Myocardial fibrosis in pathogenesis, diagnosis & treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
2021-03-29
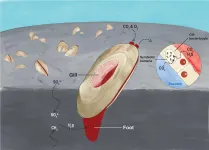
(Press-News.org) In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0008, Zeyi Cheng, Miaomiao Qi, Chengyuan Zhang and Yanxia Mao from Sichuan University, Sichuan, China, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China and The Second Medical School of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China consider myocardial fibrosis in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
The authors review the application of myocardial fibrosis in the diagnosis and treatment of HCM, focusing on research progress and the application of magnetic resonance imaging on the basis of the characteristics of fibrosis in the diagnosis and prognosis of HCM.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a type of hereditary cardiomyopathy caused by gene mutation. Its histological features include cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and disarray as well as myocardial fibrosis. Gene mutation, abnormal signal transduction, and abnormal energy metabolism are considered the main mechanisms of myocardial fibrosis. There is a strong correlation between myocardial fibrosis and the occurrence, development, and prognosis of HCM.
INFORMATION:
Citation information: Myocardial Fibrosis in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, Zeyi Cheng, Miaomiao Qi, Chengyuan Zhang and Yanxia Mao, Cardiovasc. Innov. App., 2021, https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0008
Keywords: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; myocardial fibrosis
CVIA is available on the IngentaConnect platform and at Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications. Submissions may be made using ScholarOne Manuscripts. There are no author submission or article processing fees. CVIA is indexed in the EMBASE, ESCI, OCLC, Primo Central (Ex Libris), Sherpa Romeo, NISC (National Information Services Corporation), DOAJ and Index Copernicus Databases. Follow CVIA on Twitter @CVIA_Journal; or Facebook.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-29
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0007, Sharen Lee and Gary Tse from Laboratory of Cardiovascular Physiology, Hong Kong, HKG, China, Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China and Xiamen Cardiovascular Hospital, Xiamen, China consider a case of atezolizumab-induced autoimmune diabetes mellitus presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis.
Atezolizumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor, is a humanized monoclonal, anti-programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody used for the treatment of metastatic urothelial carcinoma that has progressed after chemotherapy. PD-L1 inhibitors can induce type 1 diabetes, and patients can present with diabetic ketoacidosis. ...
2021-03-29
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0006, Li Jingxiu, Zhang Fujun, Wei Xijin and Peng Ding from Anhui Provincial Hospital, Hefei, China, Chizhou Second People's Hospital, Chizhou, China, The Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of TCM, Jinan, China and The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Qingyuan, China consider using three-dimensional Lorenz Scatter Plots to detect patients with atrioventricular node double path caused by interpolated ventricular premature systoles.
A series of related electrophysiology ...
2021-03-29
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0005, Nikhil H. Shah, Steven J. Ross, Steve A. Noutong Njapo, Justin Merritt, Andrew Kolarich, Michael Kaufmann, William M. Miles, David E. Winchester, Thomas A. Burkart, and Matthew McKillop from UF Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Gainesville, FL, USA, UVA Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Charlottesville, VA, USA, The Johns Hopkins Hospital Department of Radiology, Baltimore, MD, USA, The Heart Center, Huntsville, AL, USA, Intermountain Medical Center, St. George, UT, USA and Carolina Cardiology Consultants, Greenville, SC, USA consider appropriate use of implantable ...
2021-03-29
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0001, Zesen Han, Lihong Lai, Zhaokun Pu and Lan Yang from The People's Hospital of Hua County, Henan, China and Henan University of Science and Technology, Henan, China consider the use of nomograms to predict patients with obstructive coronary artery disease.
The authors developed and validated clinical prediction models for the development of a nomogram to estimate the probability of patients having coronary artery disease (CAD).
An individualized clinical prediction model for patients with CAD allowed an accurate estimation in Chinese populations. The Akaike information criterion is a better method in screening risk factors. The ...
2021-03-29
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0002, Pei Huang, Yi Zhang, Yi Tang, Qinghua Fu, Zhaofen Zheng, Xiaoyan Yang, Yingli Yu from The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University) Chang Sha, China and Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China consider the study of the left atrial function index in cardiovascular disease.
Some studies have shown that left ventricular structure and function play an important role in the risk stratification and prognosis of cardiovascular disease. The clinical application of left atrial function in cardiovascular disease has gradually attracted attention in the cardiovascular field.
There are ...
2021-03-29
Hail severity will increase in most regions of the world while Australia and Europe are expected to experience more hailstorms as a result of climate change, an international review led by a UNSW Sydney researcher has found.
The review study, published in Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, examined the effects climate change will have on hail in the future.
It shows a global summary of hail trends from past observations and projected future trends from simulations and models.
The review led to the general expectation that hailstorm frequency will decrease in East Asia and ...
2021-03-29
A study led by scientists at Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) has decoded the genomes of the deep-sea clam (Archivesica marissinica) and the chemoautotrophic bacteria (Candidatus Vesicomyosocius marissinica) that live in its gill epithelium cells. Through analysis of their genomic structures and profiling of their gene expression patterns, the research team revealed that symbiosis between the two partners enables the clams to thrive in extreme deep-sea environments.
The research findings have been published in the academic journal Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Due to the general lack of photosynthesis-derived organic matter, the deep-sea was once considered a ...
2021-03-29
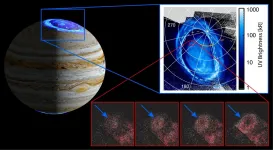
SAN ANTONIO -- March 29, 2021 -- The SwRI-led Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) orbiting Jupiter aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft has detected new faint aurora features, characterized by ring-like emissions, which expand rapidly over time. SwRI scientists determined that charged particles coming from the edge of Jupiter's massive magnetosphere triggered these auroral emissions.
"We think these newly discovered faint ultraviolet features originate millions of miles away from Jupiter, near the Jovian magnetosphere's boundary with the solar wind," said Dr. Vincent Hue, lead author of a paper accepted by the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics. "The solar wind is a supersonic ...
2021-03-29
SPOKANE, Wash. - New research led by scientists at Washington State University has found that a protein known as GBP5 appears to play a key role in suppressing inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, a potentially debilitating disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own joint tissues.
Published in the journal Arthritis & Rheumatology, the discovery could someday lead to new treatments to slow or halt the progress of the disease, which affects an estimated 1.5 million Americans. The researchers said it may also have applications in other inflammatory diseases.
First author ...
2021-03-29
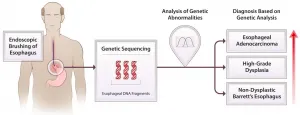
A combination of esophageal brushing and extensive genetic sequencing of the sample collected can detect chromosome alterations in people with Barrett's Esophagus, identifying patients at risk for progressing to esophageal cancer, according to a new study by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and Case Western Reserve University.
In Barrett's Esophagus (BE), chronic acid reflux from the stomach damages the cells lining the lower esophagus, causing them to become more like cells of the lower digestive system. Cells in the lower esophagus progress through several precancerous stages before sometimes developing into esophageal adenocarcinoma, a cancer with a five-year survival rate below 20 percent. BE is the only known precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Clinicians ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Myocardial fibrosis in pathogenesis, diagnosis & treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy