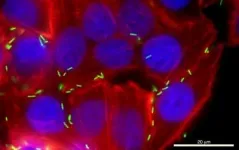
(Press-News.org) March 30, 2021 - As cancer survival rates improve, more people are living with the aftereffects of cancer treatment. For some patients, these issues include chronic radiation-induced skin injury - which can lead to potentially severe cosmetic and functional problems.
Recent studies suggest a promising new approach in these cases, using fat grafting procedures to unleash the healing and regenerative power of the body's natural adipose stem cells (ASCs). "Preliminary evidence suggests that fat grafting can make skin feel and look healthier, restore lost soft tissue volume, and help alleviate pain and fibrosis in patients with radiation-induced skin injury after cancer treatment," says J. Peter Rubin, MD, MBA, FACS, American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) President-Elect and Chair of the Department of Plastic Surgery at University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. He is one of the authors of a new review of the clinical evidence on fat grafting for radiation-induced skin and soft tissue injury.
"But while promising, available research has some key weaknesses that make it difficult for us to determine the true benefits of fat grafting right now," Dr. Rubin adds. The review appears in the April issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the ASPS.
More than half of patients diagnosed with cancer receive radiation therapy. Because skin cells turn over rapidly, they are exquisitely sensitive to the damaging effects of radiation. In the first few months after treatment, many patients develop acute radiation injury with skin inflammation, peeling, swelling, pain and itching. In most cases, symptoms resolve over time. However, if inflammation continues, radiation-induced skin injury can become a chronic problem leading to tight, stiff skin (fibrosis) with a risk of poor wound healing, ulcers, and tissue loss.
Fat grafting procedures - transferring the patient's own fat cells from one part of the body to another - have become widely used in many cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery procedures. In their review, Dr. Rubin and colleagues round up promising research on fat grafting for patients with radiation-induced skin injury.
In studies of breast cancer patients, fat grafting procedures have reduced pain and other symptoms of radiation-induced skin injury - backed up by more-normal cellular appearance of skin cells under the microscope. In other studies, fat grafting has led to reduced risks and better outcomes of breast reconstruction after mastectomy.
For patients with radiation-induced skin injury after treatment for head and neck cancer, fat grafting has led to improvements in voice, breathing, swallowing, and movement. Good outcomes have also been reported in patients with radiation-induced skin injury in the area around the eye or in the limbs.
"The good news is fat grafting has the potential to really help patients with discomfort and disability caused by radiation-induced skin damage," according to Dr. Rubin. While research is ongoing, the benefits of fat grafting seem to result from the wide-ranging effects of ASCs - including anti-scarring, antioxidant, immune-modulating, regenerative, and other actions.
"However," he adds, "the available evidence has a lot of shortcomings, including small sample sizes, lower-quality research designs, and a lack of comparison groups." Variations in fat cell collection and processing, as well as the timing and "dose" of fat grafting, make it difficult to compare results between studies. There are also unanswered questions regarding potential risks related to ASC injection and concerns that fat grafting might affect cancer follow-up.
The reviewers outline some steps for further research to clarify the benefits of fat grafting for radiation-induced skin and soft issue injury, including approaches to clinical assessment and imaging studies, testing of skin biomechanics and circulation, and cellular-level analyses. For all of these outcomes, standardized measures are needed to achieve more comparable results between studies.
"We hope our review will inform efforts to establish the benefits of specific types of fat grafting procedures in specific groups of patients," says Dr. Rubin. "To do that, we'll need studies including larger numbers of patients, adequate control groups, and consistent use of objective outcome measures."
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "Fat Grafting in Radiation-Induced Soft-Tissue Injury: A Narrative Review of the Clinical Evidence and Implications for Future Studies."
DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000007705
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
About Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
For more than 70 years, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® (http://www.prsjournal.com/) has been the one consistently excellent reference for every specialist who uses plastic surgery techniques or works in conjunction with a plastic surgeon. The official journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® brings subscribers up-to-the-minute reports on the latest techniques and follow-up for all areas of plastic and reconstructive surgery, including breast reconstruction, experimental studies, maxillofacial reconstruction, hand and microsurgery, burn repair and cosmetic surgery, as well as news on medico-legal issues.
About ASPS
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons is the largest organization of board-certified plastic surgeons in the world. Representing more than 7,000 physician members, the society is recognized as a leading authority and information source on cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery. ASPS comprises more than 94 percent of all board-certified plastic surgeons in the United States. Founded in 1931, the society represents physicians certified by The American Board of Plastic Surgery or The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the clinicians, nurses, accountants, lawyers, and tax, finance, audit, risk, compliance, and regulatory sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with advanced technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2019 annual revenues of €4.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 19,000 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students with advanced clinical decision support, learning and research and clinical intelligence. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
For more information, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
Giant trees in tropical forests, witnesses to centuries of civilization, may be trapped in a dangerous feedback loop according to a new report in Nature Plants from researchers at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) in Panama and the University of Birmingham, U.K. The biggest trees store half of the carbon in mature tropical forests, but they could be at risk of death as a result of climate change--releasing massive amounts of carbon back into the atmosphere.
Evan Gora, STRI Tupper postdoctoral fellow, studies the role of lightning in tropical forests. Adriane Esquivel-Muelbert, lecturer at the University of Birmingham, studies the effects of climate change in the Amazon. The two teamed up ...
PULLMAN, Wash. - Washington State University researchers have discovered a protein that could be key to blocking the most common bacterial cause of human food poisoning in the United States.
Chances are, if you've eaten undercooked poultry or cross contaminated food by washing raw chicken, you may be familiar with the food-borne pathogen.
"Many people that get sick think, 'oh, that's probably Salmonella,' but it is even more likely it's Campylobacter," said Nick Negretti ('20 Ph.D.), a lead member of the research team in Michael Konkel's Laboratory in WSU's School of Molecular Biosciences.
According to a study on the research recently published ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Researchers from Brown University have discovered a previously unknown type of ancient crater lake on Mars that could reveal clues about the planet's early climate.
In a study published in Planetary Science Journal, a research team led by Brown Ph.D. student Ben Boatwright describes an as-yet unnamed crater with some puzzling characteristics. The crater's floor has unmistakable geologic evidence of ancient stream beds and ponds, yet there's no evidence of inlet channels where water could have entered the crater from outside, and no evidence ...
Judges don't do court stenography. CEOs don't take minutes at meetings. So why do we expect doctors and other health care providers to spend hours recording notes -- something experts know contributes to burnout?
"Having them do so much clerical work doesn't make sense," said Lisa Merlo, Ph.D., an associate professor of psychiatry and director of wellness programs at the University of Florida College of Medicine. "In order to improve the health care experience for everyone, we need to help them focus more on the actual practice of medicine."
Physician burnout affects patients, too. Stressed doctors are less compassionate and more likely to make mistakes. Clinicians who leave the field or cut back hours reduce patient access ...
Mount Sinai researchers have found that a widely available and inexpensive drug targeting inflammatory genes has reduced morbidity and mortality in mice infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. In a study published today in the journal Cell, the team reported that the drug, Topotecan (TPT), inhibited the expression of inflammatory genes in the lungs of mice as late as four days after infection, a finding with potential implications for treatment of humans.
"So far, in pre-clinical models of SARS-CoV-2, there are no therapies--either antiviral, antibody, or plasma--shown to reduce the SARS-CoV-2 disease burden when administered after more than one day post-infection" says senior author Ivan Marazzi, PhD, Associate Professor of Microbiology ...
Research into the diets of a large number of the world's carnivores has been made publicly available through a free, online database created by a PhD student at the University of Sussex.
From stoats in the UK to tigers in India, users are now able to search for detailed information about the diets of species in different geographical locations around the globe.
Created by doctoral student Owen Middleton, CarniDIET is an open-access database which aims to catalogue the diets of the world's carnivores by bringing together past peer-reviewed research. He hopes it will be a useful resource for conservationists and researchers, as well as educators and nature-lovers alike.
Owen said: "There is so much information out ...
A simple plastic water bottle isn't so simple when it comes to the traditional manufacturing process. To appear in its final form, it has to go through a multi-step journey of synthetic procedure, casting, and molding. But what if materials scientists could tap into the same biological mechanisms that create the ridges on our fingertips or the spots on a cheetah in order to manufacture something like a water bottle?
A research paper titled END ...
Preclinical research from VCU Massey Cancer Center published recently in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences shows that the combination of two existing drugs can exploit the metabolic "hunger" of a particularly aggressive type of neuroblastoma to kill cancer cells without inflicting too much collateral damage to healthy tissue.
Neuroblastoma - a type of cancer that strikes the nervous system of very young children - is one of the deadliest pediatric cancers. And children whose neuroblastoma overexpresses the gene MYCN tend to have the worst prognosis.
While medical advancements have led to high cure ...
LOWELL, Mass. - Too often, contends UMass Lowell faculty researcher Brenna Morse, children with complex chronic medical conditions spend days in the hospital undergoing tests for what could be a simple diagnosis.
The challenges include, she says, some children with medical complexities, such as severe neurological conditions and functional impairments, cannot easily signal that they are in pain or point where in their body it is located. Where children not facing such a challenge might be able to have a medical issue resolved with a simple visit to their primary care doctor, others end up hospitalized and going through days of costly testing to arrive at similar diagnoses.
Morse, a UMass Lowell ...
Pink Floyd's Dark Side of the Moon cover, voted the greatest classical rock album of all time, intended to portray the prism and dispersion of light into a rainbow as a certain metaphorical symbolism and a light show that was never celebrated. However, they really were not aware of the fact that this image would be used by many to help illustrate the concept of refractive index and how light changes speed and direction when it encounters a different medium.
Although conceptually the drawing was not accurate, it conveyed the message that light changes its speed when it moves into another medium, and that the different speeds of different colors causes white light to disperse ...