Disparities in contraception use between women with and without diabetes persist
Sometimes worsen after the diagnosis of diabetes
2021-03-18
(Press-News.org) (Boston)-- Uncontrolled diabetes increases maternal and fetal risks during pregnancy. As a result, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends that family planning should be discussed and effective contraception should be available to the more than three percent of (more than one million) reproductive-age women in the United States with diabetes. Yet a new study has found that women with diabetes are less likely to use contraception after their diabetes diagnosis.
"Efforts are needed to ensure that women with diabetes receive the counseling and clinical services needed to carefully plan their pregnancies," said corresponding author Mara Murray Horwitz, MD, assistant professor medicine at Boston University School of Medicine.
Using claims data from a large national insurance provider to identify reproductive-age women, the researchers divided them into two groups: those who received a new diabetes diagnosis and those who did not receive a diabetes diagnosis. They then matched individuals in each group on important other variables to make the groups more similar. Using medical diagnosis, pharmacy fill and procedure codes, they measured contraception use in the two groups during the year before the diagnosis and during the year after the diagnosis. Finally, they compared the change in contraception use from the year before the diagnosis to the year after the diagnosis, in the diagnosed group versus in the undiagnosed group.
They found that being diagnosed with diabetes does not make a person more likely to use effective contraception and in fact may lead to a drop in the use of certain types of effective contraception, namely short-acting hormonal methods such as pills and injections.
The ADA states that "women with diabetes have the same contraception options and recommendations as those without diabetes," and that, "the risk of an unplanned pregnancy outweighs the risk of any given contraception option." "Nonetheless, many patients and clinicians report concerns about the need for and safety of contraception in the setting of diabetes. It is conceivable that--as our study suggests--a diabetes diagnosis leads to less, instead of more, contraception counseling, prescribing, and use," added Murray Horwitz, a physician at Boston Medical Center.
The researchers hope that this study leads to more comprehensive care, including family planning with the full range of safe and effective contraceptive options, for persons with diabetes who may become pregnant. "Ultimately we want everyone to be able to choose when and if they become pregnant and to have the information, tools and support as needed to optimize their pregnancy outcomes," she said.
These findings appear online in the journal Primary Care Diabetes.
INFORMATION:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1751991821000371?dgcid=author END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-18
When the COVID-19 pandemic forced medical students out of classrooms and clinical rotations this time last year, the state of Georgia's only public medical school had to quickly rethink its traditional curriculum.
Faculty and staff at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University were able to quickly adapt and provide an online platform for learning about the pandemic and initiating student-led service projects to aid frontline workers and help educate the public, MCG faculty and students write in a review article in the journal Medical Science Educator.
The University System of Georgia suspended in-classroom learning ...
2021-03-18
Prior infection with COVID-19 protects most people against reinfection, with 0.65% of patients returning a positive PCR test twice during Denmark's first and second waves, compared with 3.27% of people who tested positive after initially being negative.
People over the age of 65 are at greater risk of catching COVID-19 again, with only 47% protection against repeat infection compared with 80% for younger people.
Protection against reinfection remained stable for more than six months.
The findings underline that measures to protect the elderly - including social distancing and vaccinations are essential even if people have already been diagnosed with COVID-19.
The analysis focused on the original COVID-19 strain and made no assessment ...
2021-03-18
When it comes to adapting to new situations, goats are a step ahead. Compared to sheep, they can more quickly adapt to changing environmental conditions. These are the findings of a new study by researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Leibniz Institute for Farm Animal Biology (FBN) which were published in Royal Society Open Science. The study investigated how well the animals were able to navigate around obstacles to reach food.
Sheep and goats have many things in common: They are closely related genetically, roughly the same size, have similar social structures, and have both been domesticated by humans over approximately the same amount of time. They do, however, differ greatly when it comes to their foraging strategies. "While sheep ...
2021-03-18
As their name suggests, by-the-wind sailor jellyfish know how to catch a breeze. Using a stiff, translucent sail propped an inch above the surface of the ocean, these teacup-sized organisms skim along the water dangling a fringe of delicate purple tentacles just below the surface to capture zooplankton and larval fish as they travel.
At the mercy of the wind, these jellies can wash ashore and strand -- sometimes numbering in the trillions -- on beaches around the world, including up and down the U.S. West Coast. And while these mass stranding events are hard to miss, very little actually is known about how or why they happen.
Now, thanks to 20 years of observations from thousands of citizen scientists, ...
2021-03-18
When it comes to the use of driverless vehicles, an individual's support for their adoption hinges on how safe they are, rather than their economic impact or privacy concerns stemming from the data they might collect, a Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) study of 1,006 Singaporeans has found.
The NTU Singapore study led by the Wee Kim Wee School of Communication and Information exposed its participants to positive and negative blog posts about driverless vehicles and their safety, their impact on jobs and the economy, ...
2021-03-18
The collaborative work is published online in the journal Communications Biology on March 8th, 2021.
The power of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis represents the only biological process, which converts the energy of sunlight into chemically stored energy. On molecular level, the photosynthetic key enzymes called photosystems are responsible for this conversion process. Photosystem I (PSI), one of the two photosystems, is a large membrane protein complex that can be present in different forms - as monomers, dimers, trimers or even tetramers.
New isolation technique helps revealing ...
2021-03-18
An international team of scholars studied how the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted Europeans' stress levels and their trust in their national governments and the healthcare systems. They found that respondents were most stressed by the state of the national economy, and only after that, by the risk of catching COVID-19 and possibly being hospitalized. The results of the study were published in Royal Society Open Science.
The authors of the study represent over 50 universities. Among them is Dmitrii Dubrov, Junior Research Fellow at the HSE Center for Sociocultural Research, who developed and organized the global survey, COVIDiSTRESS. The researchers studied the psychological ...
2021-03-18
An international study led by the University Complutense of Madrid (UCM) proposed new computational image processing methods that improve the analysis and three-dimensional reconstruction of biological macromolecules.
Currently, determining the composition (i.e., the sequence of amino acids) of macromolecules such as proteins is relatively simple; however, determining the shape in which they are ordered in a three-dimensional structure is not. The new methodology, published in Nature Communications, improves the visualization of the 3D reconstructions obtained through cryogenic electron microscopy, as well as their quality.
"This study helps us broaden our understanding of proteins ...
2021-03-18
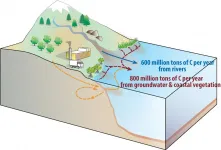
Every year 600-900 million tons of carbon flow through rivers to the ocean either as particles or in dissolved form. Researchers have known for a long time that this does not represent the total amount of carbon that gets transported from the land to the ocean. But the remaining contributors mostly from coastal ecosystems, such as carbon-rich mangrove forests, and from groundwater discharge into the ocean have been notoriously difficult to measure.
A new study published in the journal Global Biogeochemical Cycles and spearheaded by Dr. Eun Young Kwon, project leader at the IBS Center for Climate Physics South Korea provides new estimates of this elusive component of the global carbon cycle. The study makes use of the existence of two stable carbon isotopes, 12C and 13C, with the latter ...
2021-03-18
Statisticians have calculated the probability of ships of different Polar Ship Categories becoming beset in ice along the Northern Sea Route. Their data will help assess the risks of maritime traffic in the Arctic.
The results of the new study, published recently in the Cold Regions Science and Technology journal, will support safer maritime transport planning and the prevention of oil spills. The results will also benefit authorities that regulate maritime traffic by providing a foundation for statutes and legislation. A comprehensive approach to computing helps shipping companies plan transport routes.
Tankers more common on the Northern Sea Route
The Northern Sea Route is attracting more tankers and cargo ships travelling from Russia and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Disparities in contraception use between women with and without diabetes persist
Sometimes worsen after the diagnosis of diabetes