Controlling sloshing motions in sea-based fish farming cages improves fish welfare
Investigators develop a scale model to study the violent sloshing motions that endanger closed fish cages battered by ocean waves
2021-03-16
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Sea-based fish farming systems using net pens are hard on the environment and the fish. A closed cage can improve fish welfare, but fresh seawater must be continuously circulated through the cage. However, ocean waves can cause this circulating water to slosh inside the cage, creating violent motions and endangering the cage and the fish.
A study using a scale-model fish containment system is reported in Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing. The study shows why violent sloshing motions arise and how to minimize them.
Gentle currents can be artificially maintained inside cylindrical closed cages developed for salmon farming. The current is produced by injecting seawater through nozzles in the side, creating a circular flow inside. The maximum flow rate should not exceed the critical swimming speed at which salmon can swim comfortably for an extended time.
While this artificial current improves fish health, it also affects the natural frequencies of sloshing that can be excited inside the floating cage by ocean waves. These violent sloshing motions occur even when relatively small waves hit the cage, since the resonance phenomenon amplifies wave motion.
"In the scientific literature, similar problems of fluid dynamic behavior in spinning tanks have been found only in studies of stability and control of rocket fuel tanks, gas turbines, and centrifuges," co-author Claudio Lugni said.
"It is not straightforward to apply results about rocket tanks to aquaculture tanks," said co-author Andrei Tsarau.
To address this problem, a scale model of a cylindrical fish cage was attached to a mechanical rig that could move the cylinder from side to side. The scale model was partially filled with water and included nozzles to inject an artificial circular current.
When the system was oscillated sideways by the rig, sloshing motions began and were monitored by sensors in the tank.
"Depending on the forcing frequency, various sloshing regimes characterized by different wave shapes and amplitudes on the free surface of the liquid were observed in the experiment," Lugni said.
Computational and theoretical studies with and without the rotating current were carried out and compared to the experiment. The investigators found the violent sloshing observed when the liquid in the cylinder is not circulated can be suppressed at the same excitation frequencies if the liquid is rotated at high enough angular velocities.
This effect may be beneficial for relatively small cages with a radius less than 10 meters under forced-sloshing conditions. In such cages, the liquid can be rotated at high enough angular velocity without forcing the fish to swim at speeds above their critical limit.
"For larger cages, the same angular velocity would lead to flow velocities too high for the fish," said Tsarau.
INFORMATION:
The article "Sloshing in a rotating liquid inside a closed sea cage for fish farming" is authored by Andrei Tsarau, Claudio Lugni, Alessia Lucarelli, David Kristiansen, and Pål Lader. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on March 16, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0037408). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0037408.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-16
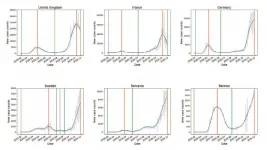
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- As Europe experienced its enormous second wave of the COVID-19 disease, researchers noticed the mortality rate -- progression from cases to deaths -- was much lower than during the first wave.
This inspired researchers from the University of Sydney and Tsinghua University to study and quantify the mortality rate on a country-by-country basis to determine how much the mortality rate from the second wave decreased from the first.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, Nick James, Max Menzies, and Peter Radchenko introduce methods to study the progression of COVID-19 cases to deaths during the pandemic's different waves. Their methods involve applied mathematics, specifically nonlinear dynamics, and time series analysis.
"We take a time series, ...
2021-03-16
Researchers from the lab of Hans Clevers (Hubrecht Institute) and the UMC Utrecht used organoid technology to grow miniature human tear glands that actually cry. The organoids serve as a model to study how certain cells in the human tear gland produce tears or fail to do so. Scientists everywhere can use the model to identify new treatment options for patients with tear gland disorders, such as dry eye disease. Hopefully in the future, the organoids can even be transplanted into patients with non-functioning tear glands. The results will be published in Cell Stem Cell on the 16th of March.
The tear gland is located in the upper part of the eye socket. It secretes tear fluid, which is essential for lubrication and nutrition of the cornea and has antibacterial components. Rachel Kalmann ...
2021-03-16
Like a well-trained soldier, a white blood cell uses specialized abilities to identify and ultimately destroy dangerous intruders, including creating a protrusion to effectively reach out, lock-on, probe, and possibly attack its prey. Researchers reporting March 16 in Biophysical Journal show in detail that these cells take seconds to morph into these highly rigid and viscous defensive units.
Senior author Julien Husson (@_julienhusson), a biophysicist at École Polytechnique near Paris, and collaborators showed previously that certain white blood cells, called T cells, ...
2021-03-16
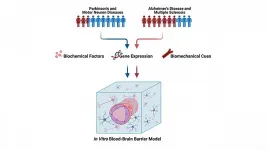
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Men and women are impacted differently by brain diseases, like Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Researchers are urging their colleagues to remember those differences when researching treatments and cures.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, University of Maryland scientists highlight a growing body of research suggesting sex differences play roles in how patients respond to brain diseases, as well as multiple sclerosis, motor neuron disease, and other brain ailments.
That is progress from just a few years ago, said Alisa Morss ...
2021-03-16
Stem-cell-derived organoids that swell up with tears could shed light on the biology of crying and dry-eye disease, suggests a study publishing March 16 in the journal Cell Stem Cell. Although regenerative therapies using human tear-gland organoids will not be possible anytime soon, these researchers have demonstrated that the organoids can engraft, integrate, and produce mature tear products upon transplantation into mouse tear glands.
"We hope that scientists will use our model to identify new treatment options for patients with tear-gland disorders by either testing new drugs on a patient's organoids or expanding healthy cells and, one day, using them for transplantation," says senior study author Hans Clevers (@HansClevers) of the Hubrecht Institute.
The ...
2021-03-16
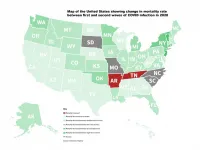
Wealthier northeastern US states and Western European countries tended to have significantly lower mortality rates during second-wave COVID-19 infections, new research from the University of Sydney and Tsinghua University has shown. However, the pattern was not as general as expected, with notable exceptions to this trend in Sweden and Germany.
Researchers say mortality change could have several explanations:
European first-wave case counts were underestimated;
First-wave deaths disproportionately affected the elderly;
Second-wave infections tended to affect younger people;
With some ...
2021-03-16
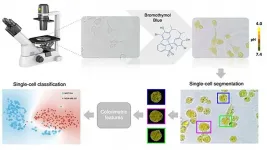
WASHINGTON, March 16, 2021 -- Cancerous cells exhibit several key differences from healthy cells that help identify them as dangerous. For instance, the pH -- the level of acidity -- within a cancerous cell is not the same as the pH within a healthy cell.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore developed a method of using machine learning to determine whether a single cell is cancerous by detecting its pH. They describe their work in the journal APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing.
"The ability to identify single cells has acquired a paramount importance in the field of precision and personalized medicine," ...
2021-03-16
What The Study Did: The findings of this study suggest that, based on a sample from an otherwise healthy population, the overall number of SARS-CoV-2 infections in the U.S. may be substantially higher than estimates based on public health case reporting.
Authors: Robert L. Stout, Ph.D., of Clinical Reference Laboratory Inc. in Lenexa, Kansas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1552)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
2021-03-16
What The Study Did: Researchers examined nursing homes in communities with the highest COVID-19 prevalence to identify characteristics associated with resident infection rates.
Authors: Hye-Young Jung, Ph.D., of Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1555)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including ...
2021-03-16
The first systematic study of its kind describes how human viruses including SARS-CoV-2 are better adapted to infecting certain types of tissues based on their ability to hijack cellular machinery and protein synthesis.
Carried out by researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), the findings could help the design of more effective antiviral treatments, gene therapies and vaccines. The study is published today in the journal Cell Reports.
Living organisms make proteins inside their cells. Each protein consists of single units of amino acids which are stitched together according to instructions encoded within DNA. The basic units of these instructions are known as a codons, each of which corresponds ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Controlling sloshing motions in sea-based fish farming cages improves fish welfare
Investigators develop a scale model to study the violent sloshing motions that endanger closed fish cages battered by ocean waves