Diet + exercise + chemo = increased survival in youth with leukemia
Children's Hospital Los Angeles study finds risk of detectable cancer cells decreased by 70% after one month of treatment in patients with ALL
2021-04-01
(Press-News.org) Los Angeles (April 1, 2021) -- Overweight children and adolescents receiving chemotherapy for treatment of leukemia are less successful battling the disease compared to their lean peers. Now, research conducted at the END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Smart glass has a bright future
2021-04-01
Buildings are responsible for 40 percent of primary energy consumption and 36 percent of total CO2 emissions. And, as we know, CO2 emissions trigger global warming, sea level rise, and profound changes in ocean ecosystems. Substituting the inefficient glazing areas of buildings with energy efficient smart glazing windows has great potential to decrease energy consumption for lighting and temperature control.
Harmut Hillmer et al. of the University of Kassel in Germany demonstrate that potential in "MOEMS micromirror arrays in smart windows for daylight steering," a paper published recently in the inaugural issue of the Journal of Optical Microsystems.
"Our smart glazing ...
Undetected coronavirus variant was in at least 15 countries before its discovery
2021-04-01
A highly contagious SARS-CoV-2 variant was unknowingly spreading for months in the United States by October 2020, according to a new study from researchers with The University of Texas at Austin COVID-19 Modeling Consortium. Scientists first discovered it in early December in the United Kingdom, where the highly contagious and more lethal variant is thought to have originated. The journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, which has published an early-release version of the study, provides evidence that the coronavirus variant B117 (501Y) had spread across the globe undetected for months when scientists discovered it.
"By the time we learned about the U.K. variant ...
Study finds why some cancer drugs may be ineffective
2021-04-01
A possible explanation for why many cancer drugs that kill tumor cells in mouse models won't work in human trials has been found by researchers with The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) School of Biomedical Informatics and McGovern Medical School.
The research was published today in Nature Communications.
In the study, investigators reported the extensive presence of mouse viruses in patient-derived xenografts (PDX). PDX models are developed by implanting human tumor tissues in immune-deficient mice, and are commonly ...
New GSA Bulletin articles published ahead of print in March
2021-04-01
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Geological Society of America regularly publishes
articles online ahead of print. For March, GSA Bulletin topics
include multiple articles about the dynamics of China and Tibet; the ups
and downs of the Missouri River; the Los Rastros Formation, Argentina; the
Olympic Mountains of Washington State; methane seep deposits; meandering
rivers; and the northwest Hawaiian Ridge. You can find these articles at
https://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent
.
Transition from a passive to active continental ...
Connecting the dots between engagement and learning
2021-04-01
We've all heard the adage, "If at first you don't succeed, try, try again," but new research from Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Pittsburgh finds that it isn't all about repetition. Rather, internal states like engagement can also have an impact on learning.
The collaborative research, published in Nature Neuroscience, examined how changes in internal states, such as arousal, attention, motivation, and engagement can affect the learning process using brain-computer interface (BCI) technology. Findings suggest that changes in internal states can systematically influence how behavior improves with learning, thus paving the way ...
African elephants' range is just 17% of what it could be, study finds
2021-04-01
A study reported in the journal Current Biology on April 1 has both good news and bad news for the future of African elephants. While about 18 million square kilometers of Africa--an area bigger than the whole of Russia--still has suitable habitat for elephants, the actual range of African elephants has shrunk to just 17%of what it could be due to human pressure and the killing of elephants for ivory.
"We looked at every square kilometer of the continent," says lead author Jake Wall of the Mara Elephant Project in Kenya. "We found that 62% of those 29.2 million ...
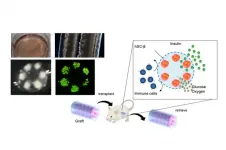
Replacing what was lost: A novel cell therapy for type I diabetes mellitus
2021-04-01
Tokyo, Japan - Type I Diabetes Mellitus (T1D) is an autoimmune disorder leading to permanent loss of insulin-producing beta-cells in the pancreas. In a new study, researchers from The University of Tokyo developed a novel device for the long-term transplantation of iPSC-derived human pancreatic beta-cells.
T1D develops when autoimmune antibodies destroy pancreatic beta-cells that are responsible for the production of insulin. Insulin regulates blood glucose levels, and in the absence of it high levels of blood glucose slowly damage the kidneys, eyes and peripheral ...
Skin deep: Aquatic skin adaptations of whales and hippos evolved independently
2021-04-01
A new study shows that the similarly smooth, nearly hairless skin of whales and hippopotamuses evolved independently. The work suggests that their last common ancestor was likely a land-dwelling mammal, uprooting current thinking that the skin came fine-tuned for life in the water from a shared amphibious ancestor. The study is published today in the journal Current Biology and was led by researchers at the American Museum of Natural History; University of California, Irvine; University of California, Riverside; Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics; and the LOEWE-Centre for Translational Biodiversity Genomics (Germany).
"How mammals left terra firma and became fully aquatic is one of the most fascinating evolutionary ...
New mechanism by which senescent cells turn on genes encoding for tumor-regulating factors
2021-04-01
PHILADELPHIA -- (April 1, 2021 -- Scientists at The Wistar Institute identified a new mechanism of transcriptional control of cellular senescence that drives the release of inflammatory molecules that influence tumor development through altering the surrounding microenvironment. The study, published in Nature Cell Biology, reports that methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) and 14 (METTL14) proteins moonlight as transcriptional regulators that allow for establishment of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP).
Cellular senescence is a stable state of growth arrest in which cells stop dividing but remain viable and produce an array of inflammatory and growth-promoting molecules collectively defined as SASP. These molecules account ...
UMD helps quantify how climate change has slowed global agricultural productivity growth
2021-04-01
The University of Maryland (UMD) has collaborated with Cornell University and Stanford University to quantify the man-made effects of climate change on global agricultural productivity growth for the first time. In a new study published in Nature Climate Change, researchers developed a robust model of weather effects on productivity, looking at productivity in both the presence and absence of climate change. Results indicate a 21% reduction in global agricultural productivity since 1961, which according to researchers is equivalent to completely losing the last 7 years ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
[Press-News.org] Diet + exercise + chemo = increased survival in youth with leukemiaChildren's Hospital Los Angeles study finds risk of detectable cancer cells decreased by 70% after one month of treatment in patients with ALL