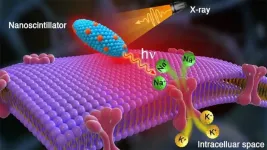
Many people worldwide suffer from movement-related brain disorders. Epilepsy accounts for more than 50 million; essential tremor, 40 million; and Parkinson's disease, 10 million.
Relief for some brain disorder sufferers may one day be on the way in the form of a new treatment invented by researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and four universities. The treatment is based on breakthroughs in both optics and genetics. It would be applicable to not only movement-related brain disorders, but also chronic depression and pain.
"Our high precision noninvasive approach could become routine with the use of a small X-ray machine, the kind commonly found in every dental office." -- Elena Rozhkova, a nanoscientist in Argonne's Center for Nanoscale Materials
This new treatment involves stimulation of neurons deep within the brain by means of injected nanoparticles that light up when exposed to X-rays (nanoscintillators) and would eliminate an invasive brain surgery currently in use.
"Our high-precision noninvasive approach could become routine with the use of a small X-ray machine, the kind commonly found in every dental office," said Elena Rozhkova, a lead author and a nanoscientist in Argonne's Center for Nanoscale Materials (CNM), a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
Traditional deep brain stimulation requires an invasive neurosurgical procedure for disorders when conventional drug therapy is not an option. In the traditional procedure, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, surgeons implant a calibrated pulse generator under the skin (similar to a pacemaker). They then connect it with an insulated extension cord to electrodes inserted into a specific area of the brain to stimulate the surrounding neurons and regulate abnormal impulses.
"The Spanish-American scientist José Manuel Rodríguez Delgado famously demonstrated deep brain stimulation in a bullring in the 1960s," said Vassiliy Tsytsarev, a neurobiologist from the University of Maryland and a co-author of the study. "He brought a raging bull charging at him to a standstill by sending a radio signal to an implanted electrode."
About 15 years ago, scientists introduced a revolutionary neuromodulation technology, "optogenetics," which relies on genetic modification of specific neurons in the brain. These neurons create a light-sensitive ion channel in the brain and, thereby, fire in response to external laser light. This approach, however, requires very thin fiberoptic wires implanted in the brain and suffers from the limited penetration depth of the laser light through biological tissues.
The team's alternative optogenetics approach uses nanoscintillators injected in the brain, bypassing implantable electrodes or fiberoptic wires. Instead of lasers, they substitute X-rays because of their greater ability to pass through biological tissue barriers.
"The injected nanoparticles absorb the X-ray energy and convert it into red light, which has significantly greater penetration depth than blue light," said Zhaowei Chen, former CNM postdoctoral fellow.
"Thus, the nanoparticles serve as an internal light source that makes our method work without a wire or electrode," added Rozhkova. Since the team's approach can both stimulate and quell targeted small areas, Rozhkova noted, it has other applications than brain disorders. For example, it could be applicable to heart problems and other damaged muscles.
One of the team's keys to success was the collaboration between two of the world-class facilities at Argonne: CNM and Argonne's Advanced Photon Source (APS), a DOE Office of Science User Facility. The work at these facilities began with the synthesis and multi-tool characterization of the nanoscintillators. In particular, the X-ray excited optical luminescence of the nanoparticle samples was determined at an APS beamline (20-BM). The results showed that the particles were extremely stable over months and upon repeated exposure to the high-intensity X-rays.
According to Zou Finfrock, a staff scientist at the APS 20-BM beamline and Canadian Light Source, "They kept glowing a beautiful orange-red light."
Next, Argonne sent CNM-prepared nanoscintillators to the University of Maryland for tests in mice. The team at University of Maryland performed these tests over two months with a small portable X-ray machine. The results proved that the procedure worked as planned. Mice whose brains had been genetically modified to react to red light responded to the X-ray pulses with brain waves recorded on an electroencephalogram.
Finally, the University of Maryland team sent the animal brains for characterization using X-ray fluorescence microscopy performed by Argonne scientists. This analysis was performed by Olga Antipova on the Microprobe beamline (2-ID-E) at APS and by Zhonghou Cai on the Hard X-ray Nanoprobe (26-ID) jointly operated by CNM and APS.
This multi-instrument arrangement made it possible to see tiny particles residing in the complex environment of the brain tissue with a super-resolution of dozens of nanometers. It also allowed visualizing neurons near and far from the injection site on a microscale. The results proved that the nanoscintillators are chemically and biologically stable. They do not wander from the injection site or degrade.
"Sample preparation is extremely important in these types of biological analysis," said Antipova, a physicist in the X-ray Science Division (XSD) at the APS. Antipova was assisted by Qiaoling Jin and Xueli Liu, who prepared brain sections only a few micrometers thick with jeweler-like accuracy.
"There is an intense level of commercial interest in optogenetics for medical applications," said Rozhkova. "Although still at the proof-of-concept stage, we predict our patent-pending wireless approach with small X-ray machines should have a bright future."
The related article "Wireless optogenetic modulation of cortical neurons enabled by radioluminescent nanoparticles" appeared in ACS Nano. In addition to Rozhkova, Chen, Finfrock, Antipova and Cai, another Argonne author is Rosemarie Wilton. University contributors include Vassiliy Tsytsarev, Dongyi Wang, Yi Liu, Brandon Gaitan, Yang Tao and Yu Chen from the University of Maryland, Department of Bioengineering; Hiroyuki Arakawa and Reha Erzurumlu from the University of Maryland School of Medicine; Fritz Lischka from the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences; Bryan Hooks from the University of Pittsburgh, Department of Neurobiology; and Huanghao Yang from Fuzhou University.
INFORMATION:
This research received support from the DOE Office of Science, National Institutes of Health and National Science Foundation.
About Argonne's Center for Nanoscale Materials
The Center for Nanoscale Materials is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers, premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE's Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge, Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories. For more information about the DOE NSRCs, please visit https://science.osti.gov/User-Facilities/User-Facilities-at-a-Glance.
About the Advanced Photon Source
The U. S. Department of Energy Office of Science's Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory is one of the world's most productive X-ray light source facilities. The APS provides high-brightness X-ray beams to a diverse community of researchers in materials science, chemistry, condensed matter physics, the life and environmental sciences, and applied research. These X-rays are ideally suited for explorations of materials and biological structures; elemental distribution; chemical, magnetic, electronic states; and a wide range of technologically important engineering systems from batteries to fuel injector sprays, all of which are the foundations of our nation's economic, technological, and physical well-being. Each year, more than 5,000 researchers use the APS to produce over 2,000 publications detailing impactful discoveries, and solve more vital biological protein structures than users of any other X-ray light source research facility. APS scientists and engineers innovate technology that is at the heart of advancing accelerator and light-source operations. This includes the insertion devices that produce extreme-brightness X-rays prized by researchers, lenses that focus the X-rays down to a few nanometers, instrumentation that maximizes the way the X-rays interact with samples being studied, and software that gathers and manages the massive quantity of data resulting from discovery research at the APS.
This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. DOE Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science.