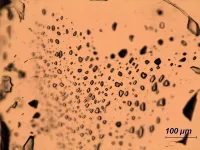
In search of the first bacterium
Evolutionary biology: Publication in Communications Biology
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) Roughly five years ago, Institute Head Prof. Dr. William (Bill) Martin and his team introduced the last universal common ancestor of all living organisms and named it "LUCA". It lived approximately 3.8 billion years ago in hot deep sea hydrothermal vents.
Now the evolutionary biologists in Duesseldorf have described a further ancient cell named "LBCA" ("Last Bacterial Common Ancestor"). It is the ancestor of today's largest domain of all living organisms: Bacteria. In Communications Biology, they report on their new research approaches which led to the successful prediction of the biochemistry of LBCA and its phylogenetic links.
Bacteria are almost as old as life itself. LBCA lived around 3.5 billion years ago in a similar environment to LUCA. In order to unlock LBCA's genetic code, its properties and its story, the research team examined the genomes of 1,089 bacterial anaerobes or bacteria that survive without oxygen. "Abandoning aerobes made sense for our work", explains first author Dr. Joana C. Xavier. "If bacteria originated at a time when the Earth was anoxic, it does not make sense to investigate their origin considering species full of adaptations caused by oxygen."
Higher life forms pass on their genetic code from parent to offspring via vertical gene transfer. As a result, the genome provides information on phylogenetic history. But bacteria are masters in another form of gene transfer, namely lateral gene transfer (LGT). This allows bacteria to exchange genetic information across different strains. This posed a major challenge in reconstructing the LBCA genome, as it renders the traditional phylogenetic methods incapable of inferring the root in the bacterial evolutionary tree.
For this reason, the researchers in Duesseldorf used biochemical networks together with thousands of individual trees. They investigated 1,089 anaerobic genomes and identified 146 protein families conserved in all bacteria. These proteins make up a nearly complete core metabolic network.
To complete LBCA's biochemistry, just nine further genes had to be added for the reconstructed metabolic network to include all essential and universal metabolites. To be fully independent and self-generated, LBCA's network would still require further genes inherited from the last universal common ancestor, LUCA, and nutrients from the environment.
With LBCA's metabolic network in hand, the authors then used statistical methods to determine which of the modern bacterial groups are most similar to LBCA. They did this using a method called Minimal Ancestor Deviation, MAD, previously developed by one of the co-authors, Fernando D. K. Tria: "The analyses revealed that the earliest branch of Bacteria to diverge was most similar to modern Clostridia, followed closely by Deltaproteobacteria, Actinobacteria and some members of Aquifex. In common, these groups have the acetyl-CoA pathway for carbon fixation and/or energy metabolism."
Prof. William Martin, senior author of the study, explains: "This is the only carbon fixation pathway present in both archaea and bacteria and that traces to LUCA. This result, obtained independently, is also in line with our most recent findings on the origin and early evolution of life in hydrothermal vents."
"We can infer with confidence that LBCA was most likely rod-shaped", says Xavier. "If it was similar to Clostridia, it is possible that LBCA was able to sporulate." This hypothesis was recently laid out by other researchers "and is highly compatible with our results", says Xavier. Forming spores would allow early cells to survive the inhospitable environment of the early Earth.
INFORMATION:
The authors went further to determine if lateral gene transfer played a role in the era of LBCA. Fernando D. K. Tria explains: "LBCA genes are much more vertical than your average bacterial gene, which indicates that they are very ancient."
Original publication
Xavier, J.C., Gerhards, R.E., Wimmer, J.L.E. et al., The metabolic network of the last bacterial common ancestor, Commun Biol 4, 413 (2021).
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-01918-4
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
Every day, people are exposed to microplastics from food, water, beverages and air. But it's unclear just how many of these particles accumulate in the human body, and whether they pose health risks. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have developed a lifetime microplastic exposure model that accounts for variable levels from different sources and in different populations. The new model indicates a lower average mass of microplastic accumulation than previous estimates.
Microplastics, which are tiny pieces of plastic ranging in size from 1 μm to 5 mm (about the ...
2021-03-31
In Brazil, researchers are puzzling over socioeconomic and environmental indicators that do not add up. They are concerned with what they call the São Paulo Macrometropolitan Area, a mega-region comprising five metropolitan areas in the state of São Paulo with a total of 180 municipalities, some of which provide ecosystem services while others receive them. The problem is that the former, which provide the others with water, food and power generation inputs, suffer from steep inequities in terms of defective human development and lack of social inclusion.
"Urban centers have always been ...
2021-03-31
Glass, rubber and plastics all belong to a class of matter called amorphous solids. And in spite of how common they are in our everyday lives, amorphous solids have long posed a challenge to scientists.
Since the 1910s, scientists have been able to map in 3D the atomic structures of crystals, the other major class of solids, which has led to myriad advances in physics, chemistry, biology, materials science, geology, nanoscience, drug discovery and more. But because amorphous solids aren't assembled in rigid, repetitive atomic structures like crystals are, they have defied researchers' ability to determine their atomic structure with the same level of precision.
Until now, that is. ...
2021-03-31
Sugar practically screams from the shelves of your grocery store, especially those products marketed to kids.
Children are the highest consumers of added sugar, even as high-sugar diets have been linked to health effects like obesity and heart disease and even impaired memory function.
However, less is known about how high sugar consumption during childhood affects the development of the brain, specifically a region known to be critically important for learning and memory called the hippocampus.
New research led by a University of Georgia faculty member in collaboration with a University ...
2021-03-31
LAWRENCE, KANSAS -- The phrase "to see red" means to become angry. But for investors, seeing red takes on a whole different meaning.
William BazleyThat's the premise behind a new article by William Bazley, assistant professor of finance at the University of Kansas.
"Visual Finance: The Pervasive Effects of Red on Investor Behavior" reveals that using the color red to represent financial data influences individuals' risk preferences, expectations of future stock returns and trading decisions. The effects are not present in people who are colorblind, and they're muted in China, where red represents prosperity. Other colors do not generate the same outcomes.
The ...
2021-03-31
As demand for low-carbon electricity rises around the world, nuclear power offers a promising solution. But how many countries are good candidates for nuclear energy development?
A new study in the journal Risk Analysis suggests that countries representing more than 80 percent of potential growth in low-carbon electricity demand--in Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa--may lack the economic or institutional quality to deploy nuclear power to meet their energy needs. The authors suggest that if nuclear power is to safely expand its role in mitigating climate change, countries need to radically improve their ability to manage the technology.
"Efforts to enhance institutional quality in these countries must be redoubled and could well be one of the ...
2021-03-31
Taking progestogens - steroid hormones - during pregnancy could reduce the risk of preterm birth in high-risk single baby pregnancies, research has shown.
Although these compounds have been in use for some time, results of individual clinical trials investigating their effectiveness in preventing preterm birth have been conflicting, and so further evaluation of the research evidence was needed.
University of York researchers led the Evaluating Progestogens for Prevention of Preterm Birth International Collaborative (EPPPIC) project, a systematic review which brought together and re-analysed datasets from 31 clinical trials of progestogens, including more than 11,000 women and 16,000 babies ...
2021-03-31
Microbial life already had the necessary conditions to exist on our planet 3.5 billion years ago. This was the conclusion reached by a research team after studying microscopic fluid inclusions in barium sulfate (barite) from the Dresser Mine in Marble Bar, Australia. In their publication "Ingredients for microbial life preserved in 3.5-billion-year-old fluid inclusions," the researchers suggest that organic carbon compounds which could serve as nutrients for microbial life already existed at this time. The study by first author Helge Mißbach (University of Göttingen, Germany) was published in the journal ...
2021-03-31
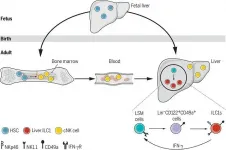
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Science (CAS), teamed up with scientists from Aix Marseille University, discovered that hematopoietic progenitors possessed the differentiation potential to type 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILC1s) in adult liver, and dissected the regulation mechanisms of such cell differentiation, revealing the pathways that lead to the development of tissue-resident lymphocytes. This study was published in Science.
Hematopoiesis occurs at different sites following the development of human body. After birth, the bone marrow (BM) has long been known to be the main hematopoietic organ ...
2021-03-31
ST segment-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a particularly severe type of heart attack associated with a high risk of mortality or long-term disability. Clinicians can reduce a patient's chances of unfavorable outcomes by performing a procedure known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), which combines coronary angioplasty--in which a balloon is inserted into a blocked artery of the heart to clear it--with stenting--inserting a tiny tube into a blocked artery to keep the line open. But studies in China have found that many patients with STEMI choose not to undergo PCI and that women with STEMI, in particular, have a reduced likelihood of undergoing guideline-based ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] In search of the first bacterium
Evolutionary biology: Publication in Communications Biology