(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA--What's the difference between a giggle and a belly laugh? Or a yelp and an all-out scream? In many species, including humans, the volume and duration of a verbal sound conveys as much information as the noise itself.
A group of scientists, led by Scripps Research, has discovered a node in the brains of male mice that modulates the sounds they make in social situations. This discovery, published in Nature, could help identify similar locations in the human brain, and potentially lead to a better understanding of social disorders such as autism or depression.
"Identifying this node gives us signatures of what to look for when human behavior goes awry," says Lisa Stowers, PhD, a neuroscientist and professor at Scripps Research who led the study. "It's giving us clues to how information is organized in the brain, and how different features of information can be separated out in different brain regions."
As part of their courtship behavior, male mice produce "songs." These complicated whistles, which are too high for the human ear to detect, are louder and longer when the female mouse is nearby or when her scent is stronger. The researchers identified a specific type of neuron in a part of the hypothalamus called the lateral preoptic area that controls the emotional regulation of these sounds.
"The hypothalamus and the rest of the limbic system control body functions such as hunger, thirst and temperature regulation, as well as the basic features of emotional behavior like sex and fear," Stowers says. "It is fitting that the emotional aspect of these social noises are generated in this region of the brain."
By directly stimulating the right nodes from these neurons, the scientists could trigger the whole array of noises that go into a mouse song. Varying the level of stimulation allowed them to control how enthusiastic those sounds were.
When the researchers blocked these nodes, male mice encountering a female would attempt to court her in silence. (Female mice responded by kicking the males and running away.) If the researchers bypassed these nodes and activated the next node downstream, the male mice only made long, loud noises.
"They're basically just shouting," Stowers says. "By finding these neurons, it's telling us that this part of the brain is doing this emotional scaling and persistence. If you take that away, then you lose all of that affect, all of that emotional range, and the ability to have effective social communication."
Most research on noise production in the brain has focused on language development, Stowers says. But the sounds that even an infant can make--a giggle, a cry, a scream--don't have to be learned and are just as vital for communication. Identifying how the brain decides on these responses is the first step to understanding where things can go wrong in social behavioral disorders such as autism and depression.
"We are starting to get a detailed look at where in the brain different types of computations are being made," Stowers says. "Now that we know that this simple behavior is regulated in the hypothalamus, we can study whether others behaviors are also using similar circuits and if so, perhaps find a common mechanism--and drug target--for when emotions are not generated appropriately."
INFORMATION:
The study, "Flexible scaling and persistence of social vocal communication," was authored by Jingyi Chen, Jeffrey Markowitz, Varoth Lilascharoen, Sandra Taylor, Pete Sheurpukdi, Jason Keller, Jennifer Jensen, Byung Kook Lim, Sandeep Robert Datta and Lisa Stowers.
Funding was provided by the Dorris Neuroscience and Skaggs Scholarships, the Anandamahidol Foundation Fellowship, Career Award at the Scientific Interface from BWF and the National Institutes of Health (R01NS097772, R01DA049787, R01NS108439).
Harvard University researchers have identified the biological mechanism of how chronic stress impairs hair follicle stem cells, confirming long-standing observations that stress might lead to hair loss.
In a mouse study published in the journal Nature, the researchers found that a major stress hormone causes hair follicle stem cells to stay in an extended resting phase, without regenerating the hair follicle and hair. The researchers identified the specific cell type and molecule responsible for relaying the stress signal to the stem cells, and showed that this pathway can be potentially targeted to restore hair growth.
"My lab is interested in understanding how stress affects ...
Swansea University physicists, as leading members of the ALPHA collaboration at CERN, have demonstrated laser cooling of antihydrogen atoms for the first time. The groundbreaking achievement produces colder antimatter than ever before and enables an entirely new class of experiments, helping scientists learn more about antimatter in future.
In a paper published today in Nature, the collaboration reports that the temperature of antihydrogen atoms trapped inside a magnetic bottle is reduced when the atoms scatter light from an ultraviolet laser beam, slowing the atoms down and reducing the space they occupy in the bottle -- both vital aspects of future more detailed ...
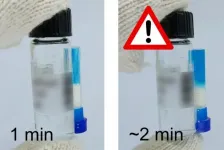
Scientists have developed vaccines for COVID-19 with record speed. The first two vaccines widely distributed in the U.S. are mRNA-based and require ultracold storage (-70 C for one and -20 C for the other). Now, researchers reporting in ACS Omega have developed a tamper-proof temperature indicator that can alert health care workers when a vial of vaccine reaches an unsafe temperature for a certain period, which could help ensure distribution of effective mRNA vaccines.
The two COVID mRNA vaccines contain instructions for building harmless pieces of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Once the vaccine is injected into the body, human cells use the mRNA instructions to make the spike protein, which they temporarily ...
Increased consumption of flavanols - a group of molecules occurring naturally in fruit and vegetables - could protect people from mental stress-induced cardiovascular events such as stroke, heart disease and thrombosis, according to new research.
Researchers have discovered that blood vessels were able to function better during mental stress when people were given a cocoa drink containing high levels of flavanols than when drinking a non-flavanol enriched drink.
A thin membrane of cells lining the heart and blood vessels, when functioning efficiently the endothelium helps ...
LAWRENCE -- New research from the University of Kansas END ...
Meat and fish fraud are global problems, costing consumers billions of dollars every year. On top of that, mislabeling products can cause problems for people with allergies, religious or cultural restrictions. Current methods to detect this fraud, while accurate, are slower than inspectors would like. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry have optimized their handheld MasSpec Pen to identify common types of meat and fish within 15 seconds.
News stories of food fraud, such as beef being replaced with horse ...
SAN ANTONIO (March 31, 2021) -- Insomnia and obstructive sleep apnea have increased dramatically among active-duty military members over a 14-year period, 2005 through 2019.
Insomnia increased 45-fold and sleep apnea went up more than 30-fold, according to a study led by The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio).
The study found that the most likely military member to be diagnosed with either sleep disorder was married, male, white, a higher-ranking enlisted Army service member and age 40 or older.
The researchers compared medical codes that represent diagnosis of sleep apnea or insomnia in active-duty Army, Navy, Marine Corps and Air Force personnel. No medical ...
Risks of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection for long-stay nursing home residents were mainly dependent on factors in their nursing homes and surrounding communities, according to a large study led by a researcher at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
By contrast, the study found that the risks of being hospitalized with, and of dying from, COVID-19, depended more on patient-specific characteristics such as age and body mass index--although the mix of factors linked to hospitalization was distinct from the mix of factors linked to mortality.
The study, which appears online March 31 in JAMA Network Open, detailed COVID-19 risk factors among more than 480,000 long-stay nursing home residents in the ...
Roughly five years ago, Institute Head Prof. Dr. William (Bill) Martin and his team introduced the last universal common ancestor of all living organisms and named it "LUCA". It lived approximately 3.8 billion years ago in hot deep sea hydrothermal vents.
Now the evolutionary biologists in Duesseldorf have described a further ancient cell named "LBCA" ("Last Bacterial Common Ancestor"). It is the ancestor of today's largest domain of all living organisms: Bacteria. In Communications Biology, they report on their new research approaches which led to the successful prediction ...
Every day, people are exposed to microplastics from food, water, beverages and air. But it's unclear just how many of these particles accumulate in the human body, and whether they pose health risks. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have developed a lifetime microplastic exposure model that accounts for variable levels from different sources and in different populations. The new model indicates a lower average mass of microplastic accumulation than previous estimates.
Microplastics, which are tiny pieces of plastic ranging in size from 1 μm to 5 mm (about the ...