Polarized photovoltaic properties emerge
2D materials combine, becoming polarized and giving rise to photovoltaic effect
2021-04-01
(Press-News.org) For the first time, researchers have discovered a way to obtain polarity and photovoltaic behavior from certain nonphotovoltaic, atomically flat (2D) materials. The key lies in the special way in which the materials are arranged. The resulting effect is different from, and potentially superior to, the photovoltaic effect commonly found in solar cells.
Solar power is considered a key technology in the move away from fossil fuels. Researchers continually innovate more efficient means to generate solar energy. And many of these innovations come from the world of materials research. Research Associate Toshiya Ideue from the University of Tokyo's Department of Applied Physics and his team are interested in the photovoltaic properties of 2D materials and their interfaces where these materials meet.
"Quite often, interfaces of multiple 2D materials exhibit different properties to the individual crystals alone," said Ideue. "We have discovered that two specific materials which ordinarily exhibit no photovoltaic effect do so when stacked in a very particular way."
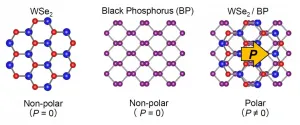
The two materials are tungsten selenide (WSe2) and black phosphorus (BP), both of which have different crystal structures. Originally, both materials are nonpolar (do not have a preferred direction of conduction) and do not generate a photocurrent under light. However, Ideue and his team found that by stacking sheets of WSe2 and BP together in the right way, the sample exhibited polarization, and when a light was cast on the material, it generated a current. The effect takes place even if the area of illumination is far from the electrodes at either end of the sample; this is different from how the ordinary photovoltaic effect works.
Key to this behavior is the way the WSe2 and BP are aligned. The crystalline structure of BP has reflective, or mirror, symmetry in one plane, whereas WSe2 has three lines of mirror symmetry. When the symmetry lines of the materials align, the sample gains polarity. This kind of layer stacking is delicate work, but it also reveals to researchers new properties and functions that could not be predicted just by looking at the ordinary form of the materials.
"The biggest challenge for us will be to find a good combination of 2D materials with higher electric-generation efficiency and also to study the effect of changing the angles of the stacks," said Ideue. "But it's so rewarding to discover never-before-seen emergent properties of materials. Hopefully, one day this research could improve solar panels. We would like to explore more unprecedented properties and functionalities in nanomaterials."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-01
Despite a reduction in the total amounts of pesticides used, the toxicity of commonly used pesticides to nontarget species, partially aquatic invertebrates and pollinators, has increased considerably in recent decades, according to a new study analyzing 25 years of pesticide use. This has been driven by the widespread use of highly toxic pyrethroid and neonicotinoid pesticides. The findings challenge claims suggesting that the overall environmental impacts of pesticide use have declined. The impacts of applied pesticides on humans and the environment are often based on comparisons of use rates (e.g., kilograms per hectare) or the total amounts used (e.g., kilograms per year). However, from an environmental perspective, these weight-based ...
2021-04-01
Technology can be biased, and its design can disadvantage certain demographic groups. While efforts to address bias and promote fairness in technologies are rapidly growing in a variety of technical disciplines, Achuta Kadambi argues that similar growth is not occurring fast enough for medical engineering. "Although computer science companies terminate lucrative but biased facial recognition systems, biased medical devices continue to be sold as commercial products," writes Kadambi in a Perspective. Bias in medical devices results in undesirable performance variation across demographic groups and can greatly influence health inequality. For example, optical biosensors that use light to monitor vital signs like blood oxygenation ...
2021-04-01
In an analysis of thousands of fossil pollen and leaves spanning the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K/Pg) boundary, researchers found that the cataclysmic asteroid impact that resulted in the destruction of nearly 75% of all terrestrial life on Earth drastically restructured tropical forests, setting the stage for the evolution of what has become one of the planet's most diverse ecosystems - the neotropical rainforest. While the end-Cretaceous impact nearly 66 million years ago was catastrophic for terrestrial ecosystems worldwide, its long-term effects on tropical forests have remained a mystery. This is largely due to the lack of palaeobotanical exploration in the region, which has only just begun to provide ...
2021-04-01
An increase of dopamine in the brain's striatum triggers auditory hallucination-like experiences in mice, revealing a possible causal role for dopamine-dependent neurological circuits in symptoms of psychosis. These findings from a new study could inform novel targeted approaches to treating those with psychotic disorders, like schizophrenia. Auditory and visual hallucinations - perceptions of hearing or seeing something without observing external sensory stimuli - are central symptoms of psychotic disorders and are thought by some to be caused by excessive dopamine ...
2021-04-01
A single "super photon" made up of many thousands of individual light particles: About ten years ago, researchers at the University of Bonn produced such an extreme aggregate state for the first time and presented a completely new light source. The state is called optical Bose-Einstein condensate and has captivated many physicists ever since, because this exotic world of light particles is home to its very own physical phenomena. Researchers led by Prof. Dr. Martin Weitz, who discovered the super photon, and theoretical physicist Prof. Dr. Johann Kroha have returned from their latest "expedition" into the quantum world with a very special observation. They report of a new, previously ...
2021-04-01
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) -- Despite the fact that our planet is mostly ocean and human maritime activity is more intense than it has ever been, we know remarkably little about the state of the ocean's biodiversity -- the variety and balance of species that support healthy and productive ecosystems. And it's no surprise -- marine biodiversity is complex, human impacts are uneven, and species respond differently to different stressors.
"It is really hard to know how a species is doing by just looking out from your local coast, or dipping underwater on SCUBA," said Ben Halpern, a marine ecologist at the Bren School of Environmental Science & Management at UC Santa ...
2021-04-01
The humble lab mouse has provided invaluable clues to understanding diseases ranging from cancer to diabetes to COVID-19. But when it comes to psychiatric conditions, the lab mouse has been sidelined, its rodent mind considered too different from that of humans to provide much insight into mental illness.
A new study, however, shows there are important links between human and mouse minds in how they function -- and malfunction. Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis devised a rigorous approach to study how hallucinations are produced in the brain, providing a promising entry point to the development of much-needed new therapies for schizophrenia.
The study, published April 2 in ...
2021-04-01
Tropical rainforests today are biodiversity hotspots and play an important role in the world's climate systems. A new study published today in Science sheds light on the origins of modern rainforests and may help scientists understand how rainforests will respond to a rapidly changing climate in the future.
The study led by researchers at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) shows that the asteroid impact that ended the reign of dinosaurs 66 million years ago also caused 45% of plants in what is now Colombia to go extinct, and it made way for the reign of flowering plants in modern tropical rainforests.
"We wondered how tropical rainforests changed after a drastic ecological perturbation such as the Chicxulub impact, so we looked for tropical plant fossils," said Mónica ...
2021-04-01
LA JOLLA--(April 1, 2021) Neurons lack the ability to replicate their DNA, so they're constantly working to repair damage to their genome. Now, a new study by Salk scientists finds that these repairs are not random, but instead focus on protecting certain genetic "hot spots" that appear to play a critical role in neural identity and function.
The findings, published in the April 2, 2021, issue of Science, give novel insights into the genetic structures involved in aging and neurodegeneration, and could point to the development of potential new therapies for diseases such Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and other age-related dementia disorders.
"This research shows for the first time that ...
2021-04-01
On the afternoon of April 13, 2018, a large wave of water surged across Lake Michigan and flooded the shores of the picturesque beach town of Ludington, Michigan, damaging homes and boat docks, and flooding intake pipes. Thanks to a local citizen's photos and other data, NOAA scientists reconstructed the event in models and determined this was the first ever documented meteotsunami in the Great Lakes caused by an atmospheric inertia-gravity wave.
An atmospheric inertia-gravity wave is a wave of air that can run from 6 to 60 miles long that is created when a mass of stable air is displaced by an air mass with significantly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Polarized photovoltaic properties emerge
2D materials combine, becoming polarized and giving rise to photovoltaic effect