Outcomes, risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in North American registry of patients with MS
2021-03-19
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: This analysis examined how patients with multiple sclerosis who have COVID-19 fare and what patient and disease characteristics are associated with worse outcomes.
Authors: Amber Salter, Ph.D., of Washington University in St Louis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.0688)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full article is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.0688?guestAccessKey=d0f66c8e-e9ff-4588-95db-c24b75b0e93e&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=031921
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-19
What The Study Did: Researchers examined if differences in vitamin D levels greater than levels traditionally considered sufficient (30 ng/mL) are associated with having test results positive for COVID-19 in White and in Black individuals.
Authors: David O. Meltzer, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4117)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article ...
2021-03-19
A multinational research team led by Dr. Adnan Sljoka (RIKEN), Prof. R. Scott Prosser (Univ. of Toronto) with collaborations with Dr. Duy Phuoc Tran and Prof. Akio Kitao (Tokyo Tech) and Prof. Roger K. Sunahara (Univ. of California San Diego) has carried out experimental and computational studies, revealing key steps associated with the activation of the human adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR). A2AR is a member of superfamily of receptors called G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) (major drug targets) which engage the G protein and initiates cell signaling. The research team discovered that A2AR is represented by at least two inactive conformations and three active conformations whose populations are dependent on ligands and activation ...
2021-03-19
A team of researchers has found disrupting the interaction between cancer cells and certain immune cells is more effective at killing cancer cells than current immunotherapy treatments.
The findings, which include studies in cell lines and animal models, appeared in JCI Insight and focus on END ...
2021-03-19
MOSCOW, RUSSIA -
Moscow Center for Diagnostics & Telemedicine and RADLogics shared the results of a large-scale study (Moscow Experiment on the Computer Vision for the Analysis of Medical Images - mosmed.ai, NCT04489992) conducted by the Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies of the Moscow Health Care Department. The clinical research found that the introduction of RADLogics' AI-Powered solution into radiology workflow to analyze Chest-CT scans during the COVID-19 pandemic reduced report turnaround ...
2021-03-19
TROY, N.Y. -- A novel form of polymerized estrogen developed at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute can provide neuroprotection when implanted at the site of a spinal cord injury -- preventing further damage. This promising result, found in a preclinical model, was recently published in ACS Chemical Neuroscience, and it lays the groundwork for further advancement of this new biomaterial.
"What we saw that gives us hope is more neuroprotection, meaning we saw more spared neurons and more spared axons in the tissue," said Ryan Gilbert, a professor of biomedical engineering at Rensselaer, and co-author on this paper. "We believe that the estrogen released from our biomaterial design is providing a neuroprotective response."
After a spinal cord injury, the body's inflammatory ...
2021-03-19
The results showed that several psychological well-being measures gradually increased within participants from the beginning to the end of the course. That was especially true for life satisfaction, perceived well-being, self-awareness and emotional self-regulation. The participants in the study also reported a significant decrease in anxiety, perceived stress, negative thoughts, rumination and anger tendencies. The researchers observed, simultaneously, improvements in the positive aspects and a reduction of negative emotions, both in the short term and longitudinally ...
2021-03-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Stress is a universal human experience that almost everyone deals with from time to time. But a new study found that not only do some people report feeling no stress at all, but that there may be downsides to not experiencing stress.
The researchers found that people who reported experiencing no stressors were more likely to experience better daily well-being and fewer chronic health conditions. However, they were also more likely to have lower cognitive function, as well.
David M. Almeida, professor of human development and family studies at Penn State, said the study suggests that small, daily stressors could potentially benefit the brain, despite being an inconvenience.
"It's possible that experiencing stressors creates opportunities for you ...
2021-03-19
Three University of Colorado Cancer Center researchers are part of a team that recently published a paper offering new insight into how the immune system relates to cancer. Quentin Vicens, PhD, Jeffrey Kieft, PhD, and Beat Vögeli, PhD, are authors on the paper, which looks at how an enzyme called ADAR1 operates in pathways associated with cancer.
"In a cell, ADAR1 edits native RNA -- or self-RNA -- so that the cell recognizes it as its own. It's a key protection against autoimmune disorders," Kieft says. "But if a virus infects, viral RNA isn't edited by ADAR1, so the cell can recognize that and react. The cell knows it has foreign RNA, and it activates immune responses to fight off that infection."
For their paper published last month in the ...
2021-03-19
Nearly two-thirds of middle-aged and older adults in Canada report adverse childhood experiences
Hamilton, ON (Mar. 19, 20121) - New research from McMaster University has found that roughly three in every five Canadian adults aged 45 to 85 have been exposed to childhood abuse, neglect, intimate partner violence or other household adversity.
The research, which estimates the prevalence of a broad range of adverse childhood experiences, was published in CMAJ Open.
"Our research showed that adverse childhood experiences are highly prevalent in the Canadian population, with 62% of Canadian adults aged 45 to 85 reporting at least one exposure," said Divya Joshi, the study's lead author and a postdoctoral fellow in the Department ...
2021-03-19
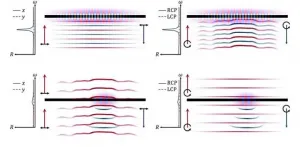
In 1961, physicist Ugo Fano provided the first theoretical explanation to an anomalous asymmetry observed in the spectral profiles of noble gases. He put forth an impactful interpretation of this phenomenon, now called "Fano resonance," stating that if a discrete excited state of a system falls within the energy range of a continuum of other possible states, these two can interfere with each other and give rise to abnormal peaks and dips in the system's frequency response.
Though Fano resonance can occur in various physical systems, recent progress in metasurfaces and nanotechnology has drawn attention to this phenomenon as a potentially powerful tool in optics. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Outcomes, risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in North American registry of patients with MS