Risk factors for complications from COVID-19, perceived chances of infection and protective behavior
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: This study documented how perception of risk of infection and severe complications from COVID-19 were associated with underlying reported health.
Authors: Robert F. Schoeni, Ph..D., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3984)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3984?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=033121
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is the new online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
What The Study Did: In this decision analytical modelling study, researchers investigated the association of school reopening or closure with new and cumulative COVID-19 case numbers compared with other community-based interventions.
Authors: David Naimark, M.D., M.Sc., of the Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3793)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict ...
2021-03-31
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Thousands of different bacterial species live within the human gut. Most are beneficial, while others can be harmful. A new study from an MIT-led team has revealed that these bacterial populations can remake themselves within the lifetime of their host, by passing genes back and forth.
The researchers also showed that this kind of gene transfer occurs more frequently in the microbiomes of people living in industrialized societies, possibly in response to their specific diets and lifestyles.
"One unexpected consequence of humans living ...
2021-03-31
For middle-aged women, exercise has many health benefits, but it may not help maintain cognitive function over the long term, according to a new UCLA Health study. The study observed a diverse group of roughly 1,700 women over a 21-year period starting when the women's average age was 45. In the study, women's cognitive ability was tested in three key areas: cognitive processing speed (how fast the mind works); verbal memory (the ability to recall a story that they heard); and working memory (the ability to manipulate information).
The study was published in JAMA Network Open, and is one of the first ...
2021-03-31
LA JOLLA, CA--What's the difference between a giggle and a belly laugh? Or a yelp and an all-out scream? In many species, including humans, the volume and duration of a verbal sound conveys as much information as the noise itself.
A group of scientists, led by Scripps Research, has discovered a node in the brains of male mice that modulates the sounds they make in social situations. This discovery, published in Nature, could help identify similar locations in the human brain, and potentially lead to a better understanding of social disorders such as autism or depression.
"Identifying this node gives us signatures of what to look for when human behavior goes awry," says Lisa Stowers, PhD, a neuroscientist and professor at Scripps Research who led the study. ...
2021-03-31
Harvard University researchers have identified the biological mechanism of how chronic stress impairs hair follicle stem cells, confirming long-standing observations that stress might lead to hair loss.
In a mouse study published in the journal Nature, the researchers found that a major stress hormone causes hair follicle stem cells to stay in an extended resting phase, without regenerating the hair follicle and hair. The researchers identified the specific cell type and molecule responsible for relaying the stress signal to the stem cells, and showed that this pathway can be potentially targeted to restore hair growth.
"My lab is interested in understanding how stress affects ...
2021-03-31
Swansea University physicists, as leading members of the ALPHA collaboration at CERN, have demonstrated laser cooling of antihydrogen atoms for the first time. The groundbreaking achievement produces colder antimatter than ever before and enables an entirely new class of experiments, helping scientists learn more about antimatter in future.
In a paper published today in Nature, the collaboration reports that the temperature of antihydrogen atoms trapped inside a magnetic bottle is reduced when the atoms scatter light from an ultraviolet laser beam, slowing the atoms down and reducing the space they occupy in the bottle -- both vital aspects of future more detailed ...
2021-03-31
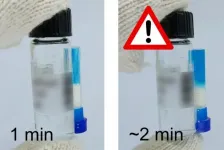
Scientists have developed vaccines for COVID-19 with record speed. The first two vaccines widely distributed in the U.S. are mRNA-based and require ultracold storage (-70 C for one and -20 C for the other). Now, researchers reporting in ACS Omega have developed a tamper-proof temperature indicator that can alert health care workers when a vial of vaccine reaches an unsafe temperature for a certain period, which could help ensure distribution of effective mRNA vaccines.
The two COVID mRNA vaccines contain instructions for building harmless pieces of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Once the vaccine is injected into the body, human cells use the mRNA instructions to make the spike protein, which they temporarily ...
2021-03-31
Increased consumption of flavanols - a group of molecules occurring naturally in fruit and vegetables - could protect people from mental stress-induced cardiovascular events such as stroke, heart disease and thrombosis, according to new research.
Researchers have discovered that blood vessels were able to function better during mental stress when people were given a cocoa drink containing high levels of flavanols than when drinking a non-flavanol enriched drink.
A thin membrane of cells lining the heart and blood vessels, when functioning efficiently the endothelium helps ...
2021-03-31
LAWRENCE -- New research from the University of Kansas END ...
2021-03-31
Meat and fish fraud are global problems, costing consumers billions of dollars every year. On top of that, mislabeling products can cause problems for people with allergies, religious or cultural restrictions. Current methods to detect this fraud, while accurate, are slower than inspectors would like. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry have optimized their handheld MasSpec Pen to identify common types of meat and fish within 15 seconds.
News stories of food fraud, such as beef being replaced with horse ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Risk factors for complications from COVID-19, perceived chances of infection and protective behavior