Catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol: Low temperature, high efficiency, and long working time
2021-03-22
(Press-News.org) Efficient conversion of CO2 is strategically significant for alleviating the energy crisis and achieving the goal of carbon neutrality. One promising conversion route is the hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol using a renewable energy-based "green hydrogen" source.
Traditional metal oxide catalysts for this reaction typically require a high temperature (>300 oC), which tends to promote undesired reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) side reactions, thus producing a large amount of CO as the by-product.
Introduction of transition metal components onto metal oxides can promote the activation of H2, thereby reducing the reaction temperature, but this also facilitates excessive hydrogenation of CO2 to CH4, leading to lowered methanol selectivity. Further improvement of the performance of conventional metal/metal oxide catalysts for low-temperature CO2 hydrogenation to methanol is severely restricted by the tradeoff between their activity and selectivity.
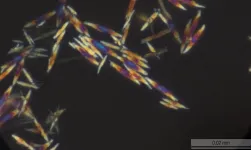
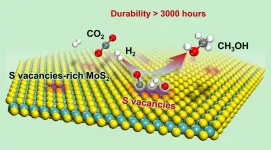
Recently, a group led by Prof. DENG Dehui from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. WANG Ye from Xiamen University, achieved for the first time low-temperature high-efficiency hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol, with a long working life over sulfur vacancy-rich few-layered MoS2, as well as remarkably higher activity and selectivity than those of the commercial Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst.
Their work which was published in Nature Catalysis, opens up a new way for the conversion of CO2 with low energy consumption and high efficiency.
They found that the sulfur vacancy-rich few-layered MoS2 could simultaneously activate and dissoCiate CO2 and H2 at low temperatures and even at room temperature, thereby facilitating the low-temperature hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol with high activity and selectivity.
In addition, they found that the RWGS reaction and excessive hydrogenation of methanol to CH4 were effectively suppressed. At 180 oC, 94.3% methanol selectivity for a CO2 conversion of 12.5% was achieved over the catalyst; this result was better than that obtained with the commercial Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst and previously reported catalysts.
The activity and selectivity were steadily maintained for over 3000 hours over the MoS2 catalyst, rendering it a promising candidate for industrial applications. In situ characterizations combined with theoretical calculations demonstrated that the in-plane sulfur vacancies on MoS2 were the active centers for catalyzing the highly selective hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol.
"This work reveals the potential of in-plane vacancies in two-dimensional materials for catalysis and provides a novel strategy for the development of new catalysts to be used in CO2 hydrogenation" said Prof. DENG.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-22
Physicians across the country have analyzed the emerging scientific data about the long-term effects of COVID-19, creating an initial knowledge base about the clinical experiences of so-called "long-haulers" - patients with COVID-19 who experience prolonged symptoms and/or the emergence of new ones well after the initial viral infection has resolved. A comprehensive review published today in Nature Medicine offers an initial glimpse of the multi-organ effects of long-term COVID-19 and suggests a framework for the care of COVID-19 long-haulers through dedicated, multidisciplinary clinics.
"It was important to respond to our patients' concerns and pay close attention to the symptoms they were experiencing beyond the acute phase of COVID-19," said Kartik Sehgal, MD, a lead ...
2021-03-22
Oncotarget published "Predictors of immunotherapy benefit in Merkel cell carcinoma" which reported that the authors retrospectively analyzed electronic health records and next-generation sequencing data of 45 patients treated at our institution from 2013 to 2020 to understand clinical and genomic correlates of benefit from immunotherapy.
They reported that their cohort predominantly included individuals with stage III disease at primary disease diagnosis and individuals with stage IV disease at recurrent/metastatic disease diagnosis.
Less advanced stages at primary disease diagnosis and shorter disease-free interval between completion of initial treatment and recurrence were each associated with greater odds of response.
Single-nucleotide ...
2021-03-22
Oncotarget published "Cytogenetic and molecular landscape and its potential clinical significance in Hispanic CMML patients from Puerto Rico" which reported that one hundred and eleven Hispanic CMML patients from Puerto Rico were diagnosed in our institute from 2009 to 2018. Karyotypes were available in one hundred and seven patients.
Compared to previously published data, Hispanic CMML patients in this study had significantly lower rates of overall cytogenetic abnormalities and trisomy 8.
Among one hundred and eleven Hispanic CMML patients, 40-gene myeloid molecular profile tests were performed in fifty-six CMML patients.
Previous studies indicated that mutated ASXL1, DNMT3A, NRAS, RUNX1, and SETBP1 may associate with an unfavorable prognosis ...
2021-03-22
Oncotarget published "Ibuprofen disrupts a WNK1/GSK3β/SRPK1 protein complex required for expression of tumor-related splicing variant RAC1B in colorectal cells" which reported that although the molecular mechanism behind the antitumor properties of NSAIDs has been largely attributed to inhibition of cyclooxygenases , several studies have shown that the chemopreventive properties of ibuprofen also involve multiple COX-independent effects.
One example is its ability to inhibit the alternative splicing event generating RAC1B, which is overexpressed in a specific subset ...
2021-03-22
Aging-US published "Aging and rejuvenation - a modular epigenome model" which reported that the view of aging has evolved in parallel with the advances in biomedical sciences.
Long considered as an irreversible process where interventions were only aimed at slowing down its progression, breakthrough discoveries like animal cloning and cell reprogramming have deeply changed our understanding of postnatal development, giving rise to the emerging view that the epigenome is the driver of aging. The idea was significantly strengthened by the converging discovery that DNA methylation at specific CpG sites could be used as a highly accurate biomarker of age defined by an algorithm known as the Horvath clock (also published in Aging-US here).
It was at this point ...
2021-03-22
Having the right tool for the job makes the job a lot easier, less expensive and faster. Chemical engineering researchers have now developed a virtual laboratory that can be used to determine the artificial intelligence (AI) tools best suited for addressing various chemical synthesis challenges in flow chemistry systems.
"Autonomous systems have tremendous potential for accelerating chemical R&D and manufacturing, but they are not in widespread use yet," says Milad Abolhasani, corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of chemical engineering at North Carolina State University. "These systems face two kinds of ...
2021-03-22
Scientists from MIPT and ITMO University and their colleagues have studied the formation and growth of crystals from simple organic molecules into large associations. These experiments will help create capsules for targeted drug delivery to specific tissues in the human body. The scientific paper was published in the journal Crystal Growth & Design.
Melamine cyanurate consists of melamine, colourless crystals, and cyanuric acid, whose molecules associate in a similar way to DNA formation. The various studies associated with it could be useful ...
2021-03-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio - As psychedelics gain ground as a potential therapy for mental health disorders, there remains a pressing concern that patients in clinical trials may have adverse effects to the drugs.
New research identifies personality traits that have been associated with positive and negative experiences on psychedelics in previous studies, information that could help predict how future clinical trial participants will respond to the drugs.
The findings suggest that people more open to new experiences and willing to surrender to the unknown may be best positioned to have a positive experience on psychedelics, and individuals who tend to be preoccupied or apprehensive could be more likely to have a ...
2021-03-22
ITHACA, N.Y. - As the COVID-19 pandemic took hold in 2020, the list of things people could not do grew increasingly long.
But while going to the office, attending live events and gathering with large groups of friends became difficult or impossible, other activities grew in popularity - including online learning.
Drawing on records from DataCamp, an online platform tailored toward programming skills, a research team at Cornell University and Arizona State University used U.S. states' staggered adoption of nonessential business closures (NBC) to estimate their effects on the demand for online learning. The gradual closure of businesses across the U.S. gave the researchers a way to make a case for the cause and effect of NBC on increased engagement with the DataCamp ...
2021-03-22
Aging-US published "Impact of adiposity on muscle function and clinical events among elders with dynapenia, presarcopenia and sarcopenia: a community-based cross-sectional study" which reported that low muscle function determined unfavorable clinical outcome than low muscle mass; nevertheless, comparison of detrimental parameters among dynapenia, presarcopenia and sarcopenia was sparse.
The authors hypothesized that adiposity is implicated in low muscle function related adverse events.
Associations of different obesity parameters, metabolic syndrome and fall among the groups were analyzed.
Among 765 participants, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol: Low temperature, high efficiency, and long working time