Electrode interphase formation
Anions and solvents direct nucleation and growth of the solid electrolyte interphase
2021-03-22
(Press-News.org) Batteries charge and recharge--apparently all thanks to a perfect interplay of electrode material and electrolyte. However, for ideal battery function, the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) plays a crucial role. Materials scientists have now studied nucleation and growth of this layer in atomic detail. According to the study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, the properties of anions and solvent molecules need to be well balanced.
In lithium-ion batteries, the SEI forms at the beginning of the first charging process, when a potential is applied. Elements from the electrolyte deposit on the graphite electrode and form a coating that soon covers the entire electrode. Only after this layer is completed, can the positive lithium ions intercalate in the electrode without exfoliating the electrode material.
Qiang Zhang and colleagues at Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, have now taken a closer look at the nucleation and growth of the SEI. The electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries contains lithium salt and a solvent. Strongly solvating solvents wrap the lithium ion, and the anions float freely. In contrast, weakly solvating electrolytes enable a closer attachment of the anions to the lithium ion. Here, the anions remain part of the inner solvation shell.
This inner solvation shell must be stripped off from the lithium to allow SEI formation and growth. The researchers demonstrated that the anions of the inner shell first adsorbed at the fresh electrode and then took up two electrons in an electrochemical reaction. This latter event triggered decomposition and nucleation of the SEI. The authors concluded that SEI formation mainly depended on how easily the anions can grab electrons and decompose compared with the solvent.
The scientists used electrochemical techniques and atomic force microscopy to investigate the crystal growth until completion of the layer. They found that a smooth layer only formed at low overpotentials. The solvent also influenced the overpotential. The authors also noted that solvents having a high affinity to the crystalline layer produced no overpotential at all.
They concluded that future designs of high-performance electrodes should focus more on the interplay between the negative ions of the lithium salt and the solvent. To allow a homogeneous inorganic, crystalline SEI to be formed, the anions should outcompete the solvent; they should more easily adsorb to the electrode surface and undertake electrochemical reactions. In addition, the decomposition products should be solid and insoluble, but still show a certain affinity to the solvent, the authors said.
INFORMATION:
About the Author
Dr. Qiang Zhang is a Professor at the Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China. He is interested in the design and development of advanced energy materials and related materials; especially those for the lithium-metal anodes, lithium-sulfur batteries, and emerging energy electrocatalysts.
http://www.chemeng.tsinghua.edu.cn/scholars/zhangqiang/Qiang-English.htm
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-22
Antibiotics have revolutionized the field of medicine by making it possible to treat most known microbial diseases today. However, their uncontrolled usage has led to the major global problem of antibiotic resistance. As we continue to exploit antibiotics, sometimes at doses much higher than needed, disease-causing bacteria are rapidly evolving defense strategies to evade them. These drug-resistant bacteria, also known as "superbugs," cause severe infections that are difficult to treat and can eventually be fatal.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a particularly vicious group of superbugs that have developed resistance to the antibiotic methicillin, is a major cause of hospital-acquired infections. Accurate and timely diagnosis ...
2021-03-22
Boulder, Colo., USA: Beneath the cold, dark depths of the Arctic ocean sit vast reserves of methane. These stores rest in a delicate balance, stable as a solid called methane hydrates, at very specific pressures and temperatures. If that balance gets tipped, the methane can get released into the water above and eventually make its way to the atmosphere. In its gaseous form, methane is one of the most potent greenhouse gases, warming the Earth about 30 times more efficiently than carbon dioxide. Understanding possible sources of atmospheric methane is critical for accurately predicting future climate change.
In the Arctic Ocean today, ice sheets exert pressure on the ground below them. That pressure diffuses ...
2021-03-22
Screenings for breast cancer and colon cancer dropped dramatically during the early months of the coronavirus pandemic, but use of the procedures returned to near-normal levels by the end of July 2020, according to a new study.
Analyzing insurance claims from more than 6 million Americans with private health coverage, researchers found that mammography rates among women aged 45 to 64 declined by 96% during March and April 2020 as compared to January and February.
Similarly, the weekly rate of colorectal cancer screenings among adults aged 45 to 64 and older declined by 95% during the period.
By the end of July 2020, however, the rate of mammograms among women had rebounded and was slightly higher than it had been before the pandemic was declared. The rate of colonoscopies also rebounded, ...
2021-03-22
Researchers at Trinity College Dublin have been shedding light on the enigmatic "spiders from Mars", providing the first physical evidence that these unique features on the planet's surface can be formed by the sublimation of CO2 ice.
Spiders, more formally referred to as araneiforms, are strange-looking negative topography radial systems of dendritic troughs; patterns that resemble branches of a tree or fork lightning. These features, which are not found on Earth, are believed to be carved into the Martian surface by dry ice changing directly from solid to gas (sublimating) in the spring. Unlike Earth, Mars' atmosphere comprises mainly of CO2 and as temperatures decrease in winter, this deposits onto the surface as CO2 ...
2021-03-22
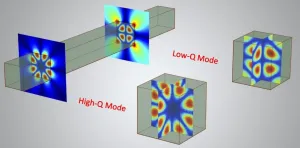
Optical resonators provide the foundation of modern photonics and optics. Thanks to its extreme energy confinement, the high-Q-factor optical resonator optimizes light-matter interaction and photonic device performance by enabling low-threshold laser and enhanced nonlinear harmonic generation.
Two typical structures, the photonic crystal cavity and the whispering gallery cavity, are frequently used to obtain extremely high-Q factors. However, these structures may require dimensions that are comparable to--or several times larger than--the operating wavelength. Whether there is a general way to find out all high-Q modes in a dielectric ...
2021-03-22
The tuberculosis (TB) burden in the WHO European Region as a whole is decreasing, and is down 19% overall for 2015-2019, according to the latest WHO/European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) report Tuberculosis surveillance and monitoring in Europe 2021 (2019 data).
Regional TB mortality has gone down, declining by 9.4% between 2018 and 2019. This is notably higher than the average global decline in TB mortality (3.7%) and enough to have reached the End TB Strategy milestone of a 35% reduction by 2020 compared to 2015.
However, TB is second only to COVID-19 as an infectious disease that kills, and drug resistance is a major concern. There are also worrying indications that the COVID-19 pandemic may stall progress or cause significant setbacks in the fight against TB.
The ...
2021-03-22
Developing a standardized drying protocol for goldenseal could lead to more predictable health applications and outcomes by preserving the alkaloids found in the plant, which is native to Appalachia, according to Penn State researchers, who conducted a new study of the medicinal forest herb.
The roots and rhizomes of goldenseal -- Hydrastis canadensis -- have been used for hundreds of years as a source of antimicrobials and compounds to treat intestinal ailments, noted study co-author Eric Burkhart, associate teaching professor, ecosystem science ...
2021-03-22
Antibody injections are a highly desirable treatment for people with chronic diseases such as cancer, psoriasis, Crohn's disease and arthritis. And recently, antibodies have been in the news as a promising treatment for severe cases of COVID-19.
But the costly, time-consuming manufacturing process to produce antibodies prevents these treatments from being accessible to most patients.
Andrew Zydney, Bayard D. Kunkle Chair and professor of chemical engineering at Penn State, has identified a new method to manufacture antibodies, which could drive down the production cost. His research results were recently published in Biotechnology Progress.
"If you look at the top 10 best-selling medications, by annual sales, eight ...
2021-03-22
A new type of rock created during large and exceptionally hot volcanic eruptions has been discovered beneath the Pacific Ocean.
An international team of researchers including the University of Leeds unearthed the previously unknown form of basalt after drilling through the Pacific ocean floor.
The discovery suggests that ocean floor eruptions sourced in the Earth's mantle were even hotter and more voluminous than previously thought. Report co-author is Dr Ivan Savov, of Leeds' Institute of Geophysics and Tectonics, in the university's School of Earth and Environment.
He said: "In an era when we rightly admire discoveries made through space exploration, our findings show there are still many discoveries still to make on our ...
2021-03-22
The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events like droughts and floods have taken a toll on the midwestern U.S. in recent years, putting a major strain on the region's farmers. From 2001 to 2010, the Federal Crop Insurance Program, a government program created to protect farmers from crop loss, covered $4.1 billion in damages; in 2011 alone, the program paid out $10.8 billion.
With the largest U.S. crop -- corn -- conservatively estimated to drop in yield anywhere from 20 to 80 percent due to extreme weather exacerbated by climate change, insurance claims may skyrocket to levels that may not be sustainable. But researchers from the Yale School of the Environment (YSE) found that by considering soil properties when determining insurance premiums ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Electrode interphase formation
Anions and solvents direct nucleation and growth of the solid electrolyte interphase