Project investigates remote control of enzymes using light
The study showed that not only the composition of the material but also its geometry influenced the effect of the nanoparticles on the enzyme.
2021-03-16
(Press-News.org) The activity of enzymes in industrial processes, laboratories, and living beings can be remotely controlled using light. This requires their immobilization on the surface of nanoparticles and irradiation with a laser. Near-infrared light can penetrate living tissue without damaging it. The nanoparticles absorb the energy of the radiation and release it back in the form of heat or electronic effects, triggering or intensifying the enzymes' catalytic activity. This configures a new field of study known as plasmonic biocatalysis.
Research conducted at the University of São Paulo's Chemistry Institute (IQ-USP) in Brazil investigated the activity of enzymes immobilized on gold nanoparticles controlled by infrared laser irradiation. An article reporting the results is published in ACS Catalysis, a journal of the American Chemical Society.
The study was supported by São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP via a postdoctoral fellowship and a scholarship for a research internship abroad awarded to the lead author, Heloise Ribeiro de Barros; a multiuser equipment grant; and the Thematic Project "Optimization of the physicochemical properties of nanostructured materials for applications in molecular recognition, catalysis and energy conversion/storage", led by Roberto Manuel Torresi.
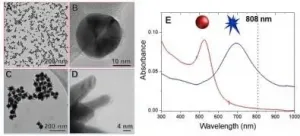
"We used a lipase [CaLB] as the model enzyme, immobilized on gold nanoparticles with two shapes - spheres and stars," Ribeiro de Barros told. "The infrared laser accelerated the enzyme's activity non-invasively merely by irradiating it with external light."
The study showed that not only the composition of the material but also its geometry influenced the effect of the nanoparticles on the enzyme. "The enzymatic activity was significantly enhanced when the lipase was immobilized on gold nanostars, displaying an increase of up to 58%," Ribeiro de Barros said. "In comparison, the gold nanospheres promoted a much smaller increase of 13%. The larger increase corresponded to the effect of resonance between the surfaces of the nanostars and radiation from the laser."
The magnitude considered here is localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR). While the LSPR of the nanospheres absorbs at 525 nanometers, that of the nanostars reaches 700 nm, much closer to the infrared laser wavelength, which is 808 nm.
"The incident light sets off energy-driven processes in the gold nanoparticles, such as a rise in temperature or electronic effects, and this affects the properties of the enzymes that are immobilized on their surfaces," Ribeiro de Barros said. "It was possible to conclude that localized photothermal heating on the surfaces of the gold nanostars promoted by LSPR excitation led to enhanced lipase biocatalysis. This conclusion can be extended to other combinations of enzymes and plasmonic nanoparticles."
The wide array of potential applications includes biocatalysis to accelerate industrial-scale chemical reactions and in vivo control of disease-causing enzymes. In the more distant future, this kind of process could conceivably be used to treat diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. More research will be required before it can become a genuine alternative, of course.
"From the medical standpoint, the main purpose of the study was to point to solutions in the near future for the treatment of diseases without the need for invasive surgery and with a specific spatial and temporal approach to avoid the side-effects of current methods," Ribeiro de Barros said.
INFORMATION:
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at http://www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at http://www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-16
FLAGSTAFF, Ariz. -- March 16, 2021 -- The findings of a recent analysis conducted by the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope, suggest that ecosystems suitable for harboring ticks that carry debilitating Lyme disease could be more widespread than previously thought in California, Oregon and Washington.
Bolstering the research were the efforts of an army of "citizen scientists" who collected and submitted 18,881 ticks over nearly three years through the Free Tick Testing Program created by the Bay Area Lyme Foundation, which funded the research, producing a wealth of data for scientists to analyze.
This new study builds on initial research led by the ...
2021-03-16
March 16, 2021, Mountain View, CA - In a comment published today in Nature Astronomy, Dr. Nathalie Cabrol, Director of the Carl Sagan Center for Research at the SETI Institute, challenges assumptions about the possibility of modern life on Mars held by many in the scientific community.
As the Perseverance rover embarks on a journey to seek signs of ancient life in the 3.7 billion years old Jezero crater, Cabrol theorizes that not only life could still be present on Mars today, but it could also be much more widespread and accessible than previously believed. Her conclusions are based on years of exploration of early Mars analogs in extreme environments in the Chilean altiplano and the Andes funded ...
2021-03-16
Billions of years ago, the Red Planet was far more blue; according to evidence still found on the surface, abundant water flowed across Mars and forming pools, lakes, and deep oceans. The question, then, is where did all that water go?
The answer: nowhere. According to new research from Caltech and JPL, a significant portion of Mars's water--between 30 and 99 percent--is trapped within minerals in the planet's crust. The research challenges the current theory that the Red Planet's water escaped into space.
The Caltech/JPL team found that around four billion years ago, Mars was home to enough water to have covered the whole planet in an ocean about 100 to 1,500 meters deep; a volume roughly ...
2021-03-16
URBANA, Ill. - Corn didn't start out as the powerhouse crop it is today. No, for most of the thousands of years it was undergoing domestication and improvement, corn grew humbly within the limits of what the environment and smallholder farmers could provide.
For its fertilizer needs, early corn made friends with nitrogen-fixing soil microbes by leaking an enticing sugary cocktail from its roots. The genetic recipe for this cocktail was handed down from parent to offspring to ensure just the right microbes came out to play.
But then the Green Revolution changed everything. Breeding tools improved dramatically, leading to faster-growing, higher-yielding hybrids than the world had ...
2021-03-16
Radio telescopes are the world's most sensitive radio receivers, capable of finding extremely faint wisps of radio emission coming from objects at the farthest reaches of the universe. Recently, a team of astronomers used the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) to take advantage of a helping hand from nature to detect a distant galaxy that likely is the faintest radio-emitting object yet found.
The discovery was part of the VLA Frontier Fields Legacy Survey, led by NRAO Astronomer Eric Murphy, which used distant clusters of galaxies as natural lenses ...
2021-03-16
Recent research shows that people are more likely to take "microbreaks" at work on days when they're tired - but that's not a bad thing. The researchers found microbreaks seem to help tired employees bounce back from their morning fatigue and engage with their work better over the course of the day.
At issue are microbreaks, which are short, voluntary and impromptu respites in the workday. Microbreaks include discretionary activities such as having a snack, chatting with a colleague, stretching or working on a crossword puzzle.
"A microbreak is, by definition, short," says Sophia Cho, co-author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor ...
2021-03-16
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- Joint Army- and Air Force-funded researchers have taken a step toward building a fault-tolerant quantum computer, which could provide enhanced data processing capabilities.
Quantum computing has the potential to deliver new computing capabilities for how the Army plans to fight and win in what it calls multi-domain operations. It may also advance materials discovery, artificial intelligence, biochemical engineering and many other disciplines needed for the future military; however, because qubits, the fundamental building blocks of quantum computers, are intrinsically fragile, a longstanding barrier to quantum computing has been effective implementation of quantum error correction.
Researchers at University of Massachusetts Amherst, ...
2021-03-16
Corporate strategies should be as unique as possible, in fact highly specific to each individual company. This enables companies to compete successfully in the long term. However, the capital market and others, including analysts, often react negatively to the idea of unique strategies. The reason is that deviating from typical industry standards makes them more complex to evaluate. This regularly discourages companies from focusing on unique strategies, even though they would be beneficial for the company in the long term. This contradiction is known as the "uniqueness paradox". A research team from the Universities of Göttingen and Groningen has investigated the influence of different types of investors on the extent of the paradox and thus on the choice of unique strategies. The results ...
2021-03-16
Higher progesterone level is protective in mild traumatic brain injury
Blood flow in brain is linked to progesterone and stress symptom levels
Most concussion research has been focused on male athletes
CHICAGO --- Could birth control pills help young female athletes recover faster from concussions and reduce their symptoms?
A new Northwestern Medicine pilot study has shown when a female athlete has a concussion injury during the phase of her menstrual cycle when progesterone is highest, she feels less stress. Feeling stressed is one symptom of a concussion. Feeling less stressed is a marker of recovery.
The study also revealed for the first time the physiological reason for the neural protection is increased ...
2021-03-16
New research from the University of Florida Warrington College of Business finds that feeling psychologically powerful makes leaders' jobs seem more demanding. And perceptions of heightened job demands both help and hurt powerful leaders.
Trevor Foulk of the University of Maryland Robert H. Smith School of Business and Klodiana Lanaj, Martin L. Schaffel Professor at UF, note that while power-induced job demands are key to helping leaders more effectively pursue their goals and feel that their jobs are meaningful each day at work, these demands can also cause pain and discomfort, felt in the evening at home.
"Power is generally considered a desirable thing, as leaders often seek power, and it's very rare for leaders to turn powerful roles down," Foulk said. "However, this view is qualified ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Project investigates remote control of enzymes using light
The study showed that not only the composition of the material but also its geometry influenced the effect of the nanoparticles on the enzyme.