Green leafy vegetables essential for muscle strength
Eating just one cup of leafy green vegetables every day could boost muscle function, according to new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research.
2021-03-24
(Press-News.org) Eating just one cup of leafy green vegetables every day could boost muscle function, according to new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research.
The study, published today in the Journal of Nutrition, found that people who consumed a nitrate-rich diet, predominantly from vegetables, had significantly better muscle function of their lower limb.
Poor muscle function is linked to greater risk of falls and fractures and is considered a key indicator of general health and wellbeing.
Researchers examined data from 3,759 Australians taking part in Melbourne's Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute AusDiab study over a 12-year period. They found those with the highest regular nitrate consumption had 11 per cent stronger lower limb strength than those with the lowest nitrate intake. Up to 4 per cent faster walking speeds were also recorded.
Lead researcher Dr Marc Sim from ECU's Institute for Nutrition Research said the findings reveal important evidence for the role diet plays in overall health.
"Our study has shown that diets high in nitrate-rich vegetables may bolster your muscle strength independently of any physical activity," he said.
"Nevertheless, to optimise muscle function we propose that a balanced diet rich in green leafy vegetables in combination with regular exercise, including weight training, is ideal."
Muscle function is vital for maintaining good overall health, especially bone strength later in life.
"With around one in three Australians aged over 65 suffering a fall each year, it's important to find ways of preventing these events and their potentially serious consequences," said Dr Sim.
Go for green
While leafy greens may be some of our least favourite vegetables, they could be the most important, according to Dr Sim.
The research found nitrate-rich vegetables, such as lettuce, spinach, kale and even beetroot, provided the greatest health benefits.
"Less than one in ten Australians eat the recommended five to six serves of vegetables per day," Dr Sim said.
"We should be eating a variety of vegetables every day, with at least one of those serves being leafy greens to gain a range of positive health benefits for the musculoskeletal and cardiovascular system."
"It's also better to eat nitrate-rich vegetables as part of a healthy diet rather than taking supplements. Green leafy vegetables provide a whole range of essential vitamins and minerals critical for health."
Building knowledge
The study, a collaboration with Deakin University's Institute of Physical Activity and Nutrition and the Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute, builds on Dr Sim's previous research into nitrate and muscle function in older women.
It also adds to growing evidence linking vegetables with cardiovascular health, including a recent ECU study into cruciferous vegetables and blood vessel health.
Dr Sim said the next step of his research will be exploring strategies to increase leafy green vegetable consumption in the general population.
"We are currently recruiting for the MODEL Study, which examines how knowledge of disease can be used to prompt people in making long-term improvements to their diet and exercise," said Dr Sim.
INFORMATION:
'Dietary nitrate intake is positively associated with muscle function in men and women independent of physical activity levels' was published in the Journal of Nutrition.
The Institute for Nutrition Research was established as an ECU Strategic Research Institute in 2020. Find out more about their work.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-24
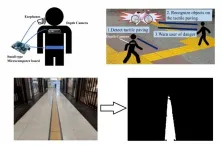
Sight is by far the sense that we humans use the most when navigating an environment. When those who are blind or visually impaired walk alone, they put themselves at great risk of falling or colliding with obstacles, especially when traversing new places. Unfortunately, the number of visually impaired people throughout the world is likely to increase in the near future because of the rapidly aging population. Thus, there is an urgent need for innovative and cost-effective solutions to help visually impaired people navigate safely.
A promising strategy that was first implemented in Japan and then replicated throughout the world is called tactile paving. Inspired by Braille, the reading system of the blind, tactile paving essentially consists of ...
2021-03-24
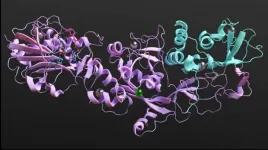
When invaded by a virus, our body cells launch an alert to neighboring cells to increase their antiviral defenses to prevent the infection from spreading. Some viruses, however, manage to bypass this system by mimicking the host's RNA, preventing them from being detected by the infected cell and avoiding this alert. In the case of SARS-CoV-2, this mimicking uses a protein known as nsp14. This protein is also very important for virus multiplication, a task which is facilitated by its binding to the nsp10 protein, resulting in a protein complex. Interfering with nsp14 binding and with the nsp10-nsp14 protein complex is the aim of the most recent ITQB NOVA research in COVID-19, led by researchers Margarida Saramago, Rute Matos and Cecília Arraiano.
The researchers ...
2021-03-24
Researchers find that the earliest bacteria had the tools to perform a crucial step in photosynthesis, changing how we think life evolved on Earth.
The finding also challenges expectations for how life might have evolved on other planets. The evolution of photosynthesis that produces oxygen is thought to be the key factor in the eventual emergence of complex life. This was thought to take several billion years to evolve, but if in fact the earliest life could do it, then other planets may have evolved complex life much earlier than previously thought.
The ...
2021-03-24
Beams of accelerated electrons power electron microscopes, X-ray lasers, medical accelerators and other devices. To optimize the performance of these applications, operators must be able to analyze the quality of the beams and adjust them as needed.
For the past few years, researchers at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have been developing "virtual diagnostics" that use machine learning to obtain crucial information about beam quality in an efficient, non-invasive way. Now, a new virtual diagnostic approach, published in Scientific Reports, incorporates additional information about the beam that allows the method to work in situations where conventional ...
2021-03-24
Despite aquaculture's potential to feed a growing world population while relieving pressure on badly depleted oceans, the industry has been plagued by questions about its environmental impacts. (Watch related video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DG_nl7-naYo)
But over the years, the diverse industry - which ranges from massive open-ocean salmon cages to family farm freshwater tilapia ponds - has made significant strides toward sustainability, according to a new Stanford-led analysis.
The study notes, however, that in order for the global aquaculture sector to deliver on its full promise, more effective oversight measures are ...
2021-03-24
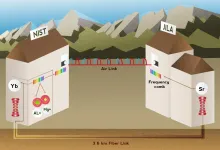
In a significant advance toward the future redefinition of the international unit of time, the second, a research team led by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has compared three of the world's leading atomic clocks with record accuracy over both air and optical fiber links.
Described in the March 25 issue of Nature, the NIST-led work is the first to compare three clocks, based on different atoms, and the first to link the most advanced atomic clocks in different locations over the air. These atomic clock comparisons place the scientific community one step closer to meeting the guidelines for redefinition of the second.
"These comparisons are really defining ...
2021-03-24
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere fuels plant growth. As carbon levels rise, it's appealing to think of supercharged plant growth and massive tree-planting campaigns drawing down the CO2 produced by fossil fuel burning, agriculture and other human activities.
New research published March 24 in Nature, however, suggests that when elevated carbon dioxide levels drive increased plant growth, it takes a surprisingly steep toll on another big carbon sink: the soil.
One likely explanation, the authors say, is that plants effectively mine the soil for nutrients they need to keep up with carbon-fueled growth. Extracting the extra nutrients requires revving up microbial activity, which then releases CO2 into the atmosphere that might otherwise remain locked in soil.
The findings contradict ...
2021-03-24
The secret to building superconducting quantum computers with massive processing power may be an ordinary telecommunications technology - optical fiber.
Physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have measured and controlled a superconducting quantum bit (qubit) using light-conducting fiber instead of metal electrical wires, paving the way to packing a million qubits into a quantum computer rather than just a few thousand. The demonstration is described in the March 25 issue of Nature.
Superconducting circuits are a leading technology for making quantum computers because they are reliable and easily mass produced. But these circuits must operate at cryogenic temperatures, and schemes for wiring them to room-temperature electronics are complex and prone to ...
2021-03-24
As the signs of today's human-caused climate change become ever more alarming, research into the ways past societies responded to natural climate changes is growing increasingly urgent. Scholars have often argued that climatic changes plunge communities into crisis and provide the conditions that lead societies to collapse, but a growing body of research shows that the impacts of climate change on past populations are rarely so straightforward.
In a new paper published in Nature, scholars in archaeology, geography, history and paleoclimatology present a framework for research into what they term 'the History of Climate and Society' (HCS). The framework uses a series of ...
2021-03-24
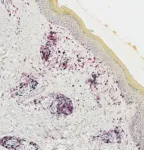
LEBANON, NH - Some melanoma patients respond very well to immunotherapy, experiencing profound and durable tumor regression. A fraction of these patients will also develop autoimmunity against their normal melanocytes--the cells that give rise to melanoma--a phenomenon called vitiligo. Melanoma survivors with vitiligo have long been recognized as a special group with an outstanding prognosis, and a strong response of immune system cells called T cells.
Immunotherapy researchers at Dartmouth's and Dartmouth-Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center (NCCC) led by Mary Jo Turk, PhD, and surgical oncologist Christina Angeles, MD (now of University of Michigan), have discovered how a subset ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Green leafy vegetables essential for muscle strength
Eating just one cup of leafy green vegetables every day could boost muscle function, according to new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research.