(Press-News.org) In a letter to The New England Journal of Medicine, published online March 23, 2021, a group of investigators from University of California San Diego School of Medicine and the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA report COVID-19 infection rates for a cohort of health care workers previously vaccinated for the novel coronavirus.
"Because of the compulsory daily symptom screening of health care personnel, patients, and visitors, and the high testing capacity at both UC San Diego Health and UCLA Health, we were able to identify symptomatic and asymptomatic infections among health care workers at our institutions," said co-author Jocelyn Keehner MD, an infectious disease fellow at UC San Diego School of Medicine.
"Moreover, we were able to describe the infection rates in a real-world scenario, where vaccine roll-out coincided with a surge of infections. We observed a low overall positivity rate among fully immunized health care workers, supporting the high protection rates of these vaccines."
The authors looked at pooled data from UC San Diego and UCLA health care workers who received either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines between December 16, 2020 and February 9, 2021 (36,659 first doses, 28,184 second doses), a time period that coincided with a significant surge in COVID-19 infections in the region.
Within this group, 379 individuals tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 at least one day following vaccination, with the majority (71 percent) testing positive within the first two weeks after the first dose. Thirty-seven health care workers tested positive after receiving two doses, which is when maximum immune protection is expected to be achieved with both vaccines.
The authors estimated that absolute risk of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 following vaccination was 1.19 percent for health care workers at UC San Diego Health and 0.97 percent at UCLA Health, both higher than the risk identified in the Moderna and Pfizer clinical trials, which were not limited to health care workers.
"There are several possible explanations for this elevated risk," said co-author Lucy E. Horton, MD, MPH, associate professor in the Division of Infectious Diseases and Global Public Health at UC San Diego School of Medicine and medical director of the UC San Diego Health Contact Tracing Unit.
"First, the health care workers surveyed have access to regular asymptomatic and symptomatic testing. Second, there was a regional surge in infections overlapping with vaccination campaigns during this time period. And third, there are differences in the demographics of health care workers compared to participants in the vaccine clinical trials. Health care workers tend to be younger and have a greater overall risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in the community."
Increased rates of infection have been strongly linked to behaviors that heighten risk of exposure, such as attending social gatherings in restaurants and bars without adequate masking and physical distancing. This connection is more strongly associated with younger age demographics.
Additionally, noted co-author Michael A. Pfeffer, MD, assistant vice chancellor and chief information officer at UCLA Health, the Moderna and Pfizer clinical trials stopped collecting data before the December-February surge and there was little to no asymptomatic testing conducted.
The authors found that risk of infection 14 days after second dose, when maximum immunity is expected to be reached, was rare. "It suggests the efficacy of these vaccines is maintained outside of the trial setting," they wrote.
Nonetheless, they also noted that risk is not zero. While both Pfizer and Moderna report efficacy levels in the mid-90s, neither is 100 percent.
"It underscores the critical importance of continued public health mitigation measures (masking, physical distancing, daily symptom screening and regular testing), even in highly vaccinated environments, until herd immunity is reached at large," said corresponding author Francesca Torriani, MD, professor of clinical medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases and Global Public Health in the UC San Diego School of Medicine and program director of Infection Prevention and Clinical Epidemiology at UC San Diego Health.
INFORMATION:
Additional co-authors include: Christopher A. Longhurst, Robert T. Schooley and Shira R. Abeles (co-senior author), all members of the COVID-19 taskforce at UC San Diego, and Judith S. Currier, UCLA.
Boulder, Colo., USA: When geobiology graduate student Katie Maloney trekked into the mountains of Canada's remote Yukon territory, she was hoping to find microscopic fossils of early life. Even with detailed field plans, the odds of finding just the right rocks were low. Far from leaving empty-handed, though, she hiked back out with some of the most significant fossils for the time period.
Eukaryotic life (cells with a DNA-containing nucleus) evolved over two billion years ago, with photosynthetic algae dominating the playing field for hundreds of millions of years as oxygen accumulated in the Earth's atmosphere. Geobiologists think that algae evolved first in freshwater environments ...
Over the past decades, the increased use of chemicals in many areas led to environmental pollution - of water, soil and also wildlife. In addition to plant protection substances and human and veterinary medical drugs, rodenticides have had toxic effects on wildlife. A new scientific investigation from scientists of the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW), the Julius Kühn Institute (JKI) and the German Environment Agency (Umweltbundesamt - UBA) demonstrate that these substances are widely found in liver tissues of birds of prey from Germany. Anticoagulant rodenticides, commonly used to kill rodents in agriculture and forestry, were frequently detected, particularly in birds of prey close to or in urban environments. ...
DALLAS - March 23, 2021 - Vaccinating health care workers resulted in an immediate and notable reduction of positive COVID-19 cases among employees, reducing the number of required isolations and quarantines by more than 90 percent, according to data at UT Southwestern Medical Center published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Health care workers were among the first groups to be eligible for vaccination.
"Real-world experience with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination at UT Southwestern demonstrated a marked reduction in the incidence of infections among our employees, preserving the workforce when it was most needed," notes Daniel K. Podolsky, M.D., president of UT Southwestern and senior author.
During ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - New research from Mildred Warner, professor of city and regional planning at Cornell University, shows that state laws designed to hinder union activity and indulge corporate entities do not enhance economic productivity.
"We find that where state policy is captured by corporate interests, this undermines inclusive growth," Warner said. "These interests see union and city power as a threat, which is why there are groups like the American Legislative Exchange Council, for example, focused on crafting state laws that erode labor protections and enhance corporate interests."
The ...
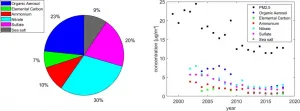
California's restrictions on vehicle emissions have been so effective that in at least one urban area, Los Angeles, the most concerning source of dangerous aerosol pollution may well be trees and other green plants, according to a new study by University of California, Berkeley, chemists.
Aerosols -- particles of hydrocarbons referred to as PM2.5 because they are smaller than 2.5 microns in diameter and easily lodge in the lungs -- are proven to cause cardiovascular and respiratory problems.
As a result of strict vehicle emissions laws, organic aerosol levels have been significantly reduced throughout the United States, but the drop has been particularly dramatic ...
Understanding the evolution of the polar sea ice is not enough to study the effects of the climate change on marine ecosystems in Antarctic seafloors. It is also necessary to determine the intensity of phytoplankton local production during the Antarctic summer, as stated in a new study by a research team of the Faculty of Biology and the Biodiversity Research Institute (IRBio) of the University of Barcelona, published in the journal Marine Environmental Research.
When the sea freezes in Antarctica
Extremely low temperatures, strong ocean currents and the broad seasonal coverage of marine ice are factors that determine the features of the Antarctic marine ecosystems. IN particular, the seasonality ...
The rate of sea-level rise in the 20th century along much of the U.S. Atlantic coast was the fastest in 2,000 years, and southern New Jersey had the fastest rates, according to a Rutgers-led study.
The global rise in sea-level from melting ice and warming oceans from 1900 to 2000 led to a rate that's more than twice the average for the years 0 to 1800 - the most significant change, according to the study in the journal Nature Communications.
The study for the first time looked at the phenomena that contributed to sea-level change over 2,000 years at six sites along the coast (in Connecticut, New York City, New Jersey and North Carolina), using a sea-level budget. A budget enhances ...
Researchers at North Carolina State University have designed and demonstrated a new system that allows them to remotely monitor the behavior of freshwater mussels. The system could be used to alert researchers to the presence of toxic substances in aquatic ecosystems.
"When mussels feed, they open their shells; but if there's something noxious in the water, they may immediately close their shells, all at once," says Jay Levine, co-author of a paper on the work and a professor of epidemiology at NC State. "Folks have been trying to find ways to measure how widely mussels or oysters open their shells off and on since the 1950s, but there have been a wide variety ...
All viruses mutate as they make copies of themselves to spread and thrive. SARS-CoV-2, the virus the causes COVID-19, is proving to be no different. There are currently more than 4,000 variants of COVID-19, which has already killed more than 2.7 million people worldwide during the pandemic.
The UK variant, also known as B.1.1.7, was first detected in September 2020, and is now causing 98 percent of all COVID-19 cases in the United Kingdom. And it appears to be gaining a firm grip in about 100 other countries it has spread to in the past several months, including France, Denmark, and the United States.
The World Health Organization says B.1.1.7 is one of several variants of concern along with others that have emerged in South Africa and Brazil.
"The UK, ...
Many organisms use sunlight to fuel cellular functions. But exactly how does this conversion of solar energy into chemical energy unfold?
In a recent experiment, an international team of scientists, including two researchers from UWM, sought answers using an advanced imaging technique called time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography to watch a pigment found in some marine bacteria as it was exposed to sunlight outside the cell.
For this experiment, the researchers documented, for the first time, the dynamics of the "chloride ion-pumping rhodopsin," an atomic "pump," which is jump-started by sunlight and moves chloride ions unidirectionally into the ...