror, the WGM cavity reflects the light by near-total internal reflection and thereby creates multiple cavity passes ...
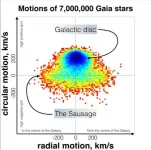
Note: The dwarf galaxy corresponding to the Gaia-Sausage structure of the Milky Way was named Enceladus by astronomers, after one of the hundred-handed giants in Greek mythology who opposed the rule of Zeus.
Looking up at the starry sky, the deep Universe appears quiet and mysterious. It is hard to imagine that the ancient dwarf galaxy Enceladus violently collided and was torn apart by our own Milky Way Galaxy, leaving behind the cries of a whole new generation of children from the hundred-handed giant. Recently, SCIENCE CHINA: Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy published an (Editor's Focus) article titled "Low-α Metal-rich stars with sausage kinematics in the LAMOST survey: Are they ...
WASHINGTON--Low doses of propylparaben--an estrogen-like chemical used as a preservative in personal care products and foods--can alter pregnancy-related changes in the breast in ways that may reduce the normal protection against breast cancer that pregnancy hormones convey, according to a new study being published in the Endocrine Society's journal Endocrinology.
These results, from an animal study that also will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, lend evidence that propylparaben is an endocrine-disrupting chemical, the researchers say.
An endocrine-disrupting chemical interferes with the actions of hormones in the body. These chemicals can affect ...
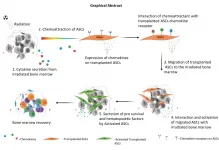
Durham, NC - Nuclear power offers an efficient, reliable way to provide energy to large populations - as long as all goes well. Accidents involving nuclear reactors such as those that took place in 1986 at Chernobyl and at Fukushima Daiichi after the March 2011 tsunami raise major concerns about what happens if the worst occurs and large numbers of people are simultaneously exposed to high levels of radiation. Currently, there are no effective, safe therapies for total body irradiation (TBI) - a condition known as acute radiation syndrome (ARS). That could change, ...
16th of March, Tuesday, 2021 -- Longevity medicine is a rapidly evolving branch of preventative precision medicine that is specifically focused on promoting healthspan and lifespan, utilizing aging biomarkers commonly referred to as aging clocks. Over the past decade advances in AI and machine learning enabled the development of deep aging clocks (DACs) and other novel tools to track the rate of aging. In parallel novel preventative and therapeutic interventions have been discovered or progressed into clinical trials. Many medical and public health professionals do not have time to read the thousands of research papers covering this new field and actively engage in cutting-edge innovation ...