Lab-created heart valves can grow with the recipient
Groundbreaking discovery could potentially reduce multiple pediatric heart valve replacement surgeries
2021-03-17
(Press-News.org) A groundbreaking new study led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers from both the College of Science and Engineering and the Medical School shows for the first time that lab-created heart valves implanted in young lambs for a year were capable of growth within the recipient. The valves also showed reduced calcification and improved blood flow function compared to animal-derived valves currently used when tested in the same growing lamb model.
If confirmed in humans, these new heart valves could prevent the need for repeated valve replacement surgeries in thousands of children born each year with congenital heart defects. The valves can also be stored for at least six months, which means they could provide surgeons with an "off the shelf" option for treatment.
The study was published today in Science Translational Medicine, an interdisciplinary medical journal by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). The valve-making procedure has also been patented and licensed to the University of Minnesota startup company Vascudyne, Inc. (Stillwater, Minn.).
"This is a huge step forward in pediatric heart research," said Robert Tranquillo, the senior researcher on the study and a University of Minnesota professor in the Departments of Biomedical Engineering and the Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science. "This is the first demonstration that a valve implanted into a large animal model, in our case a lamb, can grow with the animal into adulthood. We have a way to go yet, but this puts us much farther down the path to future clinical trials in children. We are excited and optimistic about the possibility of this actually becoming a reality in years to come."
Currently, researchers have not been able to develop a heart valve that can grow and maintain function for pediatric patients. The only accepted options for these children with heart defects are valves made from chemically treated animal tissues that often become dysfunctional due to calcification and require replacement because they don't grow with the child. These children will often need to endure up to five (or more) open heart surgeries until a mechanical valve is implanted in adulthood. This requires them to take blood thinners the rest of their lives.
In this study, Tranquillo and his colleagues used a hybrid of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine to create the growing heart valves. Over an eight-week period, they used a specialized tissue engineering technique they previously developed to generate vessel-like tubes in the lab from a post-natal donor's skin cells. To develop the tubes, researchers combined the donor sheep skin cells in a gelatin-like material, called fibrin, in the form of a tube and then provided nutrients necessary for cell growth using a bioreactor.
The researchers then used special detergents to wash away all the sheep cells from the tissue-like tubes, leaving behind a cell-free collagenous matrix that does not cause immune reaction when implanted. This means the tubes can be stored and implanted without requiring customized growth using the recipient's cells.
The next step was to precisely sew three of these tubes (about 16 mm in diameter) together into a closed ring. The researchers then trimmed them slightly to create leaflets to replicate a structure similar to a heart valve about 19 mm in diameter.
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zpRbFsAVofA
"After these initial steps, it looked like a heart valve, but the question then became if it could work like a heart valve and if it could grow," Tranquillo said. "Our findings confirmed both."
This second generation of tri-tube valves were implanted into the pulmonary artery of three lambs. After 52 weeks, the valve regenerated as its matrix became populated by cells from the recipient lamb, and the diameter increased from 19 mm to a physiologically normal valve about 25 mm. The researchers also saw a 17 to 34 percent increase in the length of the valve leaflets as measured from ultrasound images. In addition, researchers showed that the tri-tube valves worked better than current animal-derived valves with almost none of the calcification or blood clotting that the other valves showed after being implanted in lambs of the same age.
"We knew from previous studies that the engineered tubes have the capacity to regenerate and grow in a growing lamb model, but the biggest challenge was how to maintain leaflet function in a growing valved conduit that goes through 40 million cycles in a year," said Zeeshan Syedain, the lead researcher on the study and a University of Minnesota senior research associate in Tranquillo's lab. "When we saw how well the valves functioned for an entire year from young lamb to adult sheep, it was very exciting."
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rme9CZgRgsg
Tranquillo said the next steps are to implant the tri-tube valve directly into the right ventricle of the heart to emulate the most common surgical repair and then start the process of requesting approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for human clinical trials over the next few years.
"If we can get these valves approved someday for children, it would have such a big impact on the children who suffer from heart defects and their families who have to deal with the immense stress of multiple surgeries," Tranquillo said. "We could potentially reduce the number of surgeries these children would have to endure from five to one. That's the dream."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Tranquillo and Syedain, the research team included Bee Haynie (independent contractor); University of Minnesota researchers Sandra L. Johnson and Greeshma Thrivikraman (biomedical engineering), James Berry, Richard Bianco, John P. Carney, and Matthew Lahti (experimental surgical services); Jirong Li (mechanical engineering); and Ryan C. Hill and Kirk C. Hansen (University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus).
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01 HL107572).
To read the full research paper entitled "Pediatric tri-tube valved conduits made from fibroblast-produced extracellular matrix evaluated over 52 weeks in growing lambs," visit the Science Translational Medicine website.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-17
A long noncoding RNA whose function was previously unknown turns out to play a vital role in mobilizing the immune response following a bone marrow transplant or solid organ transplantation.
This RNA molecule, cataloged in scientific databases simply as Linc00402, helps activate immune defenders known as T cells in response to the presence of foreign human cells, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center and Michigan Medicine.
The investigation, which included samples from more than 50 patients who underwent a bone marrow or heart transplant, suggests inhibiting ...
2021-03-17
MEMPHIS, Tenn. - Non-Hispanic black patients with Type 1 diabetes and COVID-19 were almost four times as likely to present to the hospital with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) compared to non-Hispanic whites, according to an article published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism by Le Bonheur Pediatric Endocrinologist Kathryn Sumpter, MD.
The study examined 180 patients with Type 1 diabetes and laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 from 52 clinical sites, including Le Bonheur Children's. The objective of the study was to evaluate instances of DKA, a serious complication of Type 1 diabetes, in patients with Type 1 diabetes and COVID-19 and determine if minorities had increased ...
2021-03-17
ITHACA, N.Y. - If you want to build a fully functional nanosized robot, you need to incorporate a host of capabilities, from complicated electronic circuits and photovoltaics to sensors and antennas.
But just as importantly, if you want your robot to move, you need it to be able to bend.
Cornell researchers have created micron-sized shape memory actuators that enable atomically thin two-dimensional materials to fold themselves into 3D configurations. All they require is a quick jolt of voltage. And once the material is bent, it holds its shape - even after the voltage is removed.
As a demonstration, the team created what ...
2021-03-17
The coronavirus' structure is an all-too-familiar image, with its densely packed surface receptors resembling a thorny crown. These spike-like proteins latch onto healthy cells and trigger the invasion of viral RNA. While the virus' geometry and infection strategy is generally understood, little is known about its physical integrity.
A new study by researchers in MIT's Department of Mechanical Engineering suggests that coronaviruses may be vulnerable to ultrasound vibrations, within the frequencies used in medical diagnostic imaging.
Through computer simulations, the team has modeled the virus' mechanical response to vibrations across a range of ultrasound ...
2021-03-17
A new study has found that about 35% of Americans with a cancer history had an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease in the next decade, compared with about 23% of those who didn't have cancer.
Based on a risk calculator that estimates a person's 10-year chances of developing heart disease or stroke, researchers from The Ohio State University found that the average estimated 10-year risk for a cancer survivor was about 8%, compared to 5% for those who didn't have a history of cancer.
The new study appears in the journal PLOS ONE.
"We know that obesity, cancer and cardiovascular disease share some common risk factors, and in addition to those shared risk factors, cancer patients also receive treatments including radiation and chemotherapy that can affect their cardiovascular ...
2021-03-17
Many people have never heard of Brucellosis, but farmers and ranchers in the United States forced to cull animals that test positive for the disease and people infected by the animal-transmitted Brucella abortus (B. abortus) pathogen that suffer chronic, Malaria-type symptoms, certainly have.
Brucellosis is an agricultural and human health concern on a global scale. It was introduced over 100 years ago to Bison and elk in Yellowstone National Park by cattle and has been circulating among the wild herds ever since, leading to periodic outbreaks and reinfection. There is no vaccine for humans, and experimental studies ...
2021-03-17
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (March 16, 2021) -- Older age at the time of conception and alcohol consumption during pregnancy have long been known to impact fetal development.
Now, a new report published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences suggests older age and alcohol consumption in the year leading up to conception also may have an impact by epigenetically altering a specific gene during development of human eggs, or oocytes.
Although the study did not determine the ultimate physical effects of this change, it provides important insights into the intricate relationship between environmental exposures, genetic regulation and human development.
"While the outcome of the change isn't clear, our findings give us a valuable look into ...
2021-03-17
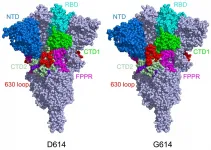
BOSTON - March 16, 2021 - The fast-spreading UK, South Africa, and Brazil coronavirus variants are raising both concerns and questions about whether COVID-19 vaccines will protect against them. New work led by Bing Chen, PhD, at Boston Children's Hospital analyzed how the structure of the coronavirus spike proteins changes with the D614G mutation -- carried by all three variants -- and showed why these variants are able to spread more quickly. The team reports its findings in Science (March 16, 2020).
Chen's team imaged the spikes with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), ...
2021-03-17
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory and their partners from Clemson University have discovered a green, low-energy process to break down polystyrene, a type of plastic that is widely used in foam packaging materials, disposable food containers, cutlery, and many other applications.
Polystyrene is part of a much larger global plastic waste problem. Hundreds of millions metric tons of polymers are produced each year, a large majority of which is discarded after use. Due to the chemical stability and durability of industrial polymers, plastic waste does not easily degrade in landfills and is often burned, which produces carbon dioxide and other hazardous gases. ...
2021-03-17
Combining tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, scientists have fabricated a series of heart valve replacements with the ability to incorporate host cells, enabling them to regenerate and grow over time. The valves expanded and maintained their function for a year when implanted into growing lambs, suggesting they could address the dire need for a long-term valve replacement for children with congenital heart disorders. These pediatric patients depend on mechanical or prosthetic heart valves for survival, but current devices often calcify over time and cannot grow alongside the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Lab-created heart valves can grow with the recipient
Groundbreaking discovery could potentially reduce multiple pediatric heart valve replacement surgeries