Could birth control pills ease concussion symptoms in female athletes?
High levels of progesterone during menstrual cycle reduce stress after concussion and speed recovery
2021-03-16
(Press-News.org) Higher progesterone level is protective in mild traumatic brain injury
Blood flow in brain is linked to progesterone and stress symptom levels
Most concussion research has been focused on male athletes
CHICAGO --- Could birth control pills help young female athletes recover faster from concussions and reduce their symptoms?
A new Northwestern Medicine pilot study has shown when a female athlete has a concussion injury during the phase of her menstrual cycle when progesterone is highest, she feels less stress. Feeling stressed is one symptom of a concussion. Feeling less stressed is a marker of recovery.
The study also revealed for the first time the physiological reason for the neural protection is increased blood flow to the brain as a result of higher levels of progesterone.
"Our findings suggest being in the luteal phase (right after ovulation) of the menstrual cycle when progesterone is highest -- or being on contraceptives, which artificially increase progesterone -- may mean athletes won't have as severe symptoms when they have a concussion injury," said co-author Amy Herrold, research assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
"Resolving those symptoms is especially problematic for our athletes who are trying to return to school, their sports and everyday life after a concussion," said lead author Jennie Chen, research assistant professor of radiology at Feinberg.
The study was published in the Journal of Neurotrauma.
The athletes in the study were in soccer, ultimate frisbee, crew, triathlon, lacrosse, women's rugby and tennis clubs. The focus on club athletes is important because more college students take part in club athletics than varsity athletics, Herrold said. In addition, club athletics are not as tightly monitored, possibly leading to increased exposure and under-reporting of concussion.
Northwestern investigators found increased blood flow in the brain when a female athlete had a higher level of progesterone due to her menstrual cycle phase. The region, the middle temporal gyrus, is important for information processing and integrating visual and auditory stimuli. It also has been implicated in social anxiety disorder.
Recovering from concussion is stressful for athletes
Following a concussion or mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), athletes are pulled from classes for a period of time and struggle to keep up with classes.
"When they are recovering from a concussion, they get very stressed trying to keep up with coursework and making up for lost time," Herrold said. "Their ratings on perceived stress are really important for their overall recovery from the injury and getting back to normal."
Big gap in research on female concussion
The bulk of sports-related concussion research has been focused on male athletes. The study fills a big gap in literature by studying female club athletes, Herrold said. "The trajectory of recovery from mild traumatic brain injury is different in female athletes than male athletes. Male athletes have shorter length of recovery than females, despite similar symptom severity."
For the study, investigators enrolled 30 female collegiate athletes and assessed them three to 10 days after a concussion or mTBI. Assessments included an MRI scan to examine brain blood flow, a blood draw to examine progesterone levels and self-reported mTBI symptom questionnaires including the perceived stress questionnaire. Once an injured athlete was studied, the investigators enrolled a healthy control athlete that was matched based on age, ethnicity contraceptive use and type, and menstrual cycle phase.
Clinicians may consider menstrual cycle phase when caring for injured athletes
It may be helpful for clinicians caring for injured athletes to consider the phase of the athlete's menstrual cycle and what, if any, hormonal contraceptives they are on, Herrold said. Both will affect progesterone levels and could affect brain blood flow and perceived stress.
"Clinicians also may want to evaluate wider use of hormonal contraceptives that raise progesterone levels for athletes who are at risk for incurring a concussion or mild TBI as there could be potential for neuroprotection," Herrold said.
In future research, Chen and Herrold plan to study if these results can be replicated in a larger more heterogenous sample of female athletes. They also want to compare what they found in males and females competing in sports with concussion risk such as soccer.
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by the Northwestern Memorial Foundation Eleanor Wood Prince Grant Initiative.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-16
New research from the University of Florida Warrington College of Business finds that feeling psychologically powerful makes leaders' jobs seem more demanding. And perceptions of heightened job demands both help and hurt powerful leaders.
Trevor Foulk of the University of Maryland Robert H. Smith School of Business and Klodiana Lanaj, Martin L. Schaffel Professor at UF, note that while power-induced job demands are key to helping leaders more effectively pursue their goals and feel that their jobs are meaningful each day at work, these demands can also cause pain and discomfort, felt in the evening at home.
"Power is generally considered a desirable thing, as leaders often seek power, and it's very rare for leaders to turn powerful roles down," Foulk said. "However, this view is qualified ...
2021-03-16
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Sea-based fish farming systems using net pens are hard on the environment and the fish. A closed cage can improve fish welfare, but fresh seawater must be continuously circulated through the cage. However, ocean waves can cause this circulating water to slosh inside the cage, creating violent motions and endangering the cage and the fish.
A study using a scale-model fish containment system is reported in Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing. The study shows why violent sloshing motions arise and how to minimize them.
Gentle currents can be artificially maintained inside cylindrical closed cages developed for salmon farming. The current is produced by injecting seawater through ...
2021-03-16
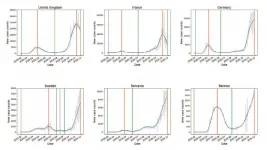
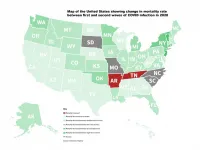
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- As Europe experienced its enormous second wave of the COVID-19 disease, researchers noticed the mortality rate -- progression from cases to deaths -- was much lower than during the first wave.
This inspired researchers from the University of Sydney and Tsinghua University to study and quantify the mortality rate on a country-by-country basis to determine how much the mortality rate from the second wave decreased from the first.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, Nick James, Max Menzies, and Peter Radchenko introduce methods to study the progression of COVID-19 cases to deaths during the pandemic's different waves. Their methods involve applied mathematics, specifically nonlinear dynamics, and time series analysis.
"We take a time series, ...
2021-03-16
Researchers from the lab of Hans Clevers (Hubrecht Institute) and the UMC Utrecht used organoid technology to grow miniature human tear glands that actually cry. The organoids serve as a model to study how certain cells in the human tear gland produce tears or fail to do so. Scientists everywhere can use the model to identify new treatment options for patients with tear gland disorders, such as dry eye disease. Hopefully in the future, the organoids can even be transplanted into patients with non-functioning tear glands. The results will be published in Cell Stem Cell on the 16th of March.
The tear gland is located in the upper part of the eye socket. It secretes tear fluid, which is essential for lubrication and nutrition of the cornea and has antibacterial components. Rachel Kalmann ...
2021-03-16
Like a well-trained soldier, a white blood cell uses specialized abilities to identify and ultimately destroy dangerous intruders, including creating a protrusion to effectively reach out, lock-on, probe, and possibly attack its prey. Researchers reporting March 16 in Biophysical Journal show in detail that these cells take seconds to morph into these highly rigid and viscous defensive units.
Senior author Julien Husson (@_julienhusson), a biophysicist at École Polytechnique near Paris, and collaborators showed previously that certain white blood cells, called T cells, ...
2021-03-16
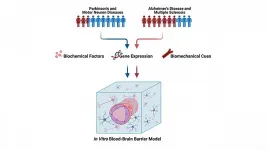
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Men and women are impacted differently by brain diseases, like Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Researchers are urging their colleagues to remember those differences when researching treatments and cures.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, University of Maryland scientists highlight a growing body of research suggesting sex differences play roles in how patients respond to brain diseases, as well as multiple sclerosis, motor neuron disease, and other brain ailments.
That is progress from just a few years ago, said Alisa Morss ...
2021-03-16
Stem-cell-derived organoids that swell up with tears could shed light on the biology of crying and dry-eye disease, suggests a study publishing March 16 in the journal Cell Stem Cell. Although regenerative therapies using human tear-gland organoids will not be possible anytime soon, these researchers have demonstrated that the organoids can engraft, integrate, and produce mature tear products upon transplantation into mouse tear glands.
"We hope that scientists will use our model to identify new treatment options for patients with tear-gland disorders by either testing new drugs on a patient's organoids or expanding healthy cells and, one day, using them for transplantation," says senior study author Hans Clevers (@HansClevers) of the Hubrecht Institute.
The ...
2021-03-16
Wealthier northeastern US states and Western European countries tended to have significantly lower mortality rates during second-wave COVID-19 infections, new research from the University of Sydney and Tsinghua University has shown. However, the pattern was not as general as expected, with notable exceptions to this trend in Sweden and Germany.
Researchers say mortality change could have several explanations:
European first-wave case counts were underestimated;
First-wave deaths disproportionately affected the elderly;
Second-wave infections tended to affect younger people;
With some ...
2021-03-16
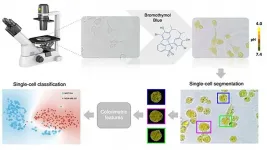
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Cancerous cells exhibit several key differences from healthy cells that help identify them as dangerous. For instance, the pH -- the level of acidity -- within a cancerous cell is not the same as the pH within a healthy cell.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore developed a method of using machine learning to determine whether a single cell is cancerous by detecting its pH. They describe their work in the journal APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing.
"The ability to identify single cells has acquired a paramount importance in the field of precision and personalized medicine," ...
2021-03-16
What The Study Did: The findings of this study suggest that, based on a sample from an otherwise healthy population, the overall number of SARS-CoV-2 infections in the U.S. may be substantially higher than estimates based on public health case reporting.
Authors: Robert L. Stout, Ph.D., of Clinical Reference Laboratory Inc. in Lenexa, Kansas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1552)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Could birth control pills ease concussion symptoms in female athletes?
High levels of progesterone during menstrual cycle reduce stress after concussion and speed recovery