Machine learning can identify cancerous cells by their acidity
Using a special dye, cells are colored according to their pH, and a machine learning algorithm can detect changes in the color spectrum due to cancer
2021-03-16
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Cancerous cells exhibit several key differences from healthy cells that help identify them as dangerous. For instance, the pH -- the level of acidity -- within a cancerous cell is not the same as the pH within a healthy cell.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore developed a method of using machine learning to determine whether a single cell is cancerous by detecting its pH. They describe their work in the journal APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing.
"The ability to identify single cells has acquired a paramount importance in the field of precision and personalized medicine," said Chwee Teck Lim, one of the authors. "This is because it is the only way to account for the inherent heterogeneity associated with any biological specimen."
Lim explained that other techniques for examining a single cell can induce toxic effects or even kill the cell. Their approach, however, can discriminate cells originating from normal tissues from cells originating from cancerous tissues, as well as among different types of cancer, while keeping the cells alive.
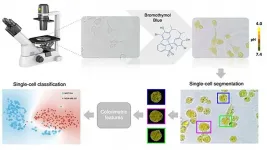
The method relies on treating the cells with bromothymol blue, a pH-sensitive dye that changes color depending on how acidic a solution is. Each type of cell exhibits its own unique fingerprint of red, green, and blue (RGB) based on its intracellular acidity. Because cancerous transformation alters the cell's pH, an unhealthy cell will respond to bromothymol blue differently, resulting in a characteristic shift of its RGB fingerprint.
By training a machine learning algorithm to map combinations of colors to the disease state of individual cells, the authors can easily recognize an undesired shift. This allows them to determine the health of a cell using only simple, standard equipment: an inverted microscope and a color camera.
"Our method allowed us to classify single cells of various human tissues, both normal and cancerous, by focusing solely on the inherent acidity levels that each cell type tends to exhibit, and using simple and inexpensive equipment," Lim said.
For practical implementations of this approach, medical professionals will need to noninvasively acquire a sample of the cells in question.
"One potential application of this technique would be in liquid biopsy, where tumor cells that escaped from the primary tumor can be isolated in a minimally invasive fashion from bodily fluids," Lim said.
The group is looking forward to advancing the concept further to try to detect different stages of malignancies from the cells. They envision a real-time version of the procedure, in which cells suspended in a solution can be automatically recognized and handled.
INFORMATION:
The article "Machine learning based approach to pH imaging and classification of single cancer cells" is authored by Y. Belotti, D.S. Jokhun, J.S. Ponnambalam, V.L M. Valerio, and C.T. Lim. The article will appear in APL Bioengineering on March 16, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0031615). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0031615.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.scitation.org/journal/apb.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-16
What The Study Did: The findings of this study suggest that, based on a sample from an otherwise healthy population, the overall number of SARS-CoV-2 infections in the U.S. may be substantially higher than estimates based on public health case reporting.
Authors: Robert L. Stout, Ph.D., of Clinical Reference Laboratory Inc. in Lenexa, Kansas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1552)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
2021-03-16
What The Study Did: Researchers examined nursing homes in communities with the highest COVID-19 prevalence to identify characteristics associated with resident infection rates.
Authors: Hye-Young Jung, Ph.D., of Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1555)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including ...
2021-03-16
The first systematic study of its kind describes how human viruses including SARS-CoV-2 are better adapted to infecting certain types of tissues based on their ability to hijack cellular machinery and protein synthesis.
Carried out by researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), the findings could help the design of more effective antiviral treatments, gene therapies and vaccines. The study is published today in the journal Cell Reports.
Living organisms make proteins inside their cells. Each protein consists of single units of amino acids which are stitched together according to instructions encoded within DNA. The basic units of these instructions are known as a codons, each of which corresponds ...
2021-03-16
When scientists at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria looked at developing zebrafish embryos, they observed an abrupt and dramatic change: within just a few minutes, the solid-like embryonic tissue becomes fluid-like. What could cause this change and, what is its role in the further development of the embryo? In a multidisciplinary study published in the journal Cell, they found answers that could change how we look at key processes in development and disease, such as tumor metastasis.
To learn more about how a tiny bunch of cells develops into complex systems ...
2021-03-16
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- In the past few years, several medications have been found to be contaminated with NDMA, a probable carcinogen. This chemical, which has also been found at Superfund sites and in some cases has spread to drinking water supplies, causes DNA damage that can lead to cancer.
MIT researchers have now discovered a mechanism that helps explain whether this damage will lead to cancer in mice: The key is the way cellular DNA repair systems respond. The team found that too little activity of one enzyme necessary for DNA repair leads to much higher cancer rates, while too much activity can produce tissue damage, especially in the liver, which can be fatal.
Activity ...
2021-03-16
Several oceans' worth of ancient water may reside in minerals buried below Mars' surface, report researchers. The new study, based on observational data and modeling, shows that much of the red planet's initial water - up to 99% - was lost to irreversible crustal hydration, not escape to space. The findings help resolve the apparent contradictions between predicted atmospheric loss rates, the deuterium to hydrogen ratio (D/H) of present-day Mars and the geological estimates of how much water once covered the Martian surface. Ancient Mars was a wet planet - dry riverbeds and relic shorelines record a time when vast volumes of liquid water flowed across the surface. Today, ...
2021-03-16
Birds breathe with greater efficiency than humans due to the structure of their lungs--looped airways that facilitate air flows that go in one direction--a team of researchers has found through a series of lab experiments and simulations.
The findings will appear Fri., March 19 in the journal Physical Review Letters (to be posted between 10 and 11 a.m. EDT).
The study, conducted by researchers at New York University and the New Jersey Institute of Technology, also points to smarter ways to pump fluids and control flows in applications such as respiratory ventilators.
"Unlike the air flows deep in the branches of our lungs, which oscillate back and forth as we breathe in and out, the flow moves in a single direction in ...
2021-03-16
PHILADELPHIA - Imposter syndrome is a considerable mental health challenge to many throughout higher education. It is often associated with depression, anxiety, low self-esteem and self-sabotage and other traits. Researchers at the Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University wanted to learn to what extent incoming medical students displayed characteristics of imposter syndrome, and found that up to 87% of an incoming class reported a high or very high degree of imposter syndrome.
"Distress and mental health needs are critical issues among medical ...
2021-03-16
PITTSBURGH (March 16, 2021) ... During the swarming of birds or fish, each entity coordinates its location relative to the others, so that the swarm moves as one larger, coherent unit. Fireflies on the other hand coordinate their temporal behavior: within a group, they eventually all flash on and off at the same time and thus act as synchronized oscillators.
Few entities, however, coordinate both their spatial movements and inherent time clocks; the limited examples are termed "swarmalators"1, which simultaneously swarm in space and oscillate in time. Japanese tree frogs are exemplar swarmalators: each frog changes both its location and rate of croaking ...
2021-03-16
How much do people have to pay for a travel permit to another country? A research team from Göttingen, Paris, Pisa and Florence has investigated the costs around the world. What they found revealed a picture of great inequality. People from poorer countries often pay many times what Europeans would pay. The results have been published in the journal Political Geography.
Dr Emanuel Deutschmann from the Institute of Sociology at the University of Göttingen, together with Professor Ettore Recchi, Dr Lorenzo Gabrielli and Nodira Kholmatova (from Sciences Po Paris, CNR-ISTI Pisa and EUI Florence respectively) compiled a new dataset on visa costs for travel between countries worldwide. The analysis shows that on average people ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Machine learning can identify cancerous cells by their acidity
Using a special dye, cells are colored according to their pH, and a machine learning algorithm can detect changes in the color spectrum due to cancer