Study explores how environmental exposures before conception may impact fetal development
2021-03-17
(Press-News.org) GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (March 16, 2021) -- Older age at the time of conception and alcohol consumption during pregnancy have long been known to impact fetal development.
Now, a new report published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences suggests older age and alcohol consumption in the year leading up to conception also may have an impact by epigenetically altering a specific gene during development of human eggs, or oocytes.
Although the study did not determine the ultimate physical effects of this change, it provides important insights into the intricate relationship between environmental exposures, genetic regulation and human development.
"While the outcome of the change isn't clear, our findings give us a valuable look into how environmental factors affect gene regulation through epigenetics and imprinting," said Peter A. Jones, Ph.D., D.Sc. (hon), Van Andel Institute chief scientific officer and the study's senior author. "A better understanding of these complex processes further our understanding of health and disease and -- one day -- may be the foundation for new disease prevention measures."
Today's study centers on a gene called nc886, which is one of about 100 "imprinted" genes that pass from the mother to the fetus. Imprinted genes retain important chemical tags applied by either the mother or the father before conception. The result is an "epigenetic memory" through which non-genetic information, such as maternal age, may flow directly from parent to offspring. To date, nc886 is the only known imprinted gene that exhibits variation in the likelihood of imprinting based on maternal factors.
Using data from 1,100 mother-child pairs from South Africa, Jones and colleagues found the imprinting of nc886 was increased in older mothers but decreased in mothers who drank alcohol the year before conception. The team also investigated cigarette smoking but found no impact on imprinting of nc886.
A 2018 study published by Jones and his collaborators demonstrated that failure to imprint nc886 was associated with higher body mass in children at five years of age. Research by other groups also have linked failure to imprint nc886 with increased survival in people with acute myeloid leukemia, an aggressive type of blood cancer. Most recently, a group in Taiwan found that lack of imprinting on nc886 may reduce response to an anti-diabetic drug.
INFORMATION:
Authors include Brittany L. Carpenter, Ph.D., Tanaka K. Remba, Stacey L. Thomas, Ph.D., Zachary Madaj, M.S., and Rochelle L. Tiedemann, Ph.D., of VAI; and Lucy T. Brink, M.Sc., and Hein J. Odendaal, M.B.Ch.B., F.C.O.G.(S.A.), M.Med., M.D., F.R.C.O.G., of Stellenbosch University. The VAI Bioinformatics and Biostatistics Core contributed to this work. Blood spot and cord blood samples were provided by the Prenatal Alcohol and SIDS and Stillbirth Network.
Research reported in this publication was supported by Van Andel Institute and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number F32GM129987 (Carpenter). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
The Safe Passage Study, which provided access to samples and drinking and smoking data, was funded by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders under award numbers U01 HD055154, U01 HD045935, U01 HD055155, U01 HD045991 and U01 AA016501 (Odendaal).
ABOUT VAN ANDEL INSTITUTE
Van Andel Institute (VAI) is committed to improving the health and enhancing the lives of current and future generations through cutting edge biomedical research and innovative educational offerings. Established in Grand Rapids, Michigan, in 1996 by the Van Andel family, VAI is now home to more than 400 scientists, educators and support staff, who work with a growing number of national and international collaborators to foster discovery. The Institute's scientists study the origins of cancer, Parkinson's and other diseases and translate their findings into breakthrough prevention and treatment strategies. Our educators develop inquiry-based approaches for K-12 education to help students and teachers prepare the next generation of problem-solvers, while our Graduate School offers a rigorous, research-intensive Ph.D. program in molecular and cellular biology. Learn more at vai.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-17
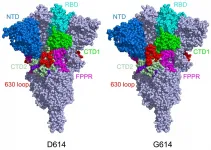
BOSTON - March 16, 2021 - The fast-spreading UK, South Africa, and Brazil coronavirus variants are raising both concerns and questions about whether COVID-19 vaccines will protect against them. New work led by Bing Chen, PhD, at Boston Children's Hospital analyzed how the structure of the coronavirus spike proteins changes with the D614G mutation -- carried by all three variants -- and showed why these variants are able to spread more quickly. The team reports its findings in Science (March 16, 2020).
Chen's team imaged the spikes with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), ...
2021-03-17
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory and their partners from Clemson University have discovered a green, low-energy process to break down polystyrene, a type of plastic that is widely used in foam packaging materials, disposable food containers, cutlery, and many other applications.
Polystyrene is part of a much larger global plastic waste problem. Hundreds of millions metric tons of polymers are produced each year, a large majority of which is discarded after use. Due to the chemical stability and durability of industrial polymers, plastic waste does not easily degrade in landfills and is often burned, which produces carbon dioxide and other hazardous gases. ...
2021-03-17
Combining tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, scientists have fabricated a series of heart valve replacements with the ability to incorporate host cells, enabling them to regenerate and grow over time. The valves expanded and maintained their function for a year when implanted into growing lambs, suggesting they could address the dire need for a long-term valve replacement for children with congenital heart disorders. These pediatric patients depend on mechanical or prosthetic heart valves for survival, but current devices often calcify over time and cannot grow alongside the ...
2021-03-17
WASHINGTON-- The stormy, centuries-old maelstrom of Jupiter's Great Red Spot was shaken but not destroyed by a series of anticyclones that crashed into it over the past few years.
The smaller storms cause chunks of red clouds to flake off, shrinking the larger storm in the process. But the new study found that these disruptions are "superficial." They are visible to us, but they are only skin deep on the Red Spot, not affecting its full depth.
The new study was published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, AGU's journal for research on the formation and evolution of the planets, moons and objects of our solar system and beyond.
"The intense vorticity of the [Great Red Spot], together with its larger size and depth compared to the interacting vortices, ...
2021-03-17
Toronto, ON -A new study published in the journal Substance Use and Misuse has found that adverse childhood experiences, such as physical and sexual abuse and neglect, predict greater performance-enhancing substance use in young adults.
Analyzing a sample of over 14,000 U.S. young adults from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health, researchers found that adverse childhood experiences are strongly associated with both legal (e.g., creatine monohydrate) and illegal (e.g., anabolic-androgenic steroids) performance-enhancing substance use. This relationship was especially strong among individuals who experienced ...
2021-03-17
(March 17, 2021) -- Eric Shattuck, assistant professor of research in the UTSA Institute for Health Disparities Research (IHDR) at The University of Texas at San Antonio, is studying the phenomenon of social distancing in response to infectious disease and its effects on pathogen transmission and the health of individuals and communities.
Many animals, including humans, exhibit behavioral changes during the early stages of an infection, including reduced social contacts, called sickness behavior. His findings suggest innate social distancing might help prevent the infection ...
2021-03-17
Gun violence in popular prime-time broadcast television dramas has increased steadily over almost two decades, a trend that parallels the rise in U.S. homicide deaths attributable to firearms, according to research by the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania.
Overall gun violence on popular prime-time dramas doubled from 2000 through 2018, according to the study, which was published in PLOS ONE. More important, gun violence as a proportion of the violence depicted in the shows rose significantly as well.
"Our research found that gun use substantially increased from 2000 to 2018 on prime-time ...
2021-03-17
A study led by researchers at the University of California San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering provides new insights for developing therapies for muscle disease, injury and atrophy. By studying how different pluripotent stem cell lines build muscle, researchers have for the first time discovered how epigenetic mechanisms can be triggered to accelerate muscle cell growth at different stages of stem cell differentiation.
The findings were published Mar. 17 in Science Advances.
"Stem cell-based approaches that have the potential to aid muscle regeneration and growth would improve the quality of life for many people, from children ...
2021-03-17
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Pharmacogenomics is a valuable tool for health care providers to help prescribe the right drug for the right patient to enhance efficacy and avoid side effects.
A new research paper funded in part by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) shows a clear advantage of genetic testing in helping health care providers choose the appropriate anti-platelet drug. Testing helps determine if a patient carries genetic variants in CYP2C19 that cause loss of its function. These variants interfere with the body's ability to metabolize and activate clopidogrel, an anti-platelet medication.
Anti-platelet drugs are given to prevent complications from blood clotting after a procedure to open clogged arteries. These patients can use one of ...
2021-03-17
While scientists have known that creatures may adjust the timing of their daily routines based on starvation and predation, these shifts have only previously been measured based on data from a population at a single point in time. Now, using data collected as 71 elephant seals undertook their foraging migrations across the North Pacific Ocean, researchers report a view of how these animals divide their time between light and darkness to optimize tradeoffs between risks and rewards based on 7 months of data per seal, collected between 2004 and 2012. Their findings refute a hypothesis about how seals prioritize feeding. To better understand how seals divide their time between light ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study explores how environmental exposures before conception may impact fetal development