Uniform drying time for goldenseal to enhance medicinal qualities of forest herb
2021-03-22
(Press-News.org) Developing a standardized drying protocol for goldenseal could lead to more predictable health applications and outcomes by preserving the alkaloids found in the plant, which is native to Appalachia, according to Penn State researchers, who conducted a new study of the medicinal forest herb.
The roots and rhizomes of goldenseal -- Hydrastis canadensis -- have been used for hundreds of years as a source of antimicrobials and compounds to treat intestinal ailments, noted study co-author Eric Burkhart, associate teaching professor, ecosystem science and management.
"Three alkaloids -- berberine, hydrastine and canadine -- are recognized as the major bioactive constituents in goldenseal," said Burkhart, who also is program director, Appalachian botany and ethnobotany, at Shaver's Creek Environmental Center. "One important postharvest processing step for goldenseal is drying. However, before this study it was not known how drying temperature influences the concentrations of these alkaloids."
To investigate this question, researchers removed goldenseal samples from three plant colonies within a wild population located in central Pennsylvania. Fourteen "ramets," or bunches, were harvested from each plot in early April while plants were dormant.
Lead researcher Grady Zuiderveen, doctoral student in ecosystem science and management, freeze-dried or air-dried goldenseal samples at six temperatures, ranging from 80 to 130 degrees Fahrenheit, to determine the relationship between drying temperature and alkaloid content in the rhizome and roots.
In findings recently published in Hortscience, high performance liquid chromatography analysis showed that berberine and hydrastine levels were unaffected by drying temperature, while canadine levels decreased as temperature increased. On average, the level of canadine dropped by slightly more than half when samples were freeze-dried and fell by nearly a third when dried at 130 F.
While canadine is the least abundant alkaloid of the three, it is known to have key antibacterial properties, Zuiderveen pointed out, so developing a more standardized drying protocol for goldenseal could lead to a more predictable phytochemical profile.
"This work is important because canadine has been found to have significant activity against numerous strains of bacteria, and in previous research it was the only one of the three major alkaloids found to be active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus," he said. "Also, canadine possesses significant antioxidant properties and has been identified as effective at strengthening the immune system."
INFORMATION:
Joshua Lambert, associate professor of food science, also contributed to the study.
The Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources' Wild Resources Conservation Program funded this research.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-22
Antibody injections are a highly desirable treatment for people with chronic diseases such as cancer, psoriasis, Crohn's disease and arthritis. And recently, antibodies have been in the news as a promising treatment for severe cases of COVID-19.
But the costly, time-consuming manufacturing process to produce antibodies prevents these treatments from being accessible to most patients.
Andrew Zydney, Bayard D. Kunkle Chair and professor of chemical engineering at Penn State, has identified a new method to manufacture antibodies, which could drive down the production cost. His research results were recently published in Biotechnology Progress.
"If you look at the top 10 best-selling medications, by annual sales, eight ...
2021-03-22
A new type of rock created during large and exceptionally hot volcanic eruptions has been discovered beneath the Pacific Ocean.
An international team of researchers including the University of Leeds unearthed the previously unknown form of basalt after drilling through the Pacific ocean floor.
The discovery suggests that ocean floor eruptions sourced in the Earth's mantle were even hotter and more voluminous than previously thought. Report co-author is Dr Ivan Savov, of Leeds' Institute of Geophysics and Tectonics, in the university's School of Earth and Environment.
He said: "In an era when we rightly admire discoveries made through space exploration, our findings show there are still many discoveries still to make on our ...
2021-03-22
The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events like droughts and floods have taken a toll on the midwestern U.S. in recent years, putting a major strain on the region's farmers. From 2001 to 2010, the Federal Crop Insurance Program, a government program created to protect farmers from crop loss, covered $4.1 billion in damages; in 2011 alone, the program paid out $10.8 billion.
With the largest U.S. crop -- corn -- conservatively estimated to drop in yield anywhere from 20 to 80 percent due to extreme weather exacerbated by climate change, insurance claims may skyrocket to levels that may not be sustainable. But researchers from the Yale School of the Environment (YSE) found that by considering soil properties when determining insurance premiums ...
2021-03-22
Less than a decade after unveiling the "Map of Life," a global database that marks the distribution of known species across the planet, Yale researchers have launched an even more ambitious and perhaps important project -- creating a map of where life has yet to be discovered.
For Walter Jetz, a professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at Yale who spearheaded the Map of Life project, the new effort is a moral imperative that can help support biodiversity discovery and preservation around the world.
"At the current pace of global environmental change, there is no doubt that many species will go extinct before we have ever learned ...
2021-03-22
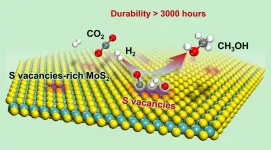
Efficient conversion of CO2 is strategically significant for alleviating the energy crisis and achieving the goal of carbon neutrality. One promising conversion route is the hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol using a renewable energy-based "green hydrogen" source.
Traditional metal oxide catalysts for this reaction typically require a high temperature (>300 oC), which tends to promote undesired reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) side reactions, thus producing a large amount of CO as the by-product.
Introduction of transition metal components onto metal oxides can promote the activation of H2, thereby reducing the reaction temperature, but this also facilitates excessive hydrogenation of CO2 to CH4, leading to lowered methanol selectivity. Further improvement of the performance ...
2021-03-22
Physicians across the country have analyzed the emerging scientific data about the long-term effects of COVID-19, creating an initial knowledge base about the clinical experiences of so-called "long-haulers" - patients with COVID-19 who experience prolonged symptoms and/or the emergence of new ones well after the initial viral infection has resolved. A comprehensive review published today in Nature Medicine offers an initial glimpse of the multi-organ effects of long-term COVID-19 and suggests a framework for the care of COVID-19 long-haulers through dedicated, multidisciplinary clinics.
"It was important to respond to our patients' concerns and pay close attention to the symptoms they were experiencing beyond the acute phase of COVID-19," said Kartik Sehgal, MD, a lead ...
2021-03-22
Oncotarget published "Predictors of immunotherapy benefit in Merkel cell carcinoma" which reported that the authors retrospectively analyzed electronic health records and next-generation sequencing data of 45 patients treated at our institution from 2013 to 2020 to understand clinical and genomic correlates of benefit from immunotherapy.
They reported that their cohort predominantly included individuals with stage III disease at primary disease diagnosis and individuals with stage IV disease at recurrent/metastatic disease diagnosis.
Less advanced stages at primary disease diagnosis and shorter disease-free interval between completion of initial treatment and recurrence were each associated with greater odds of response.
Single-nucleotide ...
2021-03-22
Oncotarget published "Cytogenetic and molecular landscape and its potential clinical significance in Hispanic CMML patients from Puerto Rico" which reported that one hundred and eleven Hispanic CMML patients from Puerto Rico were diagnosed in our institute from 2009 to 2018. Karyotypes were available in one hundred and seven patients.
Compared to previously published data, Hispanic CMML patients in this study had significantly lower rates of overall cytogenetic abnormalities and trisomy 8.
Among one hundred and eleven Hispanic CMML patients, 40-gene myeloid molecular profile tests were performed in fifty-six CMML patients.
Previous studies indicated that mutated ASXL1, DNMT3A, NRAS, RUNX1, and SETBP1 may associate with an unfavorable prognosis ...
2021-03-22
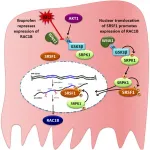
Oncotarget published "Ibuprofen disrupts a WNK1/GSK3β/SRPK1 protein complex required for expression of tumor-related splicing variant RAC1B in colorectal cells" which reported that although the molecular mechanism behind the antitumor properties of NSAIDs has been largely attributed to inhibition of cyclooxygenases , several studies have shown that the chemopreventive properties of ibuprofen also involve multiple COX-independent effects.
One example is its ability to inhibit the alternative splicing event generating RAC1B, which is overexpressed in a specific subset ...
2021-03-22
Aging-US published "Aging and rejuvenation - a modular epigenome model" which reported that the view of aging has evolved in parallel with the advances in biomedical sciences.
Long considered as an irreversible process where interventions were only aimed at slowing down its progression, breakthrough discoveries like animal cloning and cell reprogramming have deeply changed our understanding of postnatal development, giving rise to the emerging view that the epigenome is the driver of aging. The idea was significantly strengthened by the converging discovery that DNA methylation at specific CpG sites could be used as a highly accurate biomarker of age defined by an algorithm known as the Horvath clock (also published in Aging-US here).
It was at this point ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Uniform drying time for goldenseal to enhance medicinal qualities of forest herb