(Press-News.org) Those who have persistent trouble sleeping may have an especially difficult grieving process after the death of a loved one, a new study co-authored by a University of Arizona researcher finds.
Most people who lose a close friend or family member will experience sleep troubles as part of the grieving process, as the body and mind react to the stress of the event, said study co-author Mary-Frances O'Connor, a professor in the UArizona Department of Psychology.
But O'Connor and her collaborators found that those who had persistent sleep challenges before losing someone were at higher risk for developing complicated grief after a loss. Complicated grief is characterized by a yearning for a lost loved one so intense and persistent that it disrupts a person's daily functioning. It occurs in 7-10% of bereaved people, O'Connor said.
"We know that, for many people, experiencing the death of a loved one is followed by sleep disruption - not surprisingly, given how stressful it is to lose a loved one," said O'Connor, who directs the university's Grief, Loss and Social Stress Laboratory. "We also know that people who have a more prolonged grief disorder tend to have persistent sleep problems. That led us to ask: What if the reverse is possible? Could it be that people who have had sleep disruption and then experience the death of a loved one are more likely to develop complicated grief?"
O'Connor and her collaborators at Erasmus University Medical Center in the Netherlands and the Phoenix VA Health Care System looked at data from the multiyear Rotterdam Study, which followed a group of middle-aged and older adults over time and looked at various aspects of their physical and mental health.
Participants in the study were asked, among other things, to keep sleep diaries documenting the quality of their sleep. They also were asked to wear a wristwatch monitor, called an actigraph, that objectively measures how long it takes a person to fall asleep, how often a person wakes during the night and how much time spent in bed is awake versus asleep.
In addition, participants were asked in interviews if they were still grieving the loss of someone who died in recent months or years, and they completed follow-up assessments of their grief symptoms.
The researchers compared study participants' initial responses to what they said approximately six years later, focusing specifically on participants who experienced the loss of a loved one between the first interview and the follow-up.
"What we saw was that if at the first time point you had sleep disruption - both objective and self-reported - you were more likely to be in the complicated grief group than the non-complicated grief group at the second time point," O'Connor said. "So, poor sleep might not only accompany grief but also be a risk factor for developing complicated grief after a loss."
The researchers' findings are published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research.
Sleep is critical for both physical and mental health, which could be why it impacts the grieving process, O'Connor said.
"We know that sleep is important for processing emotional events that happen during the daytime," she said. "Sleep also helps us to rest and restore our physical body, and grief is a very stressful experience for the body. Being able to rest and restore probably helps us wake up the next day a little more physically prepared to deal with the grief."
O'Connor says temporary sleep disturbances prior to the death of a loved one - such as stress-induced sleeplessness while caring for a sick family member - are not of as much concern. What is of more concern is a persistent sleep issue, which is more likely to put a person at risk for complicated grief.
O'Connor suggests health care and other support professionals consider sleep history when treating a bereaved person.
"Because grief is such a disruptive and difficult event, doctors often, I think, forget to ask about history when considering how to intervene, rather than just about what's going on during this intense moment," she said. "When physicians and the helping professions are working with bereaved people, they should ask about the history of sleep problems they've had, and not just what sleep problems they're having right now."
INFORMATION:
It would surprise no one that pursuing a graduate degree can be a stressful endeavor, and for students who are transgender and nonbinary (TNB), the atmosphere can become toxic, according to University of Houston researcher Nathan Grant Smith. In a new paper published in Higher Education, Smith provides an analysis of current literature pertaining to TNB graduate student experiences and suggests interventions in graduate education to create more supportive environments for TNB students.
"Nearly 50% of graduate students report experiencing emotional or psychological distress during their enrollment in graduate school. Levels of distress are particularly high for transgender ...
It has long been understood that a parent's DNA is the principal determinant of health and disease in offspring. Yet inheritance via DNA is only part of the story; a father's lifestyle such as diet, being overweight and stress levels have been linked to health consequences for his offspring. This occurs through the epigenome - heritable biochemical marks associated with the DNA and proteins that bind it. But how the information is transmitted at fertilization along with the exact mechanisms and molecules in sperm that are involved in this process has been unclear until now.
A new study from McGill, published recently in Developmental Cell, has made a significant advance in the field by identifying how environmental information is transmitted by ...
Lightning strikes -- perhaps a quintillion of them, occurring over a billion years -- may have provided sparks of life for the early Earth.
A new study by researchers at Yale and the University of Leeds contends that over time, these bolts from the blue unlocked the phosphorus necessary for the creation of biomolecules that would be the basis of life on the planet.
"This work helps us understand how life may have formed on Earth and how it could still be forming on other, Earth-like planets," said lead author Benjamin Hess, a graduate student in Yale's Department of Earth & Planetary ...
Lightning strikes were just as important as meteorites in creating the perfect conditions for life to emerge on Earth, geologists say.
Minerals delivered to Earth in meteorites more than 4 billion years ago have long been advocated as key ingredients for the development of life on our planet.
Scientists believed minimal amounts of these minerals were also brought to early Earth through billions of lightning strikes.
But now researchers from the University of Leeds have established that lightning strikes were just as significant as meteorites in performing this essential function and allowing life to manifest.
They say this shows that life could develop on Earth-like planets through the same mechanism at any time if atmospheric conditions are right. The research ...
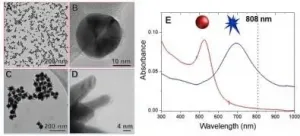
The activity of enzymes in industrial processes, laboratories, and living beings can be remotely controlled using light. This requires their immobilization on the surface of nanoparticles and irradiation with a laser. Near-infrared light can penetrate living tissue without damaging it. The nanoparticles absorb the energy of the radiation and release it back in the form of heat or electronic effects, triggering or intensifying the enzymes' catalytic activity. This configures a new field of study known as plasmonic biocatalysis.
Research conducted at the University of São Paulo's Chemistry Institute (IQ-USP) in Brazil investigated the activity of enzymes immobilized on gold ...
FLAGSTAFF, Ariz. -- March 16, 2021 -- The findings of a recent analysis conducted by the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope, suggest that ecosystems suitable for harboring ticks that carry debilitating Lyme disease could be more widespread than previously thought in California, Oregon and Washington.
Bolstering the research were the efforts of an army of "citizen scientists" who collected and submitted 18,881 ticks over nearly three years through the Free Tick Testing Program created by the Bay Area Lyme Foundation, which funded the research, producing a wealth of data for scientists to analyze.
This new study builds on initial research led by the ...
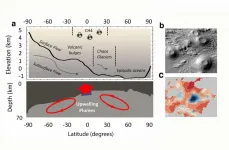
March 16, 2021, Mountain View, CA - In a comment published today in Nature Astronomy, Dr. Nathalie Cabrol, Director of the Carl Sagan Center for Research at the SETI Institute, challenges assumptions about the possibility of modern life on Mars held by many in the scientific community.
As the Perseverance rover embarks on a journey to seek signs of ancient life in the 3.7 billion years old Jezero crater, Cabrol theorizes that not only life could still be present on Mars today, but it could also be much more widespread and accessible than previously believed. Her conclusions are based on years of exploration of early Mars analogs in extreme environments in the Chilean altiplano and the Andes funded ...
Billions of years ago, the Red Planet was far more blue; according to evidence still found on the surface, abundant water flowed across Mars and forming pools, lakes, and deep oceans. The question, then, is where did all that water go?
The answer: nowhere. According to new research from Caltech and JPL, a significant portion of Mars's water--between 30 and 99 percent--is trapped within minerals in the planet's crust. The research challenges the current theory that the Red Planet's water escaped into space.
The Caltech/JPL team found that around four billion years ago, Mars was home to enough water to have covered the whole planet in an ocean about 100 to 1,500 meters deep; a volume roughly ...
URBANA, Ill. - Corn didn't start out as the powerhouse crop it is today. No, for most of the thousands of years it was undergoing domestication and improvement, corn grew humbly within the limits of what the environment and smallholder farmers could provide.
For its fertilizer needs, early corn made friends with nitrogen-fixing soil microbes by leaking an enticing sugary cocktail from its roots. The genetic recipe for this cocktail was handed down from parent to offspring to ensure just the right microbes came out to play.
But then the Green Revolution changed everything. Breeding tools improved dramatically, leading to faster-growing, higher-yielding hybrids than the world had ...
Radio telescopes are the world's most sensitive radio receivers, capable of finding extremely faint wisps of radio emission coming from objects at the farthest reaches of the universe. Recently, a team of astronomers used the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) to take advantage of a helping hand from nature to detect a distant galaxy that likely is the faintest radio-emitting object yet found.
The discovery was part of the VLA Frontier Fields Legacy Survey, led by NRAO Astronomer Eric Murphy, which used distant clusters of galaxies as natural lenses ...