Insufficient financial reporting may lead to underestimation of environmental liabilities
2021-03-25
(Press-News.org) European listed companies in the energy and mining sector provide, to say the least, sparse information on future environmental costs in their annual reports. Researchers believe that stricter guidelines are required as the lack of information may lead to underestimation of environmental liabilities, resulting in that future generations may have to bear the burden of cleanup costs.
"I believe that the future environmental liabilities such as decommissioning costs are often underestimated and few understand the burden these costs might impose on future generations. If, for example, an oil & gas company fails, it costs an incredible amount to clean up after old oil wells and the risk is great that the taxpayers will have to pay the bill. Therefore, it is important that environmental obligations are made visible to investors, lenders and the public so that we can discuss the problem," says Mari Paananen, associate professor of business administration at the School of Business, Economics and Law at the University of Gothenburg.
In fact, as there is no clear claimant for this type of future obligations, there is little demand for information either.
"The International Accounting Standards Board* needs to provide clearer requirements about what information should be included in the annual reports in order to make it possible to assess environmental liabilities. I think that such guidelines would make companies inclined to disclose more information and would also provide, for example, auditors a mandate to demand specific information," says Mari Paananen.
Using a sample of 164 European listed companies active in oil, gas, energy (nuclear power) and mining, Mari Paananen and her research colleagues have analyzed environmental disclosures in annual reports over a twelve-year period. Specifically, the researchers use computerized text analysis, to examine information on environment-related restoration costs in the notes to annual reports. Among other things, they searched for information about the discount rate and estimated time horizon for payments - key information needed to assess the size of environmental liabilities.
"Even though we could see that the disclosure of environmental information in the annual reports has increased over time, companies are, are on average, not very forthcoming with information. Approximately 60 percent of the companies provided information about discount rates and 65 percent disclosed the time horizon for the expected future cash outflow. On the other hand, only just over a third provided information about both," says Mari Paananen.
The researchers also investigated whether the level of disclosure increased when companies faced media exposure focusing on environmental issues or how companies' take responsibility for the environment.
"We clearly saw that if companies were exposed in the media, the environmental information increased and the companies provided more specific disclosure on environmental liabilities in the following annual report. Above all, there was more information if the media used an uncertain or litigious tone," says Mari Paananen.
INFORMATION:
* International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) is an international organization that works to improve the quality of international financial reporting. They are responsible for the accounting standard IFRS, International Financial Reporting Standards, which are used by listed companies in the EU.
About the study:
Mari Paananen , Emmeli Runesson & Niuosha Samani (2021): Time to
clean up environmental liabilities reporting: disclosures, media exposure and market implications, Accounting Forum.
Link to article https://doi.org/10.1080/01559982.2021.1872909
Contact:
Mari Paananen, associate professor Business Administration, Department of Business administration, School of Business, Economics & Law, University of Gothenburg.
Email: mari.paananen@handels.gu.se
Phone: +46 703 157 187
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-25
Increased allergic reactions may be tied to the corticotropin-releasing stress hormone (CRH), suggests a study published this month in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. These findings may help clarify the mechanism by which CRH induces proliferation of mast cells (MC) - agents involved in the development of allergies in the human nasal cavity.
"In my daily practice, I meet many patients with allergies who say their symptoms worsened due to psychological stress," states lead researcher Mika Yamanaka-Takaichi, a graduate student of the Department of Dermatology, Osaka City University, "This is what led me to do this research."
Together with Professor Daisuke Tsuruta of the same department, they hypothesized that due to its ...
2021-03-25
Bright but disadvantaged students from urban areas are more likely to enter elite UK universities than similar peers from rural communities due to an urban 'escalator effect', according to a new study.
Researchers from the University of Bath analysed data from 800,000 English students commencing university in the years 2008, 2010, 2012, 2014 and 2016.
They found that while in general rural areas had higher overall progression to university than city centres and surrounding areas, when controlling for factors including socio-economic status, age, ethnicity and sex, disadvantaged pupils from rural areas were less likely to progress to one of 27 'top' UK universities.
The authors suggest the difference ...
2021-03-25
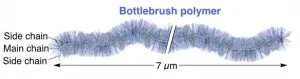
NIMS and RIKEN have succeeded in synthesizing the longest ever bottlebrush polymer. This polymer--resembling a green foxtail--is composed of a main chain and numerous side chains grafting from it. The team also succeeded in giving various chemical properties to the ultralong bottlebrush polymer. These achievements are expected to substantially advance the current synthetic methods of bottlebrush polymers. This technique may be applicable to the development of flexible and low-friction polymeric materials.
In the development of polymeric materials, it is necessary to link molecular units with desired chemical properties, called monomers, to ...
2021-03-25
Prof. ZHAO Jin's research team from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has made important progress in the development of Spin-Valley exciton dynamics. The research developed an ab initio nonadiabatic molecular dynamics (NAMD) method based on for the spin-resolved exciton dynamics. The team gained the first clear and complete physical picture of valley exciton dynamics in MoS2 from the perspective of first-principles calculations based on GW plus real-time Bethe-Salpeter equation (GW + rtBSE-NAMD).
It can accurately include many-body effects at the level of first principles and break through the bottleneck of GW+BSE method in ...
2021-03-25
When we grow crystals, atoms first group together into small clusters - a process called nucleation. But understanding exactly how such atomic ordering emerges from the chaos of randomly moving atoms has long eluded scientists.
Classical nucleation theory suggests that crystals form one atom at a time, steadily increasing the level of order. Modern studies have also observed a two-step nucleation process, where a temporary, high-energy structure forms first, which then changes into a stable crystal. But according to an international research team co-led by the ...
2021-03-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- A 10-week muscle-building and dietary program involving 50 middle-aged adults found no evidence that eating a high-protein diet increased strength or muscle mass more than consuming a moderate amount of protein while training. The intervention involved a standard strength-training protocol with sessions three times per week. None of the participants had previous weightlifting experience.
Published in the American Journal of Physiology: Endocrinology and Metabolism, the study is one of the most comprehensive investigations of the health effects of diet and resistance training in middle-aged adults, the researchers say. Participants were 40-64 years ...
2021-03-25
Fossil fuel producers in the U.S. are directly benefiting from implicit subsidies on the order of $62 billion a year because of inefficient pricing that doesn't properly account for the costs of damages to the environment, climate, and human health.
That's the finding of a newly published study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) by Yale School of the Environment Economics Professor Matthew Kotchen that analyzed gasoline, natural gas, diesel, and coal.
The total annual implicit subsidy is equivalent to an average of 3% of the U.S. gross domestic product, according to the study which examined data from 2010-2018. ...
2021-03-25
A recent Oregon State University study found that when people feel they have resolved an argument, the emotional response associated with that disagreement is significantly reduced and, in some situations, almost entirely erased.
That reduction in stress may have a major impact on overall health, researchers say.
"Everyone experiences stress in their daily lives. You aren't going to stop stressful things from happening. But the extent to which you can tie them off, bring them to an end and resolve them is definitely going to pay dividends in terms of your well-being," said Robert Stawski, senior author on the study and an associate professor ...
2021-03-25
The Gerontological Society of America's highly cited, peer-reviewed journals are continuing to publish scientific articles on COVID-19. The following were published between January 8 and March 15; all are free to access:
Comment on: "Beyond chronological age: Frailty and multimorbidity predict in-hospital mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019": Letter to the editor in The Journals of Gerontology, Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences by Noémie Girard, MS, Geoffrey Odille, MS, Stéphane Sanchez, MD, Sarah Lelarge, ...
2021-03-25
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Long before Tyrone, Jermaine and Darnell came along, there were Isaac, Abe and Prince.
A new study reveals the earliest evidence of distinctively Black first names in the United States, finding them arising in the early 1700s and then becoming increasingly common in the late 1700s and early 1800s.
The results confirm previous work that shows the use of Black names didn't start during the civil rights movement of the 1960s, as some scholars have argued, said Trevon Logan, co-author of the study and professor of economics at The Ohio State University.
"Even ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Insufficient financial reporting may lead to underestimation of environmental liabilities