Gene therapy using 'zinc fingers' may help treat Alzheimer's disease, animal study shows
Treatment involving a single injection has long-lasting effects
2021-03-19
(Press-News.org) BOSTON - Researchers have used a genetic engineering strategy to dramatically reduce levels of tau--a key protein that accumulates and becomes tangled in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease--in an animal model of the condition. The results, which come from investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Sangamo Therapeutics Inc., could lead to a potentially promising treatment for patients with this devastating illness.
As described in Science Advances, the strategy involves a gene regulation technology called zinc finger protein transcription factors (ZFP-TFs), which are DNA-binding proteins that can be harnessed to target and affect the expression of specified genes. In this case, the therapy was designed to target and silence the expression of the gene that codes for tau. Mice with Alzheimer's disease received a single injection of the treatment--which employed a harmless virus to deliver the ZFP-TFs to cells--directly into the hippocampus region of the brain or intravenously into a blood vessel. Treatment with ZFP-TFs reduced tau protein levels in the brain by 50% to 80% out to 11 months, the longest time point studied. Importantly, the therapy reversed some of the Alzheimer's-related damage that was present in the animals' brain cells.
"The technology worked just the way we had hoped--reducing tau substantially for as long as we looked, causing no side effects that we could see even over many, many months, and improving the pathological changes in the brains of the animals," says senior author Bradley Hyman, MD, PhD, who directs the Alzheimer's disease research unit at the MassGeneral Institute for Neurodegenerative Disease. "This suggests a plan forward to try to help patients."
The simplicity of the therapy makes it an especially attractive approach. "This was the result of a single treatment of gene regulation therapy, which could be given by an injection into the bloodstream," says Hyman. "While this therapy is far from patients--as much more development and safety testing would need to be done--it is a promising and exciting first step."
INFORMATION:
The study was primarily supported by Sangamo, pursuant to a sponsored research agreement with MGH. Funding was also provided by MGH and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) of the Helmholtz Foundation, the JPB Foundation, the National Institute on Aging, and the BrightFocus Foundation.
About the Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The Mass General Research Institute conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the nation, with annual research operations of more than $1 billion and comprises more than 9,500 researchers working across more than 30 institutes, centers and departments. In August 2020, Mass General was named #6 in the U.S. News & World Report list of "America's Best Hospitals."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-19
A team of scientists, led by researchers at Northwestern University, Shirley Ryan AbilityLab and the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC), has developed novel technology promising to increase understanding of how brains develop, and offer answers on repairing brains in the wake of neurotrauma and neurodegenerative diseases.
Their research is the first to combine the most sophisticated 3-D bioelectronic systems with highly advanced 3-D human neural cultures. The goal is to enable precise studies of how human brain circuits develop and repair themselves in vitro. The study is the cover story for ...
2021-03-19
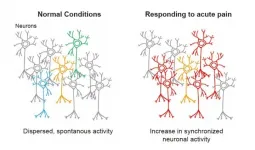
In a world first, a cross-institutional research collaboration has used a two-photon microscope (*1) with a combination of calcium imaging (*2) and holographic stimulation (*3) to reveal that the functional connectivity between neurons located in the primary somatosensory cortex is increased in response to acute pain.
Pain occurs as a result of injury, such as peripheral neuron damage or inflammation stemming from peripheral tissue violation. Research findings have been published on the involvement of central nervous system abnormalities in the onset of pain and sustained pain. The primary somatosensory cortex ...
2021-03-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Most stroke victims don't receive treatment fast enough to prevent brain damage. Scientists at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, College of Engineering and College of Medicine have developed technology to "retrain" cells to help repair damaged brain tissue. It's an advancement that may someday help patients regain speech, cognition and motor function, even when administered days after an ischemic stroke.
Engineering and medical researchers use a process created by Ohio State called tissue nanotransfection (TNT) to introduce genetic material into cells. This allows them to reprogram skin cells to become something ...
2021-03-19
New York, NY--March 19, 2020--Columbia Engineering researchers, working with Brookhaven National Laboratory, report today that they have built designed nanoparticle-based 3D materials that can withstand a vacuum, high temperatures, high pressure, and high radiation. This new fabrication process results in robust and fully engineered nanoscale frameworks that not only can accommodate a variety of functional nanoparticle types but also can be quickly processed with conventional nanofabrication methods.
"These self-assembled nanoparticles-based materials are so resilient that they could fly in space," says Oleg Gang, professor ...
2021-03-19
PITTSBURGH, March 19, 2021 - Non-circulating memory T cells, whose main function is to provide local protection against re-infection, contribute to chronic transplant rejection, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers reveal in a paper published today in Science Immunology.
The scientists show that these "tissue-resident memory T cells" are harmful in situations where antigens that the cells recognize are present in the body for a long time, such as in cases of an organ or tissue transplant. This finding is an important step toward improving therapies to help prevent organ rejection in transplant recipients.
"Tissue-resident memory T cells serve an important surveillance function," said co-senior author Martin Oberbarnscheidt, ...
2021-03-19
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Many viruses infect their hosts through mucosal surfaces such as the lining of the respiratory tract. MIT researchers have now developed a vaccination strategy that can create an army of T cells that are ready and waiting at those surfaces, offering a quicker response to viral invaders.
The researchers showed that they could induce a strong memory T cell response in the lungs of mice by giving them a vaccine modified to bind to a protein naturally present in mucus. This can help ferry the vaccine across mucosal barriers, such as the lining of the lungs.
"In this paper, we specifically focused on T cell responses that would be useful against viruses or cancer, and our idea was to use this protein, albumin, as sort of a Trojan horse to ...
2021-03-19
To understand the fundamental properties of an industrial solvent, chemists with the University of Cincinnati turned to a supercomputer.
UC chemistry professor and department head Thomas Beck and UC graduate student Andrew Eisenhart ran quantum simulations to understand glycerol carbonate, a compound used in biodiesel and as a common solvent.
They found that the simulation provided detail about hydrogen bonding in determining the structural and dynamic properties of the liquid that was missing from classical models. The study was published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry B.
Glycerol carbonate could be a more environmentally ...
2021-03-19
During a public health crisis like the COVID-19 pandemic, U.S. hospitals need to allocate scarce medical resources in an equitable manner, according to clinicians and ethicists at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine.
"Significant concerns have been raised that crisis standards of care may be biased against certain patients based on race or ethnicity," said Hayley Gershengorn, M.D., associate professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine. "To examine that issue, we analyzed over a thousand medical records from two academic hospitals where University of Miami faculty see patients and found no disparities ...
2021-03-19
In-school COVID-19 transmission is rare - even among close school contacts of those who test positive for the virus - when schools heed public health precautions such as mandatory masking, social distancing and frequent hand-washing, according to results of a pilot study in Missouri aimed at identifying ways to keep elementary and secondary schools open and safe during the pandemic. A close contact is anyone who has been within 6 feet for more than 15 minutes in a 24-hour period with someone infected with COVID-19.
The study is part of a larger, ongoing collaboration involving the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, ...
2021-03-19
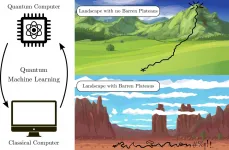
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 19, 2021--Many machine learning algorithms on quantum computers suffer from the dreaded "barren plateau" of unsolvability, where they run into dead ends on optimization problems. This challenge had been relatively unstudied--until now. Rigorous theoretical work has established theorems that guarantee whether a given machine learning algorithm will work as it scales up on larger computers.
"The work solves a key problem of useability for quantum machine learning. We rigorously proved the conditions under which certain architectures of variational quantum algorithms will or will not have barren plateaus as they are scaled up," said Marco Cerezo, lead author on the paper published in Nature Communications ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Gene therapy using 'zinc fingers' may help treat Alzheimer's disease, animal study shows
Treatment involving a single injection has long-lasting effects