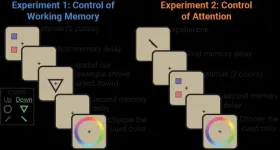
(Press-News.org) In 1890, psychologist William James described attention as the spotlight we shine not only on the world around us, but also on the contents of our minds. Most cognitive scientists since then have drawn a sharp distinction between what James termed "sensorial attention" and "intellectual attention," now usually called "attention" and "working memory," but James saw them as two varieties of the same mental process.
New research by Princeton neuroscientists suggests that James was on to something, finding that attention to the outside world and attention to our own thoughts are actually two sides of the same neural coin. What's more, they have observed the coin as it flips inside the brain.
A paper published in Nature on March 31 by END
Attention and working memory: Two sides of the same neural coin?
Princeton neuroscientists have demonstrated that attention and working memory are two sides of the same neural coin; what's more, they have observed the coin as it flips inside the brain
2021-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Quantum material's subtle spin behavior proves theoretical predictions
2021-03-31
Using complementary computing calculations and neutron scattering techniques, researchers from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge and Lawrence Berkeley national laboratories and the University of California, Berkeley, discovered the existence of an elusive type of spin dynamics in a quantum mechanical system.
The team successfully simulated and measured how magnetic particles called spins can exhibit a type of motion known as Kardar-Parisi-Zhang, or KPZ, in solid materials at various temperatures. Until now, scientists had not found evidence of this particular phenomenon outside of soft matter ...
Blacks, Latinos and Native Americans severely underrepresented in health workforce
2021-03-31
WASHINGTON (March 31, 2021) -- In 2019, Blacks, Latinos and Native Americans were severely underrepresented in the health care workforce, a trend that shows limited signs of improvement, according to a study published today by George Washington University researchers.
"Our findings suggest that Blacks, Latinos and other people of color have been left behind when it comes to the health professions," Edward Salsberg, senior research scientist and co-director of the Health Workforce Diversity Tracker project at the GW Fitzhugh Mullan Institute for Health Workforce Equity, said. The Fitzhugh Mullan Institute ...
How much are invasive species costing us?
2021-03-31
An invasive exotic species is one deliberately or unwittingly introduced by humans into a new habitat, where it becomes an environmental menace. In addition to the loss of biodiversity and other ecological impacts resulting from its presence, an invasive species can lead to economic losses in certain sectors, including agriculture, tourism, and public health. Though biological invasion is the second leading cause of species extinction, decision makers and the general public are still largely unaware of the issue.
After five years of study, the international research team* directed by scientists from the Écologie, Systématique et Évolution (CNRS ...
How comorbidities increase risks for COVID patients
2021-03-31
Comorbidities such as heart disease, respiratory disease, renal disease and cancer lead to an increased risk of death from Covid-19 according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA) and the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital (NNUH).
At the start of the pandemic, there was concern that specific medications for high blood pressure could be linked with worse outcomes for Covid-19 patients.
Previous research from the UEA team showed this wasn't the case and that medications for high blood pressure could, in fact, improve Covid-19 survival rates and reduce the severity of infection.
New findings, published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Network Open, additionally show that it is comorbidities such as heart disease, respiratory ...
Mount Sinai study reveals genetic and cellular mechanisms of Crohn's disease
2021-03-31
Mount Sinai researchers have identified genetic and cellular mechanisms of Crohn's disease, providing new insights for future treatments that could offer a tailored approach to patients with the chronic inflammatory disease, according to a study published in END ...
Mice naturally engage in physical distancing, study finds
2021-03-31
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When someone is sick, it's natural to want to stay as far from them as possible. It turns out this is also true for mice, according to an MIT study that also identified the brain circuit responsible for this distancing behavior.
In a study that explores how otherwise powerful instincts can be overridden in some situations, researchers from MIT's Picower Institute for Learning and Memory found that when male mice encountered a female mouse showing signs of illness, the males interacted very little with the females and made no attempts to mate with them as they normally would. The researchers also showed that this behavior is controlled by a circuit in the amygdala, which detects distinctive odors from sick animals and triggers a warning signal ...
Changing hypertension definition may identify more high-risk pregnancies
2021-03-31
NEW YORK, NY (March 31, 2021)--A shift in the definition of high blood pressure may help identify more women who are at risk of developing life-threatening complications during pregnancy and delivery, suggests a new study from Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
Under the stricter definition, more than 50,000 additional women each year in the United States could become eligible for treatment with aspirin in pregnancy, which lowers the risk of developing preeclampsia, a sudden increase in blood pressure that can lead to stroke, seizures, hemorrhage, and death.
The ...
Dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation, future use after COVID-19
2021-03-31
What The Study Did: This study sought to assess dermatologists' perceptions of and experiences with teledermatology in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic and new regulatory changes including parity in reimbursements between video and in-person visits.
Authors: Jules B. Lipoff, M.D., of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0195)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Association between renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors, clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19
2021-03-31
What The Study Did: Researchers compared mortality and severe adverse events in this systematic review and meta-analysis of 52 studies that evaluated clinical outcomes among nearly 102,000 patients with COVID-19 who did and didn't receive angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
Authors: Vassilios S. Vassiliou, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., of the University of East Anglia in Norwich, United Kingdom is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3694)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 infections, hospitalization, mortality among US nursing home residents
2021-03-31
What The Study Did: This study identified risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 incidence, hospitalization and death among nursing home residents in the United States.
Authors: James S. Goodwin, M.D., of the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.6315)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
[Press-News.org] Attention and working memory: Two sides of the same neural coin?Princeton neuroscientists have demonstrated that attention and working memory are two sides of the same neural coin; what's more, they have observed the coin as it flips inside the brain