Covid-19 pandemic severely impacts mental health of young people
2021-03-22
(Press-News.org) The Covid-19 pandemic severely impacted the mental health of young people, with increased levels of clinical depression being identified, a new study published in the journal Psychiatry Research reports. A decrease in alcohol consumption was also identified amongst young people during the pandemic.
During this unique study researchers from the University of Surrey surveyed 259 young people pre- pandemic (autumn 2019) and in the midst of initial lockdown measures (May/June 2020) on their levels of depression, anxiety, wellbeing, alcohol use and sleep quality.
Researchers found evidence of a substantial impact on the mental health of these young adults due to the Covid-19 pandemic, with a significant rise in depression symptoms and a reduction in overall wellbeing during lockdown compared to the previous autumn. Levels of clinical depression in those surveyed were found to have more than doubled, rising from 14.9 per cent in autumn 2019 to 34.7 per cent in May/June 2020.
Sleep quality was not seen to decline in the overall sample but, importantly, a correlation was seen between the rise in depression and lower sleep quality under lockdown. Also of concern, researchers identified a significant shift towards 'eveningness' (a preference to go to sleep and wake later), which has previously been associated with higher levels of anxiety and a greater prevalence of minor psychiatric disorders.
Interestingly, despite reports of rising worldwide sales of alcohol during the first lockdown, researchers identified a significant decrease in alcohol consumption amongst the group that could be attributed to social restrictions in place during this period. Researchers were encouraged by this finding as it suggests that young people were not using alcohol as a coping strategy during that time.
Findings from this study highlight the substantial impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on young people's mental health. The link to sleep quality could help inform strategies to support their wellbeing as the Covid-19 situation continues to evolve.
Dr Simon Evans, Lecturer in Neuroscience at the University of Surrey, said: "For many years there has been a rise in the number of young people experiencing problems with their mental health, and it is concerning to find that this has been significantly exacerbated due to Covid-19. Supporting the mental health of young people and ensuring they can access the support they need is vital to ensure their overall wellbeing. As social restrictions continue in response to the pandemic, it is crucial that we take steps to protect their mental health."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-22
Research has found that experiencing a traumatic event at close quarters changes people's political attitudes. However, in the case of the 2017 terrorist attack in Stockholm, proximity to the attack had no additional political significance. Research from the University of Gothenburg shows that Swedes' attitudes toward terrorism-related questions were affected equally, regardless of whether they happened to be close to the attack.
On 7 April 2017, Rakhmat Akilov stole a truck and ran down multiple people on Drottninggatan, a street in central Stockholm. Five people died, fifteen were injured and many people witnessed ...
2021-03-22
A study which looked at activity levels before and during the COVID-19 pandemic has found lockdown restrictions significantly reduced light activity associated with socialising and work.
The study, published recently in BMJ Neurology and led by King's College London, examined how activity levels changed in study participants with muscular dystrophy and other inheritable myopathies. The sample included people with a range of physical abilities, from highly independent to assisted mobility, including 41 wheelchair users, who are often underrepresented in research. However, the authors say the findings are likely to be relevant to adults of various ...
2021-03-22
The excavation of shell middens off two sites in the Gulf of Mexico and Northern Europe dating back to when the seabed was dry land thousands of years ago, reveal how they can offer new ground-breaking insights into the hidden history of submerged landscapes.
An international team of archaeologists from Moesgaard Museum (Denmark), the University Of Georgia (USA), the University of York (UK) Flinders University and James Cook University partnered to excavate two sites containing shell middens in the Gulf of Mexico and Eastern Jutland in Denmark in 2018, showing that middens can be ...
2021-03-22
Crystals inherently possess imperfections. Vacancies, as the simplest form of point defects, significantly alter the optical, thermal, and electrical properties of materials. Well-known examples include colour centres in many gemstones, the nitrogen-vacancy centre in diamond, vacancy migration in solid-state batteries, and the metal-insulator transition in phase-change materials. The vacancies in these cases are in frame-works with no or weak interactions. However, the role of vacancies in strongly correlated materials is thus far unclear due to the lack of an ideal prototype.
Strongly ...
2021-03-22
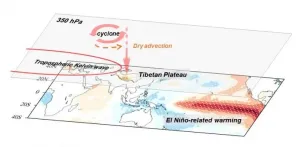
El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a recurring climate phenomenon involving changes in the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. It is one of the most important climate perturbations on Earth because it can change the global atmospheric circulation, which in turn, influences temperature and precipitation across the globe. Scientists have found ENSO has an impact on hydroclimate over the Tibetan Plateau but how it works, or its physical mechanism, remains unclear.
In a recently published research article in Journal of Climate, Shuai Hu, Tianjun Zhou and Bo Wu from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, explored the dynamical processes that ...
2021-03-22
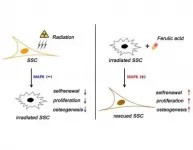
Durham, NC - The standard of treatment for bone tumors is often two-fold: surgery to remove the cancerous section followed by radiation therapy to ensure all the cancerous cells have been killed off. This is an effective way to defeat bone tumors; however, it often results in large bone defects and hampers wound healing because of extensive tissue cutoff and irradiation-induced tissue damage. A new study published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine demonstrates how stem cells primed with ferulic acid can repair such bone damage and how this occurs. The information this study provides could aid in the development of new treatments for irradiated bone injuries.
Heng Zhu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Beijing Institute of ...
2021-03-22
As World Water Day is observed around the globe, new research from UBC Okanagan suggests a systematic approach to forest and water supply research may yield an improved assessment and understanding of connections between the two.
Healthy forests play a vital role in providing a clean, stable water supply, says eco-hydrologist Dr. Adam Wei.
Acting as natural reservoirs, forests in watersheds release and purify water by slowing erosion and delaying its release into streams. But forests are changing--in part because of human activity--and that's having an impact on forests' interaction with hydrological ...
2021-03-22
Latino undergraduate male college students are involved in many leadership roles, yet how this leadership evolves in higher education has been understudied. Researchers from Florida Atlantic University in collaboration with San Diego State University and Texas A&M University explored how Latino male college students make meaning of their masculinity and how this meaning shapes their understanding and performance of leadership.
The study published in the International Journal of Leadership Education, utilized a qualitative method to delve deep into the understandings of the masculinities, gender socialization, leadership and transfer experiences of 34 Latino undergraduate male students. Using a philosophical approach, the researchers ...
2021-03-22
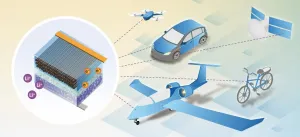
Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology have produced a structural battery that performs ten times better than all previous versions. It contains carbon fibre that serves simultaneously as an electrode, conductor, and load-bearing material. Their latest research breakthrough paves the way for essentially 'massless' energy storage in vehicles and other technology.
The batteries in today's electric cars constitute a large part of the vehicles' weight, without fulfilling any load-bearing function. A structural battery, on the other hand, is one that works as both a power source and as part of the structure - for example, in a car body. This is termed 'massless' energy storage, because in essence the battery's weight vanishes when it becomes part of ...
2021-03-22
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this review article the authors Oliver K. Semisch-Dieter, Andy H. Choi and Martin P. Stewart from the University of Technology Sydney, Ultimo, NSW, Australia discuss the use of biomaterials in dental implants.
Biomaterials have become essential for modern implants. A suitable implant biomaterial integrates into the body to perform a key function, whilst minimizing negative immune response. Focusing on dentistry, the use of dental implants for tooth replacement requires a balance between bodily response, mechanical structure and performance, and aesthetics. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Covid-19 pandemic severely impacts mental health of young people