(Press-News.org) Researchers at Trinity College Dublin have been shedding light on the enigmatic "spiders from Mars", providing the first physical evidence that these unique features on the planet's surface can be formed by the sublimation of CO2 ice.
Spiders, more formally referred to as araneiforms, are strange-looking negative topography radial systems of dendritic troughs; patterns that resemble branches of a tree or fork lightning. These features, which are not found on Earth, are believed to be carved into the Martian surface by dry ice changing directly from solid to gas (sublimating) in the spring. Unlike Earth, Mars' atmosphere comprises mainly of CO2 and as temperatures decrease in winter, this deposits onto the surface as CO2 frost and ice.
The Trinity team, along with colleagues at Durham University and the Open University, conducted a series of experiments funded by the Irish Research Council and Europlanet at the Open University Mars Simulation Chamber, under Martian atmospheric pressure (in picture above), in order to investigate whether patterns similar to Martian spiders could form by dry ice sublimation.
Its findings are detailed in a paper recently published in the Nature Journal, Scientific Reports.
Dr Lauren McKeown, who led this work during her PhD at Trinity and is now at the Open University, said:
"This research presents the first set of empirical evidence for a surface process that is thought to modify the polar landscape on Mars. Kieffer's hypothesis [explained below] has been well accepted for over a decade, but until now, it has been framed in a purely theoretical context.
"The experiments show directly that the spider patterns we observe on Mars from orbit can be carved by the direct conversion of dry ice from solid to gas. It is exciting because we are beginning to understand more about how the surface of Mars is changing seasonally today."
The research team drilled holes in the centres of CO2 ice blocks and suspended them with a claw similar to those found in arcades, above granular beds of different grain sizes. They lowered the pressure inside a vacuum chamber to Martian atmospheric pressure (6mbar) and then used a lever system to place the CO2 ice block on the surface.
They made use of an effect known as the Leidenfrost Effect, whereby if a substance comes in contact with a surface much hotter than its sublimation point, it will form a gaseous layer around itself. When the block reached the sandy surface, CO2 turned directly from solid to gas and material was seen escaping through the central hole in the form of a plume.
In each case, once the block was lifted, a spider pattern had been eroded by the escaping gas. The spider patterns were more branched when finer grain sizes were used and less branched when coarser grain sizes were used. This is the first set of empirical evidence for this extant surface process.
Dr Mary Bourke, of Trinity's Department of Geography, who supervised the PhD research, said:
"This innovative work supports the emergent theme that the current climate and weather on Mars has an important influence not only on dynamic surface processes, but also for any future robotic and/or human exploration of the planet."
The main hypothesis proposed for spider formation (Kieffer's hypothesis) suggests that in spring, sunlight penetrates this translucent ice and heats the terrain beneath it. The ice will sublimate from its base, causing pressure to build up and eventually the ice will rupture, allowing pressurised gas to escape through a crack in the ice. The paths of the escaping gas will leave behind the dendritic patterns observed on Mars today and the sandy/dusty material will be deposited on top of the ice in the form of a plume.
However, until now, it has not been known if such a theoretical process is possible and this process has never been directly observed on Mars.
Additionally, the researchers observed that when CO2 blocks were released and allowed to sublimate within the sand bed, sublimation was much more vigorous than expected and material was thrown all over the chamber.
This observation will be useful in understanding models of other CO2 sublimation-related processes on Mars, such as the formation of lateral Recurring Diffusive Flows surrounding linear dune gullies on Mars.
The methodology used can be refocused to study the geomorphic role of CO2 sublimation on other active Martian surface feature formation - and indeed, can pave the way for further research on sublimation processes on other planetary bodies with no/scant atmospheres like Europa or Enceladus.
INFORMATION:
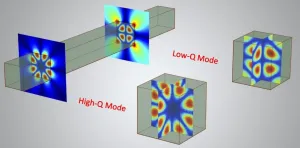
Optical resonators provide the foundation of modern photonics and optics. Thanks to its extreme energy confinement, the high-Q-factor optical resonator optimizes light-matter interaction and photonic device performance by enabling low-threshold laser and enhanced nonlinear harmonic generation.
Two typical structures, the photonic crystal cavity and the whispering gallery cavity, are frequently used to obtain extremely high-Q factors. However, these structures may require dimensions that are comparable to--or several times larger than--the operating wavelength. Whether there is a general way to find out all high-Q modes in a dielectric ...
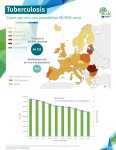
The tuberculosis (TB) burden in the WHO European Region as a whole is decreasing, and is down 19% overall for 2015-2019, according to the latest WHO/European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) report Tuberculosis surveillance and monitoring in Europe 2021 (2019 data).
Regional TB mortality has gone down, declining by 9.4% between 2018 and 2019. This is notably higher than the average global decline in TB mortality (3.7%) and enough to have reached the End TB Strategy milestone of a 35% reduction by 2020 compared to 2015.
However, TB is second only to COVID-19 as an infectious disease that kills, and drug resistance is a major concern. There are also worrying indications that the COVID-19 pandemic may stall progress or cause significant setbacks in the fight against TB.
The ...
Developing a standardized drying protocol for goldenseal could lead to more predictable health applications and outcomes by preserving the alkaloids found in the plant, which is native to Appalachia, according to Penn State researchers, who conducted a new study of the medicinal forest herb.
The roots and rhizomes of goldenseal -- Hydrastis canadensis -- have been used for hundreds of years as a source of antimicrobials and compounds to treat intestinal ailments, noted study co-author Eric Burkhart, associate teaching professor, ecosystem science ...
Antibody injections are a highly desirable treatment for people with chronic diseases such as cancer, psoriasis, Crohn's disease and arthritis. And recently, antibodies have been in the news as a promising treatment for severe cases of COVID-19.
But the costly, time-consuming manufacturing process to produce antibodies prevents these treatments from being accessible to most patients.
Andrew Zydney, Bayard D. Kunkle Chair and professor of chemical engineering at Penn State, has identified a new method to manufacture antibodies, which could drive down the production cost. His research results were recently published in Biotechnology Progress.
"If you look at the top 10 best-selling medications, by annual sales, eight ...
A new type of rock created during large and exceptionally hot volcanic eruptions has been discovered beneath the Pacific Ocean.
An international team of researchers including the University of Leeds unearthed the previously unknown form of basalt after drilling through the Pacific ocean floor.
The discovery suggests that ocean floor eruptions sourced in the Earth's mantle were even hotter and more voluminous than previously thought. Report co-author is Dr Ivan Savov, of Leeds' Institute of Geophysics and Tectonics, in the university's School of Earth and Environment.
He said: "In an era when we rightly admire discoveries made through space exploration, our findings show there are still many discoveries still to make on our ...
The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events like droughts and floods have taken a toll on the midwestern U.S. in recent years, putting a major strain on the region's farmers. From 2001 to 2010, the Federal Crop Insurance Program, a government program created to protect farmers from crop loss, covered $4.1 billion in damages; in 2011 alone, the program paid out $10.8 billion.
With the largest U.S. crop -- corn -- conservatively estimated to drop in yield anywhere from 20 to 80 percent due to extreme weather exacerbated by climate change, insurance claims may skyrocket to levels that may not be sustainable. But researchers from the Yale School of the Environment (YSE) found that by considering soil properties when determining insurance premiums ...
Less than a decade after unveiling the "Map of Life," a global database that marks the distribution of known species across the planet, Yale researchers have launched an even more ambitious and perhaps important project -- creating a map of where life has yet to be discovered.
For Walter Jetz, a professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at Yale who spearheaded the Map of Life project, the new effort is a moral imperative that can help support biodiversity discovery and preservation around the world.
"At the current pace of global environmental change, there is no doubt that many species will go extinct before we have ever learned ...
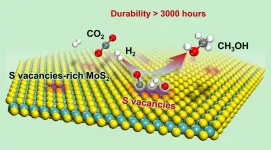
Efficient conversion of CO2 is strategically significant for alleviating the energy crisis and achieving the goal of carbon neutrality. One promising conversion route is the hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol using a renewable energy-based "green hydrogen" source.
Traditional metal oxide catalysts for this reaction typically require a high temperature (>300 oC), which tends to promote undesired reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) side reactions, thus producing a large amount of CO as the by-product.
Introduction of transition metal components onto metal oxides can promote the activation of H2, thereby reducing the reaction temperature, but this also facilitates excessive hydrogenation of CO2 to CH4, leading to lowered methanol selectivity. Further improvement of the performance ...
Physicians across the country have analyzed the emerging scientific data about the long-term effects of COVID-19, creating an initial knowledge base about the clinical experiences of so-called "long-haulers" - patients with COVID-19 who experience prolonged symptoms and/or the emergence of new ones well after the initial viral infection has resolved. A comprehensive review published today in Nature Medicine offers an initial glimpse of the multi-organ effects of long-term COVID-19 and suggests a framework for the care of COVID-19 long-haulers through dedicated, multidisciplinary clinics.
"It was important to respond to our patients' concerns and pay close attention to the symptoms they were experiencing beyond the acute phase of COVID-19," said Kartik Sehgal, MD, a lead ...
Oncotarget published "Predictors of immunotherapy benefit in Merkel cell carcinoma" which reported that the authors retrospectively analyzed electronic health records and next-generation sequencing data of 45 patients treated at our institution from 2013 to 2020 to understand clinical and genomic correlates of benefit from immunotherapy.
They reported that their cohort predominantly included individuals with stage III disease at primary disease diagnosis and individuals with stage IV disease at recurrent/metastatic disease diagnosis.
Less advanced stages at primary disease diagnosis and shorter disease-free interval between completion of initial treatment and recurrence were each associated with greater odds of response.
Single-nucleotide ...