(Press-News.org) As demand for low-carbon electricity rises around the world, nuclear power offers a promising solution. But how many countries are good candidates for nuclear energy development?
A new study in the journal Risk Analysis suggests that countries representing more than 80 percent of potential growth in low-carbon electricity demand--in Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa--may lack the economic or institutional quality to deploy nuclear power to meet their energy needs. The authors suggest that if nuclear power is to safely expand its role in mitigating climate change, countries need to radically improve their ability to manage the technology.
"Efforts to enhance institutional quality in these countries must be redoubled and could well be one of the things on which the future of nuclear power as a low carbon energy solution hinges," says co-author Michael J. Ford, a nuclear energy and public policy expert with Argonne National Laboratory who conducted much of this study while at Carnegie Mellon University.
Ford and his colleague Ahmed Abdulla, an expert in energy system design at Carleton University in Ottawa, assessed the relative nuclear power readiness of 126 countries using Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) to benchmark performance across nations.
While previous studies have evaluated the role that nuclear power could play in global decarbonization based on the low-carbon electricity needs of different countries, this research focused on developing a method to integrate economic risks and institutional risks into that evaluation.
The researchers analyzed 126 nations across a 15-year time period from 2001 to 2015, dividing them into three categories by grid size. Nations with bigger electric power systems--an installed generating capacity greater than 10 GWe-- were analyzed for their capability of installing traditional "gigawatt scale" reactors. Nations with very small electric grids (less than 500 MWe) were assumed to be best served by "micro-reactors" (producing 20MWe or less), and those in between were nations best served by a Small Modular Reactor (SMR) with an output of 20 MWe to 300MWe. SMRs and micro-reactors are emerging advanced nuclear power technologies that offer a more affordable way for countries to enter the nuclear energy market.
Once risk is taken into account, the study suggests that the vast majority (80%) of nuclear power would be deployed in richer countries with better institutions. Meanwhile, the vast majority of future low-carbon energy need (>85%) is in poorer countries with relatively weaker institutions.
Despite the weaker performance of many nations with rapidly growing energy demand, the authors note that these nations may still have the potential to develop nuclear programs if supported in developing an improved governance structure.
Several growing Asian and Middle Eastern nations--Malaysia, Vietnam, Brunei, Oman, and Qatar--demonstrated above-median economic and institutional performance. These nations would be leading candidates for new nuclear development with SMRs and micro-reactors. Others, like Thailand and Saudi Arabia, are strong economically but weaker institutionally, requiring more attention in capacity building.
The authors argue that nuclear development programs must focus on reducing institutional risks, not just cost. "Nuclear power brings security concerns regarding proliferation and weapons development," says Ford. "This is why it's prudent to investigate institutional risk factors like corruption, regulatory quality, rule of law, and political stability--especially when we're talking about deploying nuclear power in new countries."
One way to increase nuclear energy capacity in higher risk nations is an arrangement known as build-own-operate (BOO). In this situation, a technology developer finances, builds, owns, and operates a power plant--effectively transforming the electric utility from an infrastructure owner to a land provider or power purchaser.
Abdulla suggests that the impact of this study on climate change mitigation expands beyond nuclear to other investments in large energy infrastructure, such as carbon capture and sequestration and even the large renewable energy plants that we will need to build when we get serious about decarbonization.
"It is time to develop new, improved energy system models that consider things like institutional quality" he says. "This would change where and how much nuclear power to deploy. It could limit its role in certain places while encouraging deployment in others, but the overall result will be a society that steers its resources more efficiently toward a low-carbon future."
INFORMATION:
About SRA
The Society for Risk Analysis is a multidisciplinary, interdisciplinary, scholarly, international society that provides an open forum for all those interested in risk analysis. SRA was established in 1980 and has published Risk Analysis: An International Journal, the leading scholarly journal in the field, continuously since 1981. For more information, visit http://www.sra.org.
Taking progestogens - steroid hormones - during pregnancy could reduce the risk of preterm birth in high-risk single baby pregnancies, research has shown.
Although these compounds have been in use for some time, results of individual clinical trials investigating their effectiveness in preventing preterm birth have been conflicting, and so further evaluation of the research evidence was needed.
University of York researchers led the Evaluating Progestogens for Prevention of Preterm Birth International Collaborative (EPPPIC) project, a systematic review which brought together and re-analysed datasets from 31 clinical trials of progestogens, including more than 11,000 women and 16,000 babies ...
Microbial life already had the necessary conditions to exist on our planet 3.5 billion years ago. This was the conclusion reached by a research team after studying microscopic fluid inclusions in barium sulfate (barite) from the Dresser Mine in Marble Bar, Australia. In their publication "Ingredients for microbial life preserved in 3.5-billion-year-old fluid inclusions," the researchers suggest that organic carbon compounds which could serve as nutrients for microbial life already existed at this time. The study by first author Helge Mißbach (University of Göttingen, Germany) was published in the journal ...
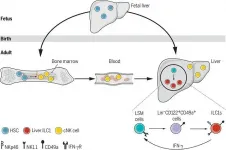
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Science (CAS), teamed up with scientists from Aix Marseille University, discovered that hematopoietic progenitors possessed the differentiation potential to type 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILC1s) in adult liver, and dissected the regulation mechanisms of such cell differentiation, revealing the pathways that lead to the development of tissue-resident lymphocytes. This study was published in Science.
Hematopoiesis occurs at different sites following the development of human body. After birth, the bone marrow (BM) has long been known to be the main hematopoietic organ ...
ST segment-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a particularly severe type of heart attack associated with a high risk of mortality or long-term disability. Clinicians can reduce a patient's chances of unfavorable outcomes by performing a procedure known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), which combines coronary angioplasty--in which a balloon is inserted into a blocked artery of the heart to clear it--with stenting--inserting a tiny tube into a blocked artery to keep the line open. But studies in China have found that many patients with STEMI choose not to undergo PCI and that women with STEMI, in particular, have a reduced likelihood of undergoing guideline-based ...
By harvesting energy from their surrounding environments, particles named 'artificial micromotors' can propel themselves in specific directions when placed in aqueous solutions. In current research, a popular choice of micromotor is the spherical 'Janus particle' - featuring two distinct sides with different physical properties. Until now, however, few studies have explored how these particles interact with other objects in their surrounding microenvironments. In an experiment detailed in EPJ E, researchers in Germany and The Netherlands, led by Larysa Baraban at Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, show for the first time how the velocities of Janus particles relate to the physical properties of nearby barriers.
The team's discoveries could help researchers to engineer micromotors which ...
Children with a common but regularly undiagnosed disorder affecting their language and communication are likely to be finding the transition back to school post-lockdown harder than most, according to a team of psychologists.
Two children in every class of 30 are estimated to have Developmental Language Disorder (DLD) (around 8%), yet public awareness, diagnosis and referral to speech and language therapists all remain low in the UK.
DLD is a condition where children have problems acquiring their own language for no obvious reasons. Unlike temporary language delay (which reflects the natural variation of age at which children learn to speak and communicate), DLD is a lifelong condition with significant impacts for individuals in childhood and in later life, in particular their ...
Lakes store huge amounts of methane. In a new study, environmental scientists at the University of Basel offer suggestions for how it can be extracted and used as an energy source in the form of methanol.
Discussion about the current climate crisis usually focuses on carbon dioxide (CO2). The greenhouse gas methane is less well known, but although it is much rarer in the atmosphere, its global warming potential is 80 to 100 times greater per unit.
More than half the methane caused by human activities comes from oil production and agricultural fertilizers. But the gas is also created by the natural decomposition of biomass by ...
Scientists from Trinity College Dublin believe they have pinpointed our most distant animal relative in the tree of life and, in doing so, have resolved an ongoing debate. Their work finds strong evidence that sponges - not more complex comb jellies - were our most distant relatives.
Sponges are structurally simple, lacking complex traits such as a nervous system, muscles, and a though-gut. Logically, you would expect these complex traits to have emerged only once during animal evolution - after our lineage diverged from that of sponges - and then be retained in newly evolved creatures thereafter.
However, a debate has been raging ever since phylogenomic studies found evidence that our most distant ...
Superalloys that withstand extremely high temperatures could soon be tuned even more finely for specific properties such as mechanical strength, as a result of new findings published today.
A phenomenon related to the invar effect - which enables magnetic materials such as nickel-iron (Ni-Fe) alloys to keep from expanding with increasing temperature - was reported to have been discovered in paramagnetic, or weakly magnetized, high-temperature alloys.
Levente Vitos, Professor at KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, says the breakthrough research, which includes a general theory explaining the new invar effect, promises to advance the design of high-temperature alloys with exceptional mechanical stability. The article was published in the Proceedings ...
The higher the number of plant and bird species in a region, the healthier the people who live there. This was found by a new study published in Landscape and Urban Planning and led by the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), the Senckenberg Biodiversity and Climate Research Centre (SBiK-F) and the Christian Albrechts University (CAU) in Kiel. The researchers found that, in particular, mental health and higher species diversity are positively related, whereas a similar relationship between plant or bird species and physical health could not be proven.
The study led by researchers from iDiv, SBiK-F and CAU provides ...