INFORMATION:
Title: The role of physical activity for recovery after surgical procedures,
http://hdl.handle.net/2077/67125
Better postoperative recovery for physically active
2021-03-25
(Press-News.org) People who are physically active on a regular basis recover better after surgery for colorectal cancer. However, starting to exercise only after the diagnosis is a fact had no effect on recovery, a University of Gothenburg thesis shows.
In working on his thesis, Aron Onerup, who obtained his doctorate in surgery at the University's Sahlgrenska Academy and is now a specialist doctor at Sahlgrenska University Hospital, carried out an observational study of 115 patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer.
The participants who had been physically inactive proved, three weeks after their surgery, to be at higher risk of not feeling that they had recovered physically. Among them, the risk of postoperative complications was also more than four times higher than it was for participants who had been physically active.
Studies with similar results were conducted for individuals scheduled for operations to treat breast cancer and biliary tract disease as well.
The question was whether the odds of recovery could be improved for patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer. In another study, 761 individuals were randomly assigned to either receive ordinary, routine care or follow an exercise program, on their own, for about two weeks before and four weeks after surgery for colorectal cancer.
However, this program - which included half an hour of moderate-intensity exercise daily - had no effect on the latter group's self-reported physical recovery, nor on their complication risk, repeat surgery, readmission to hospital, or length of hospital stay.
"Although the exercise study didn't show any effects in the brief postoperative period, it's possible that measures resulting in increased physical activity in the long term may have positive health effects. The key is not to introduce measures into health care until they've been scientifically evaluated," Onerup states.
However, the overall picture provides evidence that, at the point when it becomes clear that an operation for biliary tract disease or colorectal cancer is necessary, people's physical activity level is clearly connected with the subsequent course of their recovery.
"The research findings indicate that there are further reasons to work for a population that's as physically active as possible, besides the gains in terms of, for example, cardiovascular and mental health that are already known," Onerup says.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How tiny machines become capable of learning
2021-03-25
Microswimmers are artificial, self-propelled, microscopic particles. They are capable of directional motion in a solution. The Molecular Nanophotonics Group at Leipzig University has developed special particles that are smaller than one-thirtieth of the diameter of a hair. They can change their direction of motion by heating tiny gold particles on their surface and converting this energy into motion. "However, these miniaturised machines cannot take in and learn information like their living counterparts. To achieve this, we control the microswimmers externally so that they learn to navigate in a virtual environment through what is known as reinforcement learning," said Cichos.
With the help of virtual rewards, the microswimmers find their way through the liquid ...
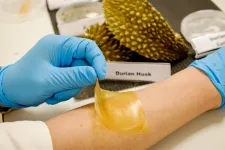
NTU Singapore scientists develop antibacterial gel bandage using durian husk
2021-03-25
Food scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have made an antibacterial gel bandage using the discarded husks of the popular tropical fruit, durian.
Known as the "King of Fruits" in Southeast Asia, the durian has a thick husk with spiky thorns which is discarded, while the sweet flesh surrounding the seeds on the inside is considered a delicacy.
By extracting high-quality cellulose from the durian husks and combining it with glycerol - a waste by-product from the biodiesel and soap industry - NTU scientists created a soft gel, similar to silicon sheets, which can be cut into bandages of various shapes and sizes.
They then added the organic molecules produced from baker's yeast known as natural yeast phenolics, making the bandage deadly ...
How improving acoustic monitoring of bats could help protecting biodiversity
2021-03-25
In order to assess the risk of bats dying at wind turbines, it is common practice to record the acoustic activity of bats within the operating range of the rotor blades. For this purpose, ultrasonic detectors are attached to the nacelles of the mast top. In a recent analysis, a team of scientists led by the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) concludes that the effectiveness of this acoustic monitoring is insufficient to reliably predict mortality risk, especially for bats at large turbines. They therefore recommend installing supplementary ultrasonic detectors at other locations on the wind turbines and developing additional techniques such as radar and thermal imaging cameras for monitoring. The results of their analysis are published in ...
Insufficient financial reporting may lead to underestimation of environmental liabilities
2021-03-25
European listed companies in the energy and mining sector provide, to say the least, sparse information on future environmental costs in their annual reports. Researchers believe that stricter guidelines are required as the lack of information may lead to underestimation of environmental liabilities, resulting in that future generations may have to bear the burden of cleanup costs.
"I believe that the future environmental liabilities such as decommissioning costs are often underestimated and few understand the burden these costs might impose on future generations. If, for example, an oil & gas company fails, it costs an incredible amount to clean up after old oil wells and the risk is great that the taxpayers will have to pay the bill. Therefore, it is important that environmental obligations ...
Relieve your stress, relieve your allergies
2021-03-25
Increased allergic reactions may be tied to the corticotropin-releasing stress hormone (CRH), suggests a study published this month in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. These findings may help clarify the mechanism by which CRH induces proliferation of mast cells (MC) - agents involved in the development of allergies in the human nasal cavity.
"In my daily practice, I meet many patients with allergies who say their symptoms worsened due to psychological stress," states lead researcher Mika Yamanaka-Takaichi, a graduate student of the Department of Dermatology, Osaka City University, "This is what led me to do this research."
Together with Professor Daisuke Tsuruta of the same department, they hypothesized that due to its ...
Urban 'escalator' means disadvantaged rural students miss out on top universities
2021-03-25
Bright but disadvantaged students from urban areas are more likely to enter elite UK universities than similar peers from rural communities due to an urban 'escalator effect', according to a new study.
Researchers from the University of Bath analysed data from 800,000 English students commencing university in the years 2008, 2010, 2012, 2014 and 2016.
They found that while in general rural areas had higher overall progression to university than city centres and surrounding areas, when controlling for factors including socio-economic status, age, ethnicity and sex, disadvantaged pupils from rural areas were less likely to progress to one of 27 'top' UK universities.
The authors suggest the difference ...
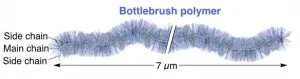
The world's longest bottlebrush polymer ever synthesized
2021-03-25
NIMS and RIKEN have succeeded in synthesizing the longest ever bottlebrush polymer. This polymer--resembling a green foxtail--is composed of a main chain and numerous side chains grafting from it. The team also succeeded in giving various chemical properties to the ultralong bottlebrush polymer. These achievements are expected to substantially advance the current synthetic methods of bottlebrush polymers. This technique may be applicable to the development of flexible and low-friction polymeric materials.
In the development of polymeric materials, it is necessary to link molecular units with desired chemical properties, called monomers, to ...
Scientists first realized real-time GW-BSE investigations on Spin-Valley exciton dynamics
2021-03-25
Prof. ZHAO Jin's research team from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has made important progress in the development of Spin-Valley exciton dynamics. The research developed an ab initio nonadiabatic molecular dynamics (NAMD) method based on for the spin-resolved exciton dynamics. The team gained the first clear and complete physical picture of valley exciton dynamics in MoS2 from the perspective of first-principles calculations based on GW plus real-time Bethe-Salpeter equation (GW + rtBSE-NAMD).
It can accurately include many-body effects at the level of first principles and break through the bottleneck of GW+BSE method in ...
Revealing nano big bang -- Scientists observe the first milliseconds of crystal formation
2021-03-25
When we grow crystals, atoms first group together into small clusters - a process called nucleation. But understanding exactly how such atomic ordering emerges from the chaos of randomly moving atoms has long eluded scientists.
Classical nucleation theory suggests that crystals form one atom at a time, steadily increasing the level of order. Modern studies have also observed a two-step nucleation process, where a temporary, high-energy structure forms first, which then changes into a stable crystal. But according to an international research team co-led by the ...
More protein doesn't mean more strength in resistance-trained middle-aged adults
2021-03-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- A 10-week muscle-building and dietary program involving 50 middle-aged adults found no evidence that eating a high-protein diet increased strength or muscle mass more than consuming a moderate amount of protein while training. The intervention involved a standard strength-training protocol with sessions three times per week. None of the participants had previous weightlifting experience.
Published in the American Journal of Physiology: Endocrinology and Metabolism, the study is one of the most comprehensive investigations of the health effects of diet and resistance training in middle-aged adults, the researchers say. Participants were 40-64 years ...