Researchers discover new type of ancient crater lake on Mars
2021-03-30
(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Researchers from Brown University have discovered a previously unknown type of ancient crater lake on Mars that could reveal clues about the planet's early climate.
In a study published in Planetary Science Journal, a research team led by Brown Ph.D. student Ben Boatwright describes an as-yet unnamed crater with some puzzling characteristics. The crater's floor has unmistakable geologic evidence of ancient stream beds and ponds, yet there's no evidence of inlet channels where water could have entered the crater from outside, and no evidence of groundwater activity where it could have bubbled up from below.
So where did the water come from?
The researchers conclude that the system was likely fed by runoff from a long-lost Martian glacier. Water flowed into the crater atop the glacier, which meant it didn't leave behind a valley as it would have had it flowed directly on the ground. The water eventually emptied into the low-lying crater floor, where it left its geological mark on the bare Martian soil.
The type of lake described in this study differs starkly from other Martian crater lakes, like those at Gale and Jezero craters where NASA rovers are currently exploring.
"This is a previously unrecognized type of hydrological system on Mars," Boatwright said. "In lake systems characterized so far, we see evidence of drainage coming from outside the crater, breaching the crater wall and in some cases flowing out the other side. But that's not what is happening here. Everything is happening inside the crater, and that's very different than what's been characterized before."
Importantly, Boatwright says, the crater provides key clues about the early climate of Mars. There's little doubt that the Martian climate was once warmer and wetter than the frozen desert the planet is today. What's less clear, however, is whether Mars had an Earthlike climate with continually flowing water for millennia, or whether it was mostly cold and icy with fleeting periods of warmth and melting. Climate simulations for early Mars suggest temperatures rarely peaking above freezing, but geological evidence for cold and icy conditions has been sparse, Boatwright says. This new evidence of ancient glaciation could change that.
"The cold and icy scenario has been largely theoretical -- something that arises from climate models," Boatwright said. "But the evidence for glaciation we see here helps to bridge the gap between theory and observation. I think that's really the big takeaway here."
Boatwright was able to map out the details of the crater's lake system using high-resolution images taken by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The images revealed a telltale signature of ancient streambeds -- features called inverted fluvial channels. When water flows across a rocky surface, it can leave behind course-grained sediment inside the valley it erodes. When these sediments interact with water, they can form minerals that are harder than the surrounding rock. As further erosion over millions of years whittles the surrounding rock away, the mineralized channels are left behind as raised ridges spidering across the landscape. These features, along with sediment deposits and shoreline features, clearly show where water flowed and ponded on the crater floor.
ut without any sign of an inlet channel where water entered the crater, "the question becomes 'how did these get here?"' Boatwright said.
To figure it out, Boatwright worked with Jim Head, his advisor and a research professor at Brown. They ruled out groundwater activity, as the crater lacked telltale sapping channels that form in groundwater systems. These channels usually appear as short, stubby channels that lack tributaries -- completely opposite from the dense, branching networks of inverted channels observed in the crater. A careful examination of the crater wall also revealed a distinct set of ridges that face upward toward the crater wall. The features are consistent with ridges formed where a glacier terminates and deposits mounds of rocky debris. Taken together, the evidence points to a glacier-fed system, the researchers concluded.
Subsequent research has shown that this crater isn't the only one of its kind. At this month's Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Boatwright presented research revealing more than 40 additional craters that appear to have related features.
Head says that these new findings could be critical in understanding the climate of early Mars.
"We have these models telling us that early Mars would have been cold and icy, and now we have some really compelling geological evidence to go with it," Head said. "Not only that, but this crater provides the criteria we need to start looking for even more evidence to test this hypothesis, which is really exciting."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-30
Judges don't do court stenography. CEOs don't take minutes at meetings. So why do we expect doctors and other health care providers to spend hours recording notes -- something experts know contributes to burnout?
"Having them do so much clerical work doesn't make sense," said Lisa Merlo, Ph.D., an associate professor of psychiatry and director of wellness programs at the University of Florida College of Medicine. "In order to improve the health care experience for everyone, we need to help them focus more on the actual practice of medicine."
Physician burnout affects patients, too. Stressed doctors are less compassionate and more likely to make mistakes. Clinicians who leave the field or cut back hours reduce patient access ...
2021-03-30
Mount Sinai researchers have found that a widely available and inexpensive drug targeting inflammatory genes has reduced morbidity and mortality in mice infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. In a study published today in the journal Cell, the team reported that the drug, Topotecan (TPT), inhibited the expression of inflammatory genes in the lungs of mice as late as four days after infection, a finding with potential implications for treatment of humans.
"So far, in pre-clinical models of SARS-CoV-2, there are no therapies--either antiviral, antibody, or plasma--shown to reduce the SARS-CoV-2 disease burden when administered after more than one day post-infection" says senior author Ivan Marazzi, PhD, Associate Professor of Microbiology ...
2021-03-30
Research into the diets of a large number of the world's carnivores has been made publicly available through a free, online database created by a PhD student at the University of Sussex.
From stoats in the UK to tigers in India, users are now able to search for detailed information about the diets of species in different geographical locations around the globe.
Created by doctoral student Owen Middleton, CarniDIET is an open-access database which aims to catalogue the diets of the world's carnivores by bringing together past peer-reviewed research. He hopes it will be a useful resource for conservationists and researchers, as well as educators and nature-lovers alike.
Owen said: "There is so much information out ...
2021-03-30
A simple plastic water bottle isn't so simple when it comes to the traditional manufacturing process. To appear in its final form, it has to go through a multi-step journey of synthetic procedure, casting, and molding. But what if materials scientists could tap into the same biological mechanisms that create the ridges on our fingertips or the spots on a cheetah in order to manufacture something like a water bottle?
A research paper titled END ...
2021-03-30
Preclinical research from VCU Massey Cancer Center published recently in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences shows that the combination of two existing drugs can exploit the metabolic "hunger" of a particularly aggressive type of neuroblastoma to kill cancer cells without inflicting too much collateral damage to healthy tissue.
Neuroblastoma - a type of cancer that strikes the nervous system of very young children - is one of the deadliest pediatric cancers. And children whose neuroblastoma overexpresses the gene MYCN tend to have the worst prognosis.
While medical advancements have led to high cure ...
2021-03-30
LOWELL, Mass. - Too often, contends UMass Lowell faculty researcher Brenna Morse, children with complex chronic medical conditions spend days in the hospital undergoing tests for what could be a simple diagnosis.
The challenges include, she says, some children with medical complexities, such as severe neurological conditions and functional impairments, cannot easily signal that they are in pain or point where in their body it is located. Where children not facing such a challenge might be able to have a medical issue resolved with a simple visit to their primary care doctor, others end up hospitalized and going through days of costly testing to arrive at similar diagnoses.
Morse, a UMass Lowell ...
2021-03-30
Pink Floyd's Dark Side of the Moon cover, voted the greatest classical rock album of all time, intended to portray the prism and dispersion of light into a rainbow as a certain metaphorical symbolism and a light show that was never celebrated. However, they really were not aware of the fact that this image would be used by many to help illustrate the concept of refractive index and how light changes speed and direction when it encounters a different medium.
Although conceptually the drawing was not accurate, it conveyed the message that light changes its speed when it moves into another medium, and that the different speeds of different colors causes white light to disperse ...
2021-03-30
Sausalito, Calif. (March 30, 2021) - After more than three decades of research, scientists have proven that the cancer affecting up to one in four adult California sea lions necrospied at The Marine Mammal Center in Sausalito, CA, is caused by a sexually transmitted herpesvirus. The cancer, known as sea lion urogenital carcinoma, has clear parallels to cervical cancer in humans and provides a helpful model for human cancer study.
Scientists have long suspected this cancer was associated with a virus, but this is the first study to prove this theory. The study, which was published in Animals, an open-access, peer-reviewed journal, concluded that genital herpesvirus is ...
2021-03-30
WASHINGTON, March 30, 2021 -- Emerging technologies can screen for cervical cancer better than Pap smears and, if widely used, could save lives both in developing nations and parts of countries, like the United States, where access to health care may be limited.
In Biophysics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, scientists at Massachusetts General Hospital write advances in nanotechnology and computer learning are among the technologies helping develop HPV screening that take the guesswork out of the precancer tests. That could mean better screening in places that lack highly trained doctors and advanced laboratories.
Cervical cancer is the world's fourth-most common cancer, with more than ...
2021-03-30
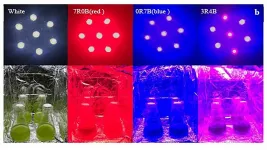
WASHINGTON, March 30, 2021 -- As ethanol, biodiesel, and other biofuels continue to present challenges, such as competing with food security or lacking the technology for more efficient and low-cost production, microalgae are gaining momentum as a biofuel energy crop.
In their paper, published in the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, Yangzhou University researchers in China show how a combination of monochromatic red and blue LED illumination on one type of microalga can enhance its growth and increase the biosynthesis of critical components, such ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers discover new type of ancient crater lake on Mars