(Press-News.org) Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have designed a new bioink which allows small human-sized airways to be 3D-bioprinted with the help of patient cells for the first time. The 3D-printed constructs are biocompatible and support new blood vessel growth into the transplanted material. This is an important first step towards 3D-printing organs. The new study has been published in Advanced Materials.
Chronic lung diseases are the third leading cause of death worldwide with an EU cost of more than €380 billion annually. For many chronic diseases there is no cure and the only end-stage option for patients is lung transplantation. However, there are not enough donor lungs to meet clinical demand.
Therefore, researchers are looking at ways to increase the amount of lungs available for transplantation. One approach is fabricating lungs in the lab by combining cells with a bioengineered scaffold.
"We started small by fabricating small tubes, because this is a feature found in both airways and in the vasculature of the lung. By using our new bioink with stem cells isolated from patient airways, we were able to bioprint small airways which had multiple layers of cells and remained open over time", explains Darcy Wagner, Associate Professor and senior author of the study.
The researchers first designed a new bioink (a printable material with cells) for 3D-bioprinting human tissue. The bioink was made by combining two materials: a material derived from seaweed, alginate, and extracellular matrix derived from lung tissue.
This new bioink supports the bioprinted material over several stages of its development towards tissue. They then used the bioink to 3D-bioprint small human airways containing two types of cells found in human airways. However, this bioink can be adapted for any tissue or organ type.
"These next generation bioinks also support the maturation of the airway stem cells into multiple cell types found in adult human airways, which means that less cell types need to be printed, simplifying the nozzle numbers needed to print tissue made of multiple cell types", says Darcy Wagner.
Wagner notes that the resolution needs to be improved to 3D-bioprint more distal lung tissue and the air sacks, known as alveoli, that are vital for gas exchange.
"We hope that further technological improvements of available 3D printers and further bioink advances will allow for bioprinting at a higher resolution in order to engineer larger tissues which could be used for transplantation in the future. We still have a long way to go", she says.
The team used a mouse model closely resembling the immunosuppression used in patients undergoing organ transplantation. When transplanted, they found that 3D-printed constructs made from the new bioink were well-tolerated and supported new blood vessels.
"The development of this new bioink is a significant step forward, but it is important to further validate the functionality of the small airways over time and to explore the feasibility of this approach in large animal models", concludes Martina De Santis, the first author of the study.
INFORMATION:
The promotion of psychosocial health among individuals, groups, and society is an increasingly important subject in the field of public health. Psychosocial health is a complex interaction between the psyche of an individual and the social environment in which that individual lives. Promoting psychosocial health is often challenging and complex for health care professionals. Therefore, an important question of public health significance is: "how can we address and improve the psychosocial health of individuals, groups, as well as society in general?"
An interdisciplinary team of specialists ...
The use of artificial light at night around the world has increased enormously in recent years, causing adverse effects on the survival and reproduction of nocturnal organisms. Artificial light at night interferes with vital ecological processes such as the nighttime pollination of plants by nocturnal insects, which could have consequences for agricultural crop yields and reproduction of wild plants.
Scientists from the University of Zurich and Agroscope have now demonstrated for the first time that artificial light at night also adversely affects insects' pollination behavior during the daytime. In an experiment, they used commercial ...
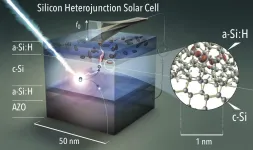
Silicon solar cells are now so cheap and efficient that they can generate electricity at prices of less than 2 cent/kWh. The most efficient silicon solar cells today are made with less than 10 nanometres thin selective amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) contact layers, which are responsible for separating the light-generated charges . Efficiencies of over 24% are achieved at HZB with such silicon heterojunction solar cells and are also part of a tandem solar cell that lead to a recently reported efficiency record of 29.15 % (A. Al-Ashouri, et al. Science 370, (2020)). The current world record from Japan for a ...
Tropical Cyclone (TC) is an intense atmospheric vortex with a warm core and low pressure structure, and generates over the tropical or subtropical warm ocean. The problem of TC genesis has been paid great attention by scientists since the 1950s, but due to the lack of the observation data over sea, this problem has become the most difficult and challenging topic in the researches of TC.
Cumulus convections are considered to be the most basic element in the TC generation process. The formation of TC in the Northwest Pacific is often associated with the mesoscale convective system (MCS) or mesoscale convective complex (MCC). Meanwhile, in the stratiform ...
Not least because of the COVID-19 pandemic, conspiracy theories are more topical than ever. They are reported and discussed in almost all media and communication channels. But what influence do they have on our behavior? Scientists led by behavioral economist Loukas Balafoutas investigated this question in a recently published study. The result: We don't need to believe in conspiracy theories for them to have an impact on us. Merely being confronted with them suffices.
Previous studies have shown that beliefs in conspiracy theories have an influence on the behavior of their adherents. For example, they lead to lower voter turnout or a lower willingness to get vaccinated. For years now, conspiracy theories have been ...
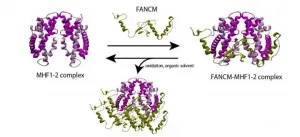
One of the most vital functions performed by the cells in our body is DNA repair, a task so crucial to our well-being that failing to execute it can lead to consequences as dreadful as cancer. The process of DNA repair involves a complex interplay between several gene pathways and proteins. One such pathway is the "Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway," whose genes participate in DNA repair. FANCM, a component of this pathway, is tasked with the elimination of harmful DNA "inter-strand cross-links," and interacts with another component called MHF in order to function. The importance of the FANCM-MHF complex is well-documented: its loss can result in chromosomal ...
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are among the major global health problems. Particularly problematic is the high number of chronic courses of the disease, causing the deaths of more than 800.000 people globally every year. So far, there is no therapy to cure the condition. "With the discovery of a new hepatitis B virus in donkeys and zebras capable of causing prolonged infections, we now have the opportunity for a better understanding of the chronic course of the disease and thus also for mitigation or prevention of severe clinical consequences," explains Prof. Dr. Jan Felix Drexler, DZIF ...
A new study uncovers which cell types can be infected by SARS-CoV-2 due to their viral entry factors. The study also suggests that increased gene expression of these viral entry factors in some individuals partially explains the differences of COVID-19 severity reported in relation to age, gender and smoking status. The study evolved from the Human Cell Atlas Lung Biological Network with main contributions from Helmholtz Zentrum München, the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, the Wellcome Sanger Institute and University Medical Center Groningen.
COVID-19 does not affect everyone in the same way. While the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 primarily ...
The health of women aged 65 and over appears to be related, in addition to their own socioeconomic characteristics, with that of their partners, as a result of traditional gender norms. This is one of the main conclusions of research led by Jordi Gumà, a researcher at the UPF Department of Political and Social Sciences, conducted in conjunction with Jeroen Spijker, a Ramon y Cajal I3 researcher at the Centre for Demographic Studies of the Autonomous University of Barcelona (CED-UAB), focusing on the case of Spain.
The study, published in Gaceta Sanitaria, analyses the health differences among the Spanish ...
An international team of scientists from the University of Turku, Finland and PennState University, USA have solved a long-standing mystery of how living organisms distinguish RNA and DNA building blocks during gene expression paving the way for the design of new antiviral drugs. The new insights were published in the journal Nature Communications.
All cellular organisms use two types of nucleic acids, RNA and DNA to store, propagate and utilize their genetic information. The synthesis of DNA is carried out by enzymes called DNA polymerases and is needed to accurately transfer the genetic information from generation to generation. ...