(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON -- Even as vaccines are becoming more readily available in the U.S., protecting against the asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic spread of the virus (SARS-CoV-2) that causes COVID-19 is key to ending the pandemic, say two Georgetown infectious disease experts.
In their Perspective, " END
Vaccines alone may not be enough to end pandemic
2021-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Found in space: Complex carbon-based molecules
2021-03-18
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Much of the carbon in space is believed to exist in the form of large molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Since the 1980s, circumstantial evidence has indicated that these molecules are abundant in space, but they have not been directly observed.
Now, a team of researchers led by MIT Assistant Professor Brett McGuire has identified two distinctive PAHs in a patch of space called the Taurus Molecular Cloud (TMC-1). PAHs were believed to form efficiently only at high temperatures -- on Earth, they occur as byproducts of burning fossil fuels, and they're also found in char marks on grilled ...
Yale researchers create 'Ancestry.com' for cells
2021-03-18
One of great mysteries of human biology is how a single cell can give rise to the 37 trillion cells contained in the average body, each with its own specialized role. Researchers at Yale University and the Mayo Clinic have devised a way to recreate the earliest stages of cellular development that gives rise to such an amazing diversity of cell types.
Using skin cells harvested from two living humans, researchers in the lab of Yale's Flora Vaccarino were able to track their cellular lineage by identifying tiny variations or mutations contained within the genomes of those cells.
These "somatic" or non-inherited mutations are generated at each cell division during a human's development. The percentage of cells bearing the traces of any ...
Double duty: Gut's immune system helps regulate food processing, too
2021-03-18
The small intestine is ground zero for survival of animals. It is responsible for absorbing the nutrients crucial to life and it wards off toxic chemicals and life-threatening bacteria.
In a new study published March 18 in the journal Science, Yale researchers report the critical role played by the gut's immune system in these key processes. The immune system, they found, not only defends against pathogens but regulates which nutrients are taken in.
The findings may provide insights into origins of metabolic disease and malnutrition that is common in ...
Discovery of a 'winged' shark in the Cretaceous seas
2021-03-18
93 million years ago, bizarre, winged sharks swam in the waters of the Gulf of Mexico. This newly described fossil species, called Aquilolamna milarcae, has allowed its discoverers to erect a new family. Like manta rays, these 'eagle sharks' are characterised by extremely long and thin pectoral fins reminiscent of wings. The specimen studied was 1.65 metres long and had a span of 1.90 metres.
Aquilolamna milarcae had a caudal fin with a well-developed superior lobe, typical of most pelagic sharks, such as whale sharks and tiger sharks. Thus, its anatomical features thus ...
How bushfire smoke traveled around the world
2021-03-18
It's not just how hot the fires burn - it's also where they burn that matters. During the recent extreme fire season in Australia, which began in 2019 and burned into 2020, millions of tons of smoke particles were released into the atmosphere. Most of those particles followed a typical pattern, settling to the ground after a day or week; yet the ones created in fires burning in one corner of the country managed to blanket the entire Southern hemisphere for months. A pair of Israeli scientists managed to track puzzling January and February 2020 spikes in a measure of particle-laden haze to those fires, and then, in a paper recently published in Science, they ...
Self-compassion can lessen feelings of work-from-home loneliness, finds study
2021-03-18
INDIANAPOLIS -- The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is keeping millions of Americans from their usual offices, as they find themselves still working at home. Even with the vaccine now being distributed, working from home may still be the future for some, and new research suggests the resulting work loneliness negatively impacts employee well-being. ...
Estimating the timing of the earliest SARS-CoV-2 case in Hubei Province, China
2021-03-18
Researchers who simulated early stages of the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in Wuhan, China, conclude that the virus was likely circulating earlier than has been described, possibly even in mid-October 2019. The findings do not reveal whether the virus that first emerged was less "fit" than the virus that spread throughout China, say the authors, but the estimates do further distance the first ("index") case from the outbreak at the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, which has received much attention. A concerted effort has been made to determine when the SARS-CoV-2 virus ...
Could leak in blood-brain barrier be cause of poor memory?
2021-03-18
Have you forgotten where you laid your keys? Ever wondered where you had parked your car? Or having trouble remembering the name of the new neighbor? Unfortunately, these things seem to get worse as one gets older. A big question for researchers is where does benign forgetfulness end and true disease begin?
One of the keys to having a healthy brain at any age is having a healthy blood-brain barrier, a complex interface of blood vessels that run through the brain. Researchers reviewed more than 150 articles to look at what happens to the blood-brain barrier as we age. Their findings were published March 15 in Nature ...
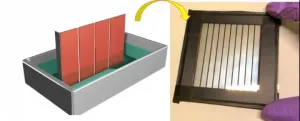
New perovskite fabrication method for solar cells paves way to large-scale production
2021-03-18
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 18, 2021--A new, simpler solution process for fabricating stable perovskite solar cells overcomes the key bottleneck to large-scale production and commercialization of this promising renewable-energy technology, which has remained tantalizingly out of reach for more than a decade.
"Our work paves the way for low-cost, high-throughput commercial-scale production of large-scale solar modules in the near future," said Wanyi Nie, a research scientist fellow in the Center of Integrated Nanotechnologies at Los Alamos National Laboratory and corresponding ...
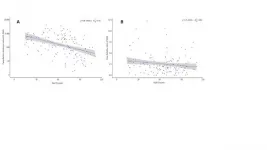
'Vulnerable' countries experience lower COVID-19 infection and death rates than the norm
2021-03-18
During a pandemic like COVID-19, vulnerable countries are traditionally the focus of global attention and concern. However, new research suggests that we need to rebuild our understanding. A study published in KeAi's Global Health Journal, examined the relationship between state vulnerabilities (measured using the Fragile States Index (FSI) from Fund for Peace) and COVID-19 incidence and death rates in 146 countries. The FSI consists of 12 specific indicators covering cohesion, economy, politics and society. "When using the total FSI score for statistical analysis, we were surprised to find that, overall, the more fragile countries had lower cumulative incidence and fatality rates for COVID-19," explains one of the study's authors, Yangmu ...