Steroid hormone could reduce risk of preterm birth for high-risk single baby pregnancies
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) Taking progestogens - steroid hormones - during pregnancy could reduce the risk of preterm birth in high-risk single baby pregnancies, research has shown.
Although these compounds have been in use for some time, results of individual clinical trials investigating their effectiveness in preventing preterm birth have been conflicting, and so further evaluation of the research evidence was needed.
University of York researchers led the Evaluating Progestogens for Prevention of Preterm Birth International Collaborative (EPPPIC) project, a systematic review which brought together and re-analysed datasets from 31 clinical trials of progestogens, including more than 11,000 women and 16,000 babies worldwide.
Professor Lesley Stewart, the project principal investigator and Director of the University of York's Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, said: "Babies born preterm are at greater risk, of health problems during infancy and of death during their first year. It is therefore essential to have reliable information about how well these interventions work, and for this we need systematic and rigorous evaluation of large amounts of data.
"We hope that our findings will help inform shared decision-making between clinicians and expectant mothers who are considered at high-risk of preterm birth."
Data was obtained from trials of vaginal progesterone given as a gel or pessary, and from trials of 17-OHPC, given as an injection. The project looked separately at trial data from twin and triplet pregnancies. It is the first meta-analysis using raw data from individual pregnancies of 17-OHPC in single baby pregnancies and the first to examine both compounds together.
Both vaginal progesterone and 17-OHPC reduced the risk of preterm birth before 34 weeks for high-risk single baby pregnancies - mostly for women who had experienced a previous preterm birth or had a short cervix in their current pregnancy.
There was a consistent benefit for other outcomes including fetal and baby deaths and serious neonatal complications, including infection and lung and eye problems.
In contrast, analysis showed no evidence that either vaginal progesterone or 17-OHPC was useful for twin or triplet pregnancies with no other risk factors.
Professor Zarko Alfirevic, Coordinating Editor of Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth and member of the EPPPIC Secretariat, said: "Consistency of the results across so many different trials is quite remarkable and should be very reassuring to clinicians, but even more importantly to pregnant women and their families."
INFORMATION:
The study, published in Lancet, is funded through a Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute® award.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
Microbial life already had the necessary conditions to exist on our planet 3.5 billion years ago. This was the conclusion reached by a research team after studying microscopic fluid inclusions in barium sulfate (barite) from the Dresser Mine in Marble Bar, Australia. In their publication "Ingredients for microbial life preserved in 3.5-billion-year-old fluid inclusions," the researchers suggest that organic carbon compounds which could serve as nutrients for microbial life already existed at this time. The study by first author Helge Mißbach (University of Göttingen, Germany) was published in the journal ...
2021-03-31
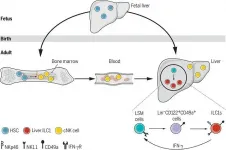
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Science (CAS), teamed up with scientists from Aix Marseille University, discovered that hematopoietic progenitors possessed the differentiation potential to type 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILC1s) in adult liver, and dissected the regulation mechanisms of such cell differentiation, revealing the pathways that lead to the development of tissue-resident lymphocytes. This study was published in Science.
Hematopoiesis occurs at different sites following the development of human body. After birth, the bone marrow (BM) has long been known to be the main hematopoietic organ ...
2021-03-31
ST segment-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a particularly severe type of heart attack associated with a high risk of mortality or long-term disability. Clinicians can reduce a patient's chances of unfavorable outcomes by performing a procedure known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), which combines coronary angioplasty--in which a balloon is inserted into a blocked artery of the heart to clear it--with stenting--inserting a tiny tube into a blocked artery to keep the line open. But studies in China have found that many patients with STEMI choose not to undergo PCI and that women with STEMI, in particular, have a reduced likelihood of undergoing guideline-based ...
2021-03-31
By harvesting energy from their surrounding environments, particles named 'artificial micromotors' can propel themselves in specific directions when placed in aqueous solutions. In current research, a popular choice of micromotor is the spherical 'Janus particle' - featuring two distinct sides with different physical properties. Until now, however, few studies have explored how these particles interact with other objects in their surrounding microenvironments. In an experiment detailed in EPJ E, researchers in Germany and The Netherlands, led by Larysa Baraban at Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, show for the first time how the velocities of Janus particles relate to the physical properties of nearby barriers.
The team's discoveries could help researchers to engineer micromotors which ...
2021-03-31
Children with a common but regularly undiagnosed disorder affecting their language and communication are likely to be finding the transition back to school post-lockdown harder than most, according to a team of psychologists.
Two children in every class of 30 are estimated to have Developmental Language Disorder (DLD) (around 8%), yet public awareness, diagnosis and referral to speech and language therapists all remain low in the UK.
DLD is a condition where children have problems acquiring their own language for no obvious reasons. Unlike temporary language delay (which reflects the natural variation of age at which children learn to speak and communicate), DLD is a lifelong condition with significant impacts for individuals in childhood and in later life, in particular their ...
2021-03-31
Lakes store huge amounts of methane. In a new study, environmental scientists at the University of Basel offer suggestions for how it can be extracted and used as an energy source in the form of methanol.
Discussion about the current climate crisis usually focuses on carbon dioxide (CO2). The greenhouse gas methane is less well known, but although it is much rarer in the atmosphere, its global warming potential is 80 to 100 times greater per unit.
More than half the methane caused by human activities comes from oil production and agricultural fertilizers. But the gas is also created by the natural decomposition of biomass by ...
2021-03-31
Scientists from Trinity College Dublin believe they have pinpointed our most distant animal relative in the tree of life and, in doing so, have resolved an ongoing debate. Their work finds strong evidence that sponges - not more complex comb jellies - were our most distant relatives.
Sponges are structurally simple, lacking complex traits such as a nervous system, muscles, and a though-gut. Logically, you would expect these complex traits to have emerged only once during animal evolution - after our lineage diverged from that of sponges - and then be retained in newly evolved creatures thereafter.
However, a debate has been raging ever since phylogenomic studies found evidence that our most distant ...
2021-03-31
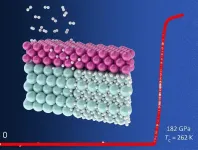
Superalloys that withstand extremely high temperatures could soon be tuned even more finely for specific properties such as mechanical strength, as a result of new findings published today.
A phenomenon related to the invar effect - which enables magnetic materials such as nickel-iron (Ni-Fe) alloys to keep from expanding with increasing temperature - was reported to have been discovered in paramagnetic, or weakly magnetized, high-temperature alloys.
Levente Vitos, Professor at KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, says the breakthrough research, which includes a general theory explaining the new invar effect, promises to advance the design of high-temperature alloys with exceptional mechanical stability. The article was published in the Proceedings ...
2021-03-31
The higher the number of plant and bird species in a region, the healthier the people who live there. This was found by a new study published in Landscape and Urban Planning and led by the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), the Senckenberg Biodiversity and Climate Research Centre (SBiK-F) and the Christian Albrechts University (CAU) in Kiel. The researchers found that, in particular, mental health and higher species diversity are positively related, whereas a similar relationship between plant or bird species and physical health could not be proven.
The study led by researchers from iDiv, SBiK-F and CAU provides ...
2021-03-31
University of Rochester researchers who demonstrated superconducting materials at room temperatures last fall, now report a new technique in the quest to also create the materials at lower pressures.
In a paper published in Physical Review Letters, the lab of Ranga Dias, assistant professor of mechanical engineering and of physics and astronomy, describes separating hydrogen atoms from yttrium with a thin film of palladium.
"This is a completely new technique that nobody has used before for high pressure superhydride synthesis," Dias says.
Hydrogen rich materials are critical in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Steroid hormone could reduce risk of preterm birth for high-risk single baby pregnancies