(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio - Long before Tyrone, Jermaine and Darnell came along, there were Isaac, Abe and Prince.
A new study reveals the earliest evidence of distinctively Black first names in the United States, finding them arising in the early 1700s and then becoming increasingly common in the late 1700s and early 1800s.
The results confirm previous work that shows the use of Black names didn't start during the civil rights movement of the 1960s, as some scholars have argued, said Trevon Logan, co-author of the study and professor of economics at The Ohio State University.
"Even during slavery, Black people had names that were unlikely to be held by whites. It is not just a recent phenomenon," Logan said.
Logan conducted the study with Lisa Cook of Michigan State University and John Parman of the College of William and Mary. It was published online this month in the journal Historical Methods.
The study focuses on names for Black males, partly because earlier research suggests less distinctiveness of Black women's names historically.
This research is a follow-up to a 2014 study by the same researchers that found distinctive Black names were being used in the period following the Civil War.
It was more difficult to find records that document the names of the enslaved, Logan said. Many official records only list slaves as numbers without names.
The researchers found three sources that did contain the names of enslaved people in the United States. Two of the three sources also included the names of the buyers or sellers of the enslaved, which allowed comparisons between Black and white names. The researchers supplemented the evidence of racial name distinctiveness by analyzing white names in the 1850 Census.
The names given Blacks in the United States were distinctively African American, Logan said. None of them had roots in Africa. Many of them had Biblical origins, like Abraham and Isaac. Other Black names that appeared more frequently in one or more of the data sets included Titus and Prince.
Results showed a clear increase in the use of Black names over the period of the study. In one data set, 3.17% of enslaved males born between 1770 to 1790 were likely to hold a Black name, but that increased to 4.5% of those born between 1810 and 1830.
And they were truly distinctive from white people. Depending on the data source, enslaved people were more than four to nine times as likely to have a Black name than was a slave owner.
The appearance of distinctively Black names wasn't only the result of more African Americans using them, Logan said.
"Our results suggest a strong decline in the use of Black names among whites over time," he said. "The actions of both Black and white people fed into the process that resulted in distinctive Black names."
For white people born before 1770, more than 4.75% held Black names, but that declined to less than 2% for those born from 1810 to 1830.
Many of the Black names identified in this study were the same that the researchers found in the post-Civil War period, but there were some differences.
"Post-emancipation we found more Blacks being named Master and Freeman, which for obvious reasons were not found in the antebellum era," Logan said.
While this study revealed the existence and growth of Black names in the United States, it can't answer why it happened, Logan said.
"We believe these naming practices could say something about culture, about family, and about social formation among Black people of the time," Logan said.
"But we don't have any records of people talking about it at the time, so we're not sure. We know there's this pattern, but we can't say for sure what it means."
INFORMATION:
Contact: Trevon Logan, Logan.155@osu.edu
Written by Jeff Grabmeier, 614-292-8457; Grabmeier.1#@osu.edu
The Amazon rainforest is teeming with creatures unknown to science--and that's just in broad daylight. After dark, the forest is a whole new place, alive with nocturnal animals that have remained even more elusive to scientists than their day-shift counterparts. In a new paper in Zootaxa, researchers described two new species of screech owls that live in the Amazon and Atlantic forests, both of which are already critically endangered.
"Screech owls are considered a well-understood group compared to some other types of organisms in these areas," says John Bates, curator of birds at the Field Museum in Chicago and one of the study's authors. "But when you start listening to them and comparing ...
Scientists estimate that dark matter and dark energy together are some 95% of the gravitational material in the universe while the remaining 5% is baryonic matter, which is the "normal" matter composing stars, planets, and living beings. However for decades almost one half of this matter has not been found either. Now, using a new technique, a team in which the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has participated, has shown that this "missing" baryonic matter is found filling the space between the galaxies as hot, low density gas. The same technique also gives a new tool that shows that the gravitational attraction experienced by ...
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London have developed a machine learning algorithm that ranks drugs based on their efficacy in reducing cancer cell growth. The approach may have the potential to advance personalised therapies in the future by allowing oncologists to select the best drugs to treat individual cancer patients.
The method, named Drug Ranking Using Machine Learning (DRUML), was published today in Nature Communications and is based on machine learning analysis of data derived from the study of proteins expressed in cancer cells. Having been trained on ...
The interiors of nonflowering trees such as pine and ginkgo contain sapwood lined with straw-like conduits known as xylem, which draw water up through a tree's trunk and branches. Xylem conduits are interconnected via thin membranes that act as natural sieves, filtering out bubbles from water and sap.
MIT engineers have been investigating sapwood's natural filtering ability, and have previously fabricated simple filters from peeled cross-sections of sapwood branches, demonstrating that the low-tech design effectively filters bacteria.
Now, the same team has advanced the technology and shown that it works in real-world situations. They have fabricated new xylem filters that can filter out pathogens ...
An international team of scientists has found evidence that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, infects cells in the mouth. While it's well known that the upper airways and lungs are primary sites of SARS-CoV-2 infection, there are clues the virus can infect cells in other parts of the body, such as the digestive system, blood vessels, kidneys and, as this new study shows, the mouth. The potential of the virus to infect multiple areas of the body might help explain the wide-ranging symptoms experienced by COVID-19 patients, including oral symptoms such as taste loss, ...
Philadelphia, March 25, 2021 - Dining out is a popular activity worldwide, but there has been little research into its association with health outcomes. Investigators looked at the association between eating out and risk of death and concluded that eating out very frequently is significantly associated with an increased risk of all-cause death, which warrants further investigation. Their results appear in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, published by Elsevier.
Eating out is a popular activity. The US Department of Agriculture recently estimated that Americans' daily energy intake from food away from home increased from 17 percent in 1977-1978 to 34 percent in 2011-2012. At the same time, the number of restaurants has ...
WASHINGTON - A food preservative used to prolong the shelf life of Pop-Tarts, Rice Krispies Treats, Cheez-Its and almost 1,250 other popular processed foods may harm the immune system, according to a new peer-reviewed study by Environmental Working Group.
For the study, published this week in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, EWG researchers used data from the Environmental Protection Agency's Toxicity Forecaster, or ToxCast, to assess the health hazards of the most common chemicals added to food, as well as the "forever chemicals" known as PFAS, which can migrate to food from packaging.
EWG's analysis of ToxCast data showed that the preservative tert-butylhydroquinone, ...
New Edith Cowan University (ECU) research has found that despite having the best intentions, most people give up on their New Year resolutions within the first month.
The study also revealed that approximately half the people surveyed had the same, or nearly the same, resolution as in the previous year, and more than half of the resolutions listed focused on either diet or exercise.
The research, led by ECU Associate Professor Joanne Dickson, investigated personal goal factors that predicted greater wellbeing and sticking with one's most important New Year resolution over time. Around 180 Australian and UK participants took part in an online survey over a two-month period. ...
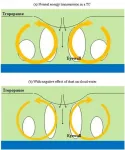
The thermodynamic state of the tropical atmosphere plays an important role in the development of tropical cyclone (TC) intensity. A TC imports thermodynamic energy from ocean-air heat and moisture fluxes and exports heat aloft at the much colder upper troposphere, through a radially and vertically directed overturning circulation in a TC. The work done through this cycle drives the TC's winds.
A negative response of cloud water in the lower troposphere to dust aerosol optical depth (AOD) has recently been reported in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aosl.2020.100028) by Dr. Zhenxi Zhang from the Inner Mongolia University of Technology, Hohhot, China, by analyzing MERRA-2 reanalysis data and GCM simulations from CMIP6.
"The ...
Philadelphia, March 25, 2021 - Anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS), a synthetic version of the male sex hormone testosterone, are sometimes used as a medical treatment for hormone imbalance. But the vast majority of AAS is used to enhance athletic performance or build muscle because when paired with strength training. AAS use increases muscle mass and strength, and its use is known to have many side effects, ranging from acne to heart problems to increased aggression. A new study now suggests that AAS can also have deleterious effects on the brain, causing it to age prematurely.
The report appears in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and ...