New diagnostic tool for the management of patients with sepsis
Dipeptidyl Peptidase 3 (DPP3)
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) Hennigsdorf/Berlin, Germany, March 23, 2021 - Diagnostics company SphingoTec GmbH ("SphingoTec") announced today the first published data (1) on the biomarker DPP3 that can predict the evolution of organ function and survival in septic patients. Measured on top of routinely used standard parameters, such as Lactate and Procalcitonin, DPP3 is an early indicator of short-term outcomes and patient severity. Sepsis is a medical emergency caused by a dysregulated host response to an infection, with mortality rates increasing rapidly for each hour that appropriate treatment is delayed (2). The rapid evolution of sepsis into its severe form, septic shock, raises the need for more precise and faster testing to support better clinical decision-making.
DPP3 is an enzyme at the core of a newly discovered disease mechanism responsible for cardiovascular depression and short-term organ failure in critically ill patients. Although intracellular DPP3 is involved in normal metabolic processes (3), massive cell death leads to DPP3 release into the bloodstream. Circulating DPP3 inactivates Angiotensin II, a hormone regulating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which ultimately controls hemodynamics (4,5). Angiotensin II depletion leads to cardiovascular depression (6,7,9,10) and reduced vascular tone (6,8), a hemodynamic instability that quickly escalates in multiple organ failure. DPP3 was already shown to add value in various critical care settings such as cardiogenic shock (7,9) and burn shock (10).
The data from the prospective observational multi-center AdrenoOSS-1 study enrolling about 600 patients with sepsis and septic shock have shown that DPP3 levels can predict multiple short-term organ failure and the need for organ support therapies in this population (1). High or increasing DPP3 blood levels precede organ injury and predict the need for vasopressor/inotropic use, mechanical ventilation, and renal replacement therapy. DPP3 blood levels also reflect patient severity, with septic shock patients having a significantly higher DPP3 concentration than patients with severe sepsis (1,3). The study data further show that low or decreasing levels of DPP3 in the first 24 hours of ICU admission predict an improvement of organ function and better outcomes. The dynamic nature of the biomarker can guide intensivists in the early management of septic shock patients.
Dr. Andreas Bergmann, founder of various companies, where new tools to fight sepsis mortality are developed, and CEO of critical care diagnostics company SphingoTec commented: "This newly discovered biomarker makes it easy to identify a distinct pathophysiological mechanism leading to mortality in sepsis and uncovers the etiology of clinical symptoms. The published data show that measuring DPP3 levels add value in the clinical practice by early revealing organ injury and adding information on top of standard parameters. This can help guide intensivists in the early management of septic patients."
The in vitro diagnostic test for DPP3 is available as a microtiter plate as well as a near-patient rapid test (IB10 sphingotest® DPP3). SphingoTec has made the test available for the critical care community to further assess the clinical utility of the DPP3 biomarker in acute care settings.
INFORMATION:
References
1. Blet et al (2021), Monitoring Circulating dipeptidyl peptidase 3 (DPP3) predicts improvement of organ failure and survival in sepsis: a prospective observational multinational study
2. Bai et al (2014) Early versus delayed administration of norepinephrine in patients with septic shock Crit Care..doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-014-0532-y
3. Rehfeld et al (2019). Novel Methods for the Quantification of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 3 (DPP3) Concentration and Activity in Human Blood Samples. J Appl Lab Med. DOI: 10.1373/jalm.2018.027995
4. Picod et al (2020), Alteration of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Shock: Role of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase 3, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2020, DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202010-3873LE
5. Jha et al (2020), Dipeptidyl peptidase 3 modulates the renin-angiotensin system in mice, J Biol Chem., DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014183.
6. Deniau et al.(2020) Inhibition of circulating dipeptidyl-peptidase 3 restores cardiac function in a sepsis-induced model in rats: A proof of concept study. PloS One. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0238039
7. Takagi et al.(2019) Circulating dipeptidyl peptidase 3 and alteration in haemodynamics in cardiogenic shock: results from the OptimaCC trial. Eur J Heart Fail., DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.1600
8. van Lier (2020), Promotion of vascular integrity in sepsis through modulation of bioactive adrenomedullin and dipeptidyl peptidase 3, J. Intern. Med., DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13220
9. Deniau et al. (2019), Circulating dipeptidyl peptidase is a myocardial depressant factor: dipeptidyl peptidase 3 inhibition rapidly and sustainably improves haemodynamics. Eur J Heart Fail. DOI : 10.1002/ejhf.1601
10. Dépret et al.(2020) Circulating dipeptidyl peptidase-3 at admission is associated with circulatory failure, acute kidney injury and death in severely ill burn patients. Crit Care , DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-02888-5
About SphingoTec
SphingoTec GmbH ("SphingoTec"; Hennigsdorf near Berlin, Germany) develops and markets innovative in vitro diagnostic (IVD) tests for novel and proprietary biomarkers for the diagnosis, prediction and monitoring of acute medical conditions, such as sepsis, acute heart failure, circulatory shock, and acute kidney injury in order to support patient management and provide guidance for treatment strategies. SphingoTec's proprietary biomarker portfolio includes bioactive Adrenomedullin (bio-ADM), a biomarker for real-time assessment of endothelial function in conditions like sepsis or congestive heart failure, Proenkephalin (penKid), a biomarker for real-time assessment of kidney function, and Dipeptidyl Peptidase 3 (DPP3), a biomarker for cardiac depression. IVD tests for SphingoTec's proprietary biomarkers are made available as sphingotest® microtiter plate tests as well as point-of-care tests on the Nexus IB10 immunoassay platform by SphingoTec's subsidiary Nexus Dx Inc. (San Diego, CA, USA) alongside a broad menu of established and commonly used tests for acute and critical care. http://www.sphingotec.com
About DPP3
sphingotest® DPP3 measures Dipeptidyl peptidase 3 an active enzyme which, when released into the blood, inactivates Angiotensin II, a hormone that is important for heart function. The depletion of Angiotensin II affects the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), ultimately leading to cardiovascular depression and reduced vascular tone, a deadly combination in need of selective treatment strategies. The DPP3 release is a newly identified disease mechanism explaining short-term organ failure in critically ill patients. Early identification of DPP3 release may allow better patient stratification and earlier therapy escalation to improve outcomes.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-23
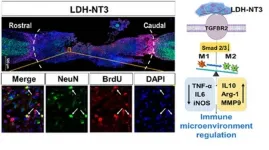
Researchers from the Department of Orthopedics of Tongji Hospital at Tongji University in Shanghai have successfully used a nanobiomaterial called layered double hydroxide (LDH) to inhibit the inflammatory environment surrounding spinal cord injuries in mice, accelerating regeneration of neurons and reconstruction of the neural circuit in the spine. The researchers were also able to identify the underlying genetic mechanism by which LDH works. This understanding should allow further modification of the therapy which, in combination with other elements, could finally produce a comprehensive, clinically applicable system for spinal cord injury relief in humans.
The ...
2021-03-23
Researchers at the University of Toronto have found that food industry interactions with government heavily outnumbered non-industry interactions on Bill S-228, also known as the Child Health Protection Act, which died in the Senate of Canada in 2019.
The researchers looked at more than 3,800 interactions, which included meetings, correspondence and lobbying, in the three years before the bill failed. They found that over 80 per cent were by industry, compared to public health or not-for-profit organizations.
They also found that industry accounted for over 80 per cent of interactions with the highest-ranking government offices, including elected parliamentarians and their staff and unelected ...
2021-03-23
BINGHAMTON, NY -- When it comes to local government, does the gender of a mayor or county executive matter in sustainability policymaking? Yes, but only in certain ways, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
Kristina Lambright, associate professor of public administration, and George Homsy, associate professor of public administration and director of the environmental studies program, explored the correlation between female leadership and local government adoption of sustainability policies in "Beyond community characteristics: a leader's gender and local government adoption of energy conservation practices and redistributive programmes," published recently ...
2021-03-23
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, have developed a novel type of thermometer that can simply and quickly measure temperatures during quantum calculations with extremely high accuracy. The breakthrough provides a benchmarking tool for quantum computing of great value - and opens up for experiments in the exciting field of quantum thermodynamics.
A key component in quantum computers are coaxial cables and waveguides - structures which guide waveforms, and act as the vital connection between the quantum processor, and the classical electronics which control it. Microwave pulses travel along the waveguides to the quantum processor, and are cooled ...
2021-03-23
Incorporating Black churches and clergy in COVID-19 vaccination education and distribution has been found to be an effective model in helping to increase vaccination delivery to historically at-risk populations in San Bernardino County, a study says.
Focused education efforts and an on-site mobile clinic in Black church parking lots resulted in the vaccinations of 417 people, 84% of whom were Black. The study also found an increase in Black attendance of mass vaccination clinics to 3.6% of total patients, up from 3%, in the week post-initiative.
Researchers at Loma Linda University School of Pharmacy published their findings on March 10 in The Lancet Global Health, ...
2021-03-23
Almost 90 percent of infectious travelers could be detected with rapid SARS-CoV-2 tests at the airport, and most imported infections could be prevented with a combination of pre-travel testing and a five-day post-travel quarantine that would only lift with a negative test result, according to a computer simulation by UC San Francisco researchers.
The study offers much-needed data to airlines and states that have struggled through a year of the pandemic with little guidance on how to enable safe travel.
The issue is becoming more pressing as states ...
2021-03-22
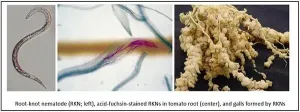
Root-knot nematodes (RKNs, Meloidogyne spp.) infect a broad range of plants, including several agriculturally important species such as cotton, soybean and corn, as well as various vegetables and ornamentals. These parasites cause roots to develop galls that result in severe plant damage and, ultimately, important crop losses. Growers currently use synthetic nematicides to manage RKNs; however, these compounds are detrimental to the microbial diversity of soil and harmful for the environment. Thus, it is necessary to develop alternative sustainable control methods.
"We have been seeking natural compounds that activate plant defense ...
2021-03-22
A team of scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have developed the thinnest and most sensitive flow sensor, which could have significant implications for medical research and applications, according to new research published recently in Nature Communications.
The research was led by Jinglei Ping, assistant professor of mechanical and industrial engineering, along with a trio of mechanical engineering Ph.D. students: Xiaoyu Zhang, who fabricated the sensor and made the measurement, Eric Chia and Xiao Fan. The findings pave the way for future research on all-electronic, in-vivo flow monitoring in investigating ...
2021-03-22
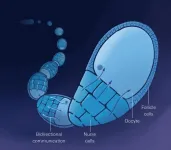
A cast of so-called 'nurse cells' surrounds and supports the growing fruit fly egg during development, supplying the egg -- or 'oocyte' -- with all the nutrients and molecules it needs to thrive. Long viewed as passive in this process, the Drosophila egg actually plays an active role not only in its own growth, but also in the growth of the surrounding nurse cells, Princeton University researchers report on March 21 in Developmental Cell.
"Here we show an example of bidirectional communication -- a dialogue -- between different cells. The egg is taking an active hand in controlling its own feeding ...
2021-03-22
Scientists from the Department of Physiology of the University of Granada (UGR) have shown that caffeine (about 3 mg/kg, the equivalent of a strong coffee) ingested half an hour before aerobic exercise significantly increases the rate of fat-burning. They also found that if the exercise is performed in the afternoon, the effects of the caffeine are more marked than in the morning.
In their study, published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, the researchers aimed to determine whether caffeine--one of the most commonly-consumed ergogenic substances in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New diagnostic tool for the management of patients with sepsis
Dipeptidyl Peptidase 3 (DPP3)