New study finds satellites contribute significant light pollution to night skies
2021-03-29
(Press-News.org) Scientists reported new research results today suggesting that artificial objects in orbit around the Earth are brightening night skies on our planet significantly more than previously understood.
The research, accepted for publication in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters, finds that the number of objects orbiting Earth could elevate the overall brightness of the night sky by more than 10 percent above natural light levels across a large part of the planet. This would exceed a threshold that astronomers set over 40 years ago for considering a location "light polluted".
"Our primary motivation was to estimate the potential contribution to night sky brightness from external sources, such as space objects in Earth's orbit," said Miroslav Kocifaj of the Slovak Academy of Sciences and Comenius University in Slovakia, who led the study. "We expected the sky brightness increase would be marginal, if any, but our first theoretical estimates have proved extremely surprising and thus encouraged us to report our results promptly."
The work is the first to consider the overall impact of space objects on the night sky rather than the effect of individual satellites and space debris affecting astronomers' images of the night sky. The team of researchers, based at institutions in Slovakia, Spain and the US, modelled the space objects' contribution to the overall brightness of the night sky, using the known distributions of the sizes and brightnesses of the objects as inputs to the model.
The study includes both functioning satellites as well as assorted debris such as spent rocket stages. While telescopes and sensitive cameras often resolve space objects as discrete points of light, low-resolution detectors of light such as the human eye see only the combined effect of many such objects. The effect is an overall increase in the diffuse brightness of the night sky, potentially obscuring sights such as the glowing clouds of stars in the Milky Way, as seen away from the light pollution of cities.
"Unlike ground-based light pollution, this kind of artificial light in the night sky can be seen across a large part of the Earth's surface," explained John Barentine, Director of Public Policy for the International Dark-Sky Association and a study co-author. "Astronomers build observatories far from city lights to seek dark skies, but this form of light pollution has a much larger geographical reach."
Astronomers have expressed unease in recent years about the growing number of objects orbiting the planet, particularly large fleets of communications satellites known informally as 'mega-constellations'.
In addition to crowding the night sky with more moving sources of artificial light, the arrival of this technology increases the probability of collisions among satellites or between satellites and other objects, generating further debris. Recent reports sponsored by the US National Science Foundation and the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs identified mega-constellations as a threat to the continued utility of astronomy facilities on the ground and in low-Earth orbit. In the UK the Royal Astronomical Society has established several working groups to understand the impact of mega-constellations on optical and radio astronomical facilities used by scientists.
The results published today imply a further brightening of the night sky proportional to the number of new satellites launched and their optical characteristics in orbit. Satellite operators like SpaceX have recently worked to lower the brightness of their spacecraft through design changes. Despite these mitigating efforts though, the collective effect of a sharp increase in the number of orbiting objects stands to change the experience of the night sky for many across the globe.
The researchers hope that their work will change the nature of the ongoing dialog between satellite operators and astronomers concerning how best to manage the orbital space around the Earth.
"Our results imply that many more people than just astronomers stand to lose access to pristine night skies," Barentine said. "This paper may really change the nature of that conversation."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-29
A team of scientists led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a diagnostic test that can detect the virus that causes COVID-19 even after it has gone through mutations.
Called the VaNGuard (Variant Nucleotide Guard) test, it makes use of a gene-editing tool known as CRISPR, which is used widely in scientific research to alter DNA sequences and modify gene function in human cells under lab conditions, and more recently, in diagnostic applications.
Since viruses have the ability to evolve over time, a diagnostic test robust against potential mutations ...
2021-03-29
Scientists at MIPT have found a possible explanation for the anomalously fast release of gas from nuclear fuel. Supercomputer simulations have uncovered an unexpected mechanism for accelerating the escape of gas bubbles from the uranium dioxide crystal matrix to the surface. The result points the way to eliminate the paradoxical discrepancy of several orders of magnitude between existing theoretical models and experimental results. The paper was published in the Journal of Nuclear Materials.
The diffusion of gas bubbles during reactor operation is one of the important topics in nuclear power relating to radiation safety. Bubbles of gaseous fission products (mainly xenon), accumulating in the fuel, affect many of its properties. Therefore, it is important, ...
2021-03-29
Researchers at the University of Southampton have developed a new way of using nanomaterials to identify and enrich skeletal stem cells - a discovery which could eventually lead to new treatments for major bone fractures and the repair of lost or damaged bone.
Working together, a team of physicists, chemists and tissue engineering experts used specially designed gold nanoparticles to 'seek out' specific human bone stem cells - creating a fluorescent glow to reveal their presence among other types of cells and allow them to be isolated or 'enriched'.
The researchers concluded their new technique is simpler and quicker than other methods and up to 50-500 times more effective at enriching stem cells.
The study, led by Professor ...
2021-03-29
The vast majority of the world's largest meat and dairy companies have not made an explicit commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, finds a new analysis by researchers at New York University.
The study, which appears in the journal Climatic Change, examines the climate impacts of the biggest 35 largest meat and dairy companies around the globe as well as their influence in shaping political responses to climate change.
It is the first peer-reviewed study to assess climate responsibilities of the largest meat and dairy companies.
"Large meat and dairy companies are not doing enough to tackle climate change, and countries are not doing enough in terms of holding them accountable," says Jennifer ...
2021-03-29
Research into the flower preferences of pollinating moths may have delivered a vital clue to the simple factors needed for the emergence of new species.
Strong coevolutionary relationships between plants and animal pollinators have long been recognised as a potential driver of high rates of speciation in the 275,000 extant flowering plants.
Shifts between pollinators, such as bumblebees, hummingbirds, hawkmoths and bats, often coincide with plant speciation events.
Each of these pollinator "guilds" is attracted by a different set of floral traits such as colour, patterns, scent, shape, and nectar reward, collectively known as a pollination ...
2021-03-29
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Why do some people with cold sores around their lips experience painful lesions, while others have no symptoms at all, yet still spread the virus? A new study conducted at Penn State finds that these differences could be due to variations in the way certain strains of herpes simplex (HSV-1) -- the virus that causes cold sores, as well as genital herpes -- activate gene expression in neurons.
"HSV-1 occurs in more than half the global population," said Moriah Szpara, associate professor of biology and biochemistry and molecular biology. "Not only does it cause recurrent problems, such as cold sores ...
2021-03-29
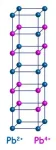
Transition metal perovskites oxides exhibit several desirable properties, including high-temperature superconductivity and electrocatalysis. Now, scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology explore the structure and properties of a perovskite oxide, PbFeO3, in anticipation of the unusual charge distribution and exotic magnetic transitions displayed by such systems. They report two of the magnetic transitions, with a distinctive transition above room temperature and look into its causes, opening doors to potential applications in realizing new spintronic devices.
The advent of electronics has revolutionized our lives to an extent where it is impossible to imagine going about our day without relying on an electronic device in some form. What is even more remarkable, ...
2021-03-29
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0008, Zeyi Cheng, Miaomiao Qi, Chengyuan Zhang and Yanxia Mao from Sichuan University, Sichuan, China, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China and The Second Medical School of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China consider myocardial fibrosis in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
The authors review the application of myocardial fibrosis in the diagnosis and treatment of HCM, focusing on research progress and the application ...
2021-03-29
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0007, Sharen Lee and Gary Tse from Laboratory of Cardiovascular Physiology, Hong Kong, HKG, China, Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China and Xiamen Cardiovascular Hospital, Xiamen, China consider a case of atezolizumab-induced autoimmune diabetes mellitus presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis.
Atezolizumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor, is a humanized monoclonal, anti-programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody used for the treatment of metastatic urothelial carcinoma that has progressed after chemotherapy. PD-L1 inhibitors can induce type 1 diabetes, and patients can present with diabetic ketoacidosis. ...
2021-03-29
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0006, Li Jingxiu, Zhang Fujun, Wei Xijin and Peng Ding from Anhui Provincial Hospital, Hefei, China, Chizhou Second People's Hospital, Chizhou, China, The Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of TCM, Jinan, China and The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Qingyuan, China consider using three-dimensional Lorenz Scatter Plots to detect patients with atrioventricular node double path caused by interpolated ventricular premature systoles.
A series of related electrophysiology ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study finds satellites contribute significant light pollution to night skies