INFORMATION:
A brain signature that predicts vulnerability to addiction
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) A team of neurobiologists at the Institut de Neurosciences de la Timone (CNRS/Aix-Marseille Université) has just shown that within a population of rats it can predict which will become cocaine addicts. One of the criteria for addiction in rats is the compulsive search for a drug despite its negative consequences. Scientists observed abnormal activity in a specific region of the brain, the subthalamic nucleus, only in future addicted individuals, and did so before they were exposed to 'punishment' associated with the seeking for the drug. These results, which have just been published online by PNAS, also indicate that it is possible to reduce this compulsive cocaine-seeking behaviour in rats by stimulating the subthalamic nucleus, confirming its interest as a target in the treatment of addiction.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
International study shows alternative seafood networks provided resiliency during pandemic
2021-03-31
Local alternative seafood networks (ASNs) in the United States and Canada, often considered niche segments, experienced unprecedented growth in the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic while the broader seafood system faltered, highlighting the need for greater functional diversity in supply chains, according to a new international study led by the University of Maine.
The spike in demand reflected a temporary relocalization phenomenon that can occur during periods of systemic shock -- an inverse yet complementary relationship between global and local seafood systems that contributes to the resilience of regional food systems, according to the research team, which published its findings in Frontiers in Sustainable ...
Study reveals large and unequal health burden from air pollution in California's Bay Area
2021-03-31
WASHINGTON (March 31, 2021)-- New research published today in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives from Environmental Defense Fund and the George Washington University shows air pollution takes an enormous toll on health in the San Francisco Bay Area, and the impacts vary dramatically within neighborhoods. The magnitude of the health burden from pollution demonstrates the need for urgent action to cut air pollution and protect health, particularly in areas facing the highest impacts.
The analysis estimated that exposure to particle pollution (soot) resulted in more than 3,000 deaths and 5,500 new childhood asthma cases every year in the ...
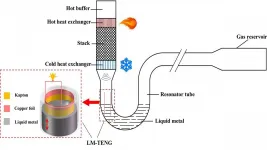
Thermal power nanogenerator created without solid moving parts
2021-03-31
WASHINGTON, March 31, 2021 -- As environmental and energy crises become increasingly more common occurrences around the world, a thermal energy harvester capable of converting abundant thermal energy -- such as solar radiation, waste heat, combustion of biomass, or geothermal energy -- into mechanical energy appears to be a promising energy strategy to mitigate many crises.
The majority of thermal power generation technologies involve solid moving parts, which can reduce their reliability and lead to frequent maintenance. This inspired researchers in China to develop a thermal power nanogenerator without solid moving parts.
In Applied Physics Letters, from ...
Why SARS-CoV-2 replicates better in the upper respiratory tract
2021-03-31
"SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV are highly similar genetically, generate a homologous repertoire of viral proteins, and use the same receptor to infect human cells. However, despite these similarities, there are also important differences between the two viruses", says Ronald Dijkman from the Institute for Infectious Diseases (IFIK) at the University of Bern. For example, SARS-CoV infection is characterized by severe disease and inflammation in the lower respiratory tract and infected individuals are only contagious after the onset of symptoms, making it easier to identify and interrupt infection chains.
In contrast, SARS-CoV-2 preferentially replicates in the upper airways (nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea) and can be efficiently transmitted ...
Study: Firms recruit dark personalities for earnings management
2021-03-31
Companies could be hiring that bad boss on purpose. According to new research in the Journal of Business Ethics, the "dark" personality traits - questionable ethical standards, narcissistic tendencies - that make a boss bad also make that person much more likely to go along with manipulating earnings and may be the reason they got the job in the first place.
Co-authors Nick Seybert (University of Maryland's Robert H. Smith School of Business), Ling Harris (University of Nebraska-Lincoln), Scott Jackson (University of South Carolina) and Joel Owens (Portland State University) studied the process of hiring executive ...
For people with dementia in assisted living, quality of life improves with mindful care
2021-03-31
ATLANTA -- Assisted living communities can improve the quality of life for residents with dementia by approaching them as individuals and attempting to include all residents in activities, according to a study led by a Georgia State University gerontology researcher.
The typical "activity programming" at many assisted living residences can leave people with dementia on the sidelines, according to the study, "Meaningful Engagement Among Assisted Living Residents With Dementia: Successful Approaches," published in the Journal of Applied Gerontology.
The study found that the keys to improving ...
Field hospitals: The role of an academic medical center
2021-03-31
ANN ARBOR--By April last year, up to 28 free-standing alternate care sites ranging in size from 50 to 3,000 beds were underway or finished in the U.S.--the Michigan Medicine Field Hospital among them.
This 500-bed alternate care site was planned and construction underway from March through May to meet the estimated surge in COVID-19 patients, expected to overrun hospitals nationwide and in Michigan. Sue Anne Bell, assistant professor of nursing and a disaster expert, was one of the field hospital's five-member leadership team.
Bell and her ...
Study finds that masks make little difference to facial identification
2021-03-31
But the study also shows for the first time that performance may be improved by using super recognisers - people who are very skilled at recognising faces. It also reveals that masks do make recognising someone's emotions more difficult.
There are many questions surrounding face masks and the impact that masks will have on face identification. Can we recognise the faces of people who we know well if they are wearing a mask? And, relevant to policing and security scenarios or a supermarket ID check, can an unfamiliar face be recognized across images if it is masked? And how do masks impact our ability to recognize a person's emotions?
Dr Noyes is Senior Lecturer in Cognitive Psychology and conducted the study, published by the Royal ...
Studies of U.S. national parks focused on popular parks, trending down
2021-03-31
Research conducted in U.S. national parks has focused largely on five iconic parks, with more than a third of academic papers focused on Yellowstone National Park, researchers from North Carolina State University found in a new analysis.
They also found that the number of publications per year increased during the 1990s and 2000s, but has dropped since 2013. The findings, published in the journal Conservation Science and Practice, were drawn from an analysis of nearly 7,000 published, peer-reviewed studies conducted at U.S. designated national parks since 1970.
"Looking at the data was a surprise and perhaps a wake-up call," said the study's lead author Jelena Vukomanovic, assistant professor of ...
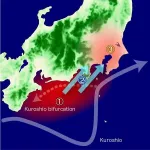
Kuroshio current may be responsible for climatic discomfort in Tokyo, scientists find
2021-03-31
Forty million people living in the Kanto region of Japan, which includes Tokyo, may be able to blame a meandering ocean current for increasing hot and humid summers, according to an analysis conducted by an international team of researchers. The Kuroshio Current flows north, bringing warm water from the tropics to Japan's southern coast. Since 2017, however, it has meandered off its traditional path, turning south before continuing north again. Now, scientists have found that the "large meander" is responsible for the uptick in humidity and temperature.
The researchers, from Tohoku University in Japan and the University of Hawaii in the United States, published ...