(Press-News.org) A new study has found that about 35% of Americans with a cancer history had an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease in the next decade, compared with about 23% of those who didn't have cancer.
Based on a risk calculator that estimates a person's 10-year chances of developing heart disease or stroke, researchers from The Ohio State University found that the average estimated 10-year risk for a cancer survivor was about 8%, compared to 5% for those who didn't have a history of cancer.
The new study appears in the journal PLOS ONE.
"We know that obesity, cancer and cardiovascular disease share some common risk factors, and in addition to those shared risk factors, cancer patients also receive treatments including radiation and chemotherapy that can affect their cardiovascular health - we call that cardiotoxicity," said lead researcher Xiaochen Zhang, a PhD candidate in Ohio State's College of Public Health.
But those risks may be underestimated or poorly understood, leading Zhang and fellow researchers to urge steps to boost recognition among health care providers and their patients.
"The good news is that we're getting really good at treating cancer and we have more survivors, but we need to start thinking more carefully about the non-cancer risks following a diagnosis, one of which is cardiovascular disease," said study senior author Ashley Felix, an associate professor of epidemiology at Ohio State.
"We don't want people to survive cancer only to die prematurely of heart disease or stroke, so we need to make sure that cancer patients, and their health care team, are aware of this increased risk."
The data used in the study comes from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The nationally representative sample of people surveyed from 2007 to 2016 should provide a good picture of the elevated risk for cancer survivors in the U.S., the researchers said.
For this analysis, they examined data provided by 15,095 adults aged 40 to 79 years with no history of cardiovascular disease. Almost 13% reported a history of cancer.
One of the strengths of this research is the large study size, which allowed for analysis based on type of cancer and by age group. Survivors of testicular, prostate, bladder and kidney cancers had particularly high 10-year cardiovascular disease risk, as did those in their 60s.
When the researchers compared individual cardiovascular disease risk factors by cancer status, they found that older age, higher systolic blood pressure and a personal history of diabetes were more common in the cancer survivors.
Looking forward, it's important that researchers and health care providers keep their eyes on the growing number of cancer survivors, including younger adults, Felix said. Almost 17 million Americans live with a cancer diagnosis, a number that is expected to grow to 26 million by 2040.
"If we continue to see the increasing incidence of cancer among younger adults, we can expect to see a larger burden of cardiovascular disease among those individuals - our future studies need to go in that direction," she said.
Added Zhang, "The good news is that those younger individuals have a lot of time to make lifestyle changes that could move their cardiovascular risk in a positive direction.
"In addition to monitoring cancer survivors carefully for cardiovascular disease - and making them aware of the elevated risk - health care providers have the opportunity to guide patients toward interventions that can lower their risk," she said.
There's also potential for developing a risk-assessment tool that specifically takes cancer survivorship into account - which would allow for more precise assessments for that population, the researchers said.
INFORMATION:
The all-Ohio State research team also included Meghan Pawlikowski, Susan Olivo-Marston, Karen Patricia Williams and Julie Bower.
CONTACTS: Ashley Felix,
Felix.20@osu.edu; Xiaochen Zhang,
Zhang.8303@buckeyemail.osu.edu
Written by Misti Crane,
614-293-3739;
Crane.11@osu.edu
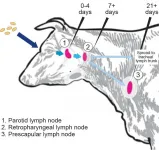
Many people have never heard of Brucellosis, but farmers and ranchers in the United States forced to cull animals that test positive for the disease and people infected by the animal-transmitted Brucella abortus (B. abortus) pathogen that suffer chronic, Malaria-type symptoms, certainly have.
Brucellosis is an agricultural and human health concern on a global scale. It was introduced over 100 years ago to Bison and elk in Yellowstone National Park by cattle and has been circulating among the wild herds ever since, leading to periodic outbreaks and reinfection. There is no vaccine for humans, and experimental studies ...
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (March 16, 2021) -- Older age at the time of conception and alcohol consumption during pregnancy have long been known to impact fetal development.
Now, a new report published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences suggests older age and alcohol consumption in the year leading up to conception also may have an impact by epigenetically altering a specific gene during development of human eggs, or oocytes.
Although the study did not determine the ultimate physical effects of this change, it provides important insights into the intricate relationship between environmental exposures, genetic regulation and human development.
"While the outcome of the change isn't clear, our findings give us a valuable look into ...
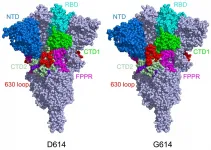
BOSTON - March 16, 2021 - The fast-spreading UK, South Africa, and Brazil coronavirus variants are raising both concerns and questions about whether COVID-19 vaccines will protect against them. New work led by Bing Chen, PhD, at Boston Children's Hospital analyzed how the structure of the coronavirus spike proteins changes with the D614G mutation -- carried by all three variants -- and showed why these variants are able to spread more quickly. The team reports its findings in Science (March 16, 2020).
Chen's team imaged the spikes with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), ...
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory and their partners from Clemson University have discovered a green, low-energy process to break down polystyrene, a type of plastic that is widely used in foam packaging materials, disposable food containers, cutlery, and many other applications.
Polystyrene is part of a much larger global plastic waste problem. Hundreds of millions metric tons of polymers are produced each year, a large majority of which is discarded after use. Due to the chemical stability and durability of industrial polymers, plastic waste does not easily degrade in landfills and is often burned, which produces carbon dioxide and other hazardous gases. ...
Combining tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, scientists have fabricated a series of heart valve replacements with the ability to incorporate host cells, enabling them to regenerate and grow over time. The valves expanded and maintained their function for a year when implanted into growing lambs, suggesting they could address the dire need for a long-term valve replacement for children with congenital heart disorders. These pediatric patients depend on mechanical or prosthetic heart valves for survival, but current devices often calcify over time and cannot grow alongside the ...
WASHINGTON-- The stormy, centuries-old maelstrom of Jupiter's Great Red Spot was shaken but not destroyed by a series of anticyclones that crashed into it over the past few years.
The smaller storms cause chunks of red clouds to flake off, shrinking the larger storm in the process. But the new study found that these disruptions are "superficial." They are visible to us, but they are only skin deep on the Red Spot, not affecting its full depth.
The new study was published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, AGU's journal for research on the formation and evolution of the planets, moons and objects of our solar system and beyond.
"The intense vorticity of the [Great Red Spot], together with its larger size and depth compared to the interacting vortices, ...
Toronto, ON -A new study published in the journal Substance Use and Misuse has found that adverse childhood experiences, such as physical and sexual abuse and neglect, predict greater performance-enhancing substance use in young adults.
Analyzing a sample of over 14,000 U.S. young adults from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health, researchers found that adverse childhood experiences are strongly associated with both legal (e.g., creatine monohydrate) and illegal (e.g., anabolic-androgenic steroids) performance-enhancing substance use. This relationship was especially strong among individuals who experienced ...
(March 17, 2021) -- Eric Shattuck, assistant professor of research in the UTSA Institute for Health Disparities Research (IHDR) at The University of Texas at San Antonio, is studying the phenomenon of social distancing in response to infectious disease and its effects on pathogen transmission and the health of individuals and communities.
Many animals, including humans, exhibit behavioral changes during the early stages of an infection, including reduced social contacts, called sickness behavior. His findings suggest innate social distancing might help prevent the infection ...
Gun violence in popular prime-time broadcast television dramas has increased steadily over almost two decades, a trend that parallels the rise in U.S. homicide deaths attributable to firearms, according to research by the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania.
Overall gun violence on popular prime-time dramas doubled from 2000 through 2018, according to the study, which was published in PLOS ONE. More important, gun violence as a proportion of the violence depicted in the shows rose significantly as well.
"Our research found that gun use substantially increased from 2000 to 2018 on prime-time ...
A study led by researchers at the University of California San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering provides new insights for developing therapies for muscle disease, injury and atrophy. By studying how different pluripotent stem cell lines build muscle, researchers have for the first time discovered how epigenetic mechanisms can be triggered to accelerate muscle cell growth at different stages of stem cell differentiation.
The findings were published Mar. 17 in Science Advances.
"Stem cell-based approaches that have the potential to aid muscle regeneration and growth would improve the quality of life for many people, from children ...